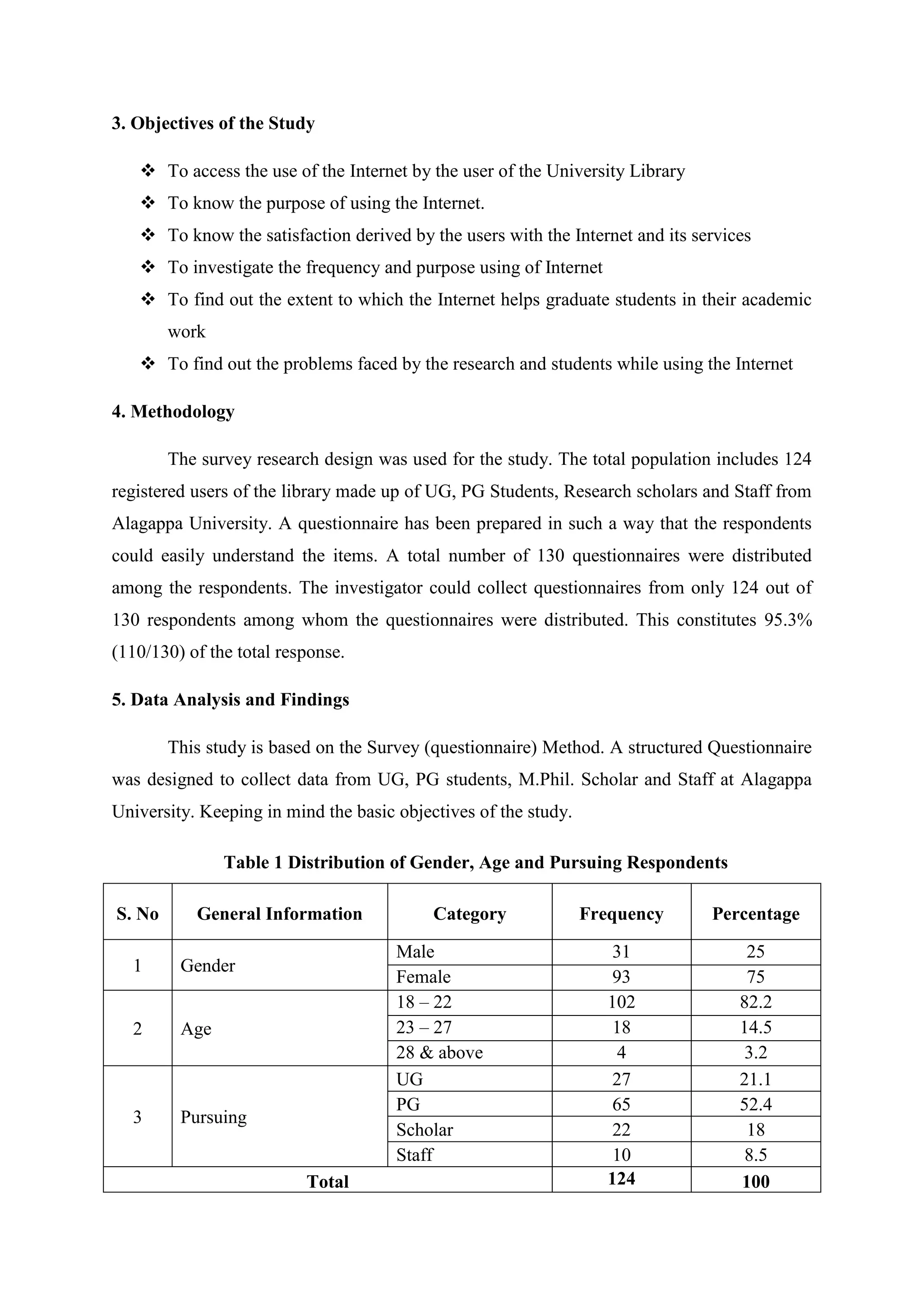
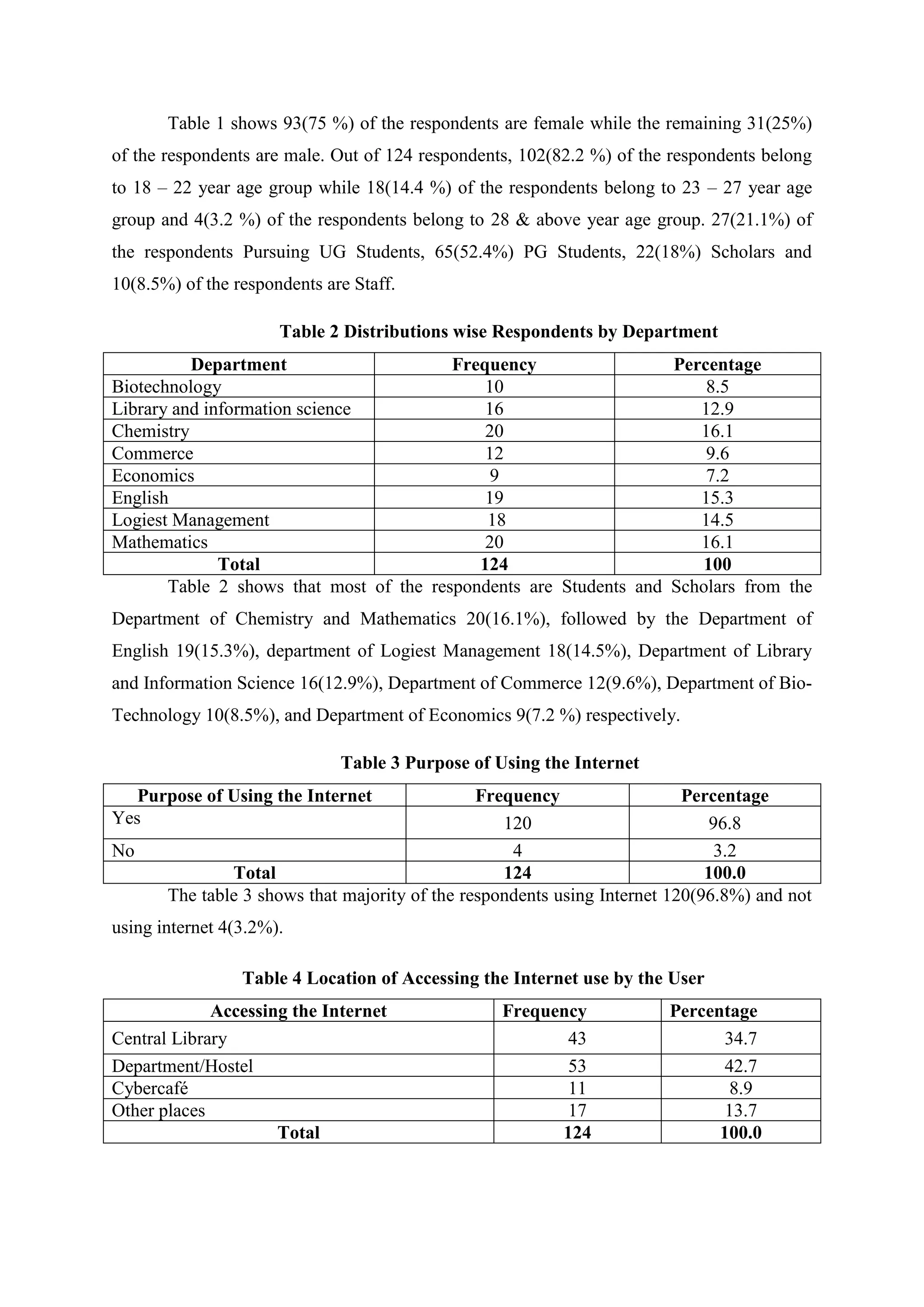
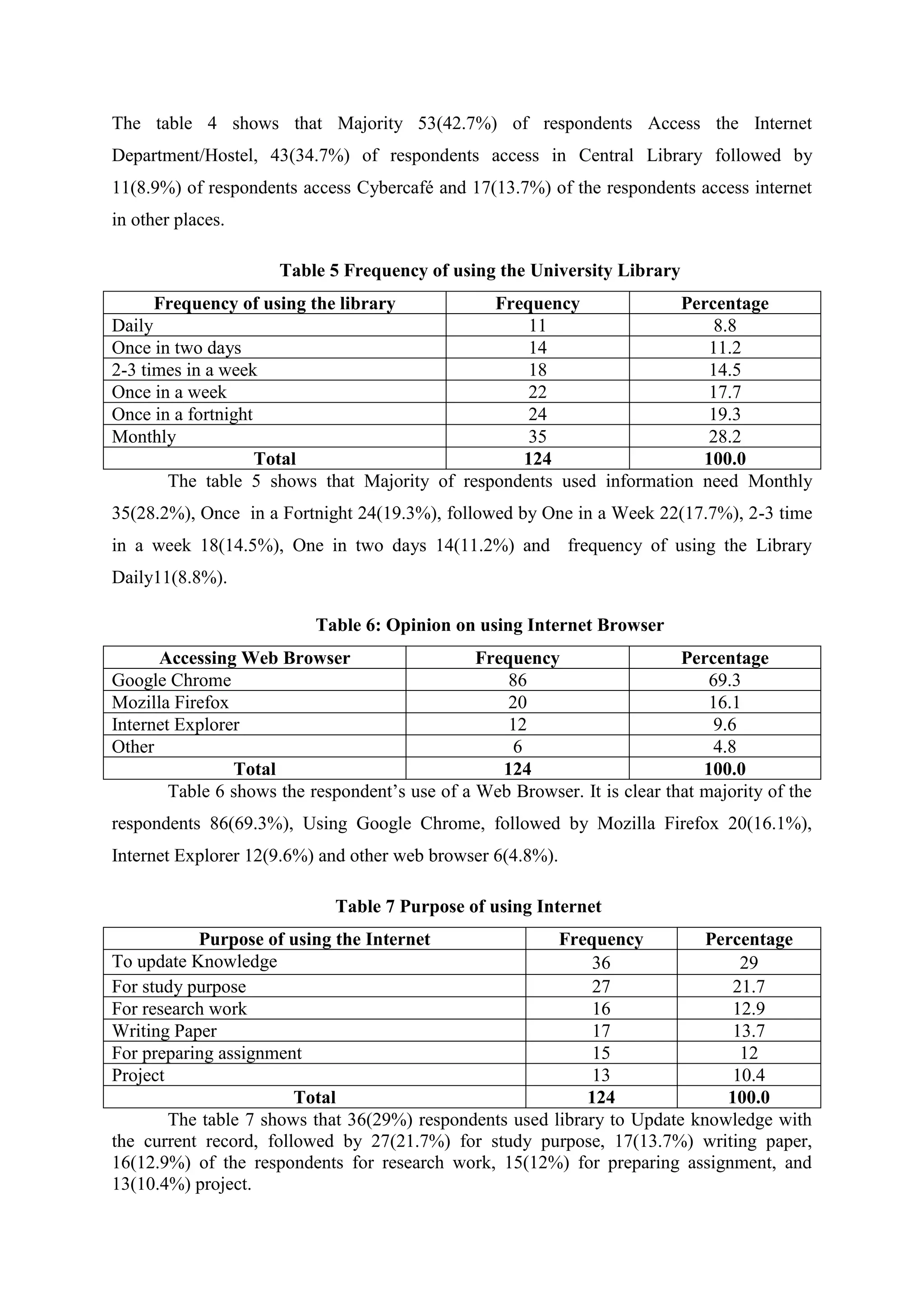
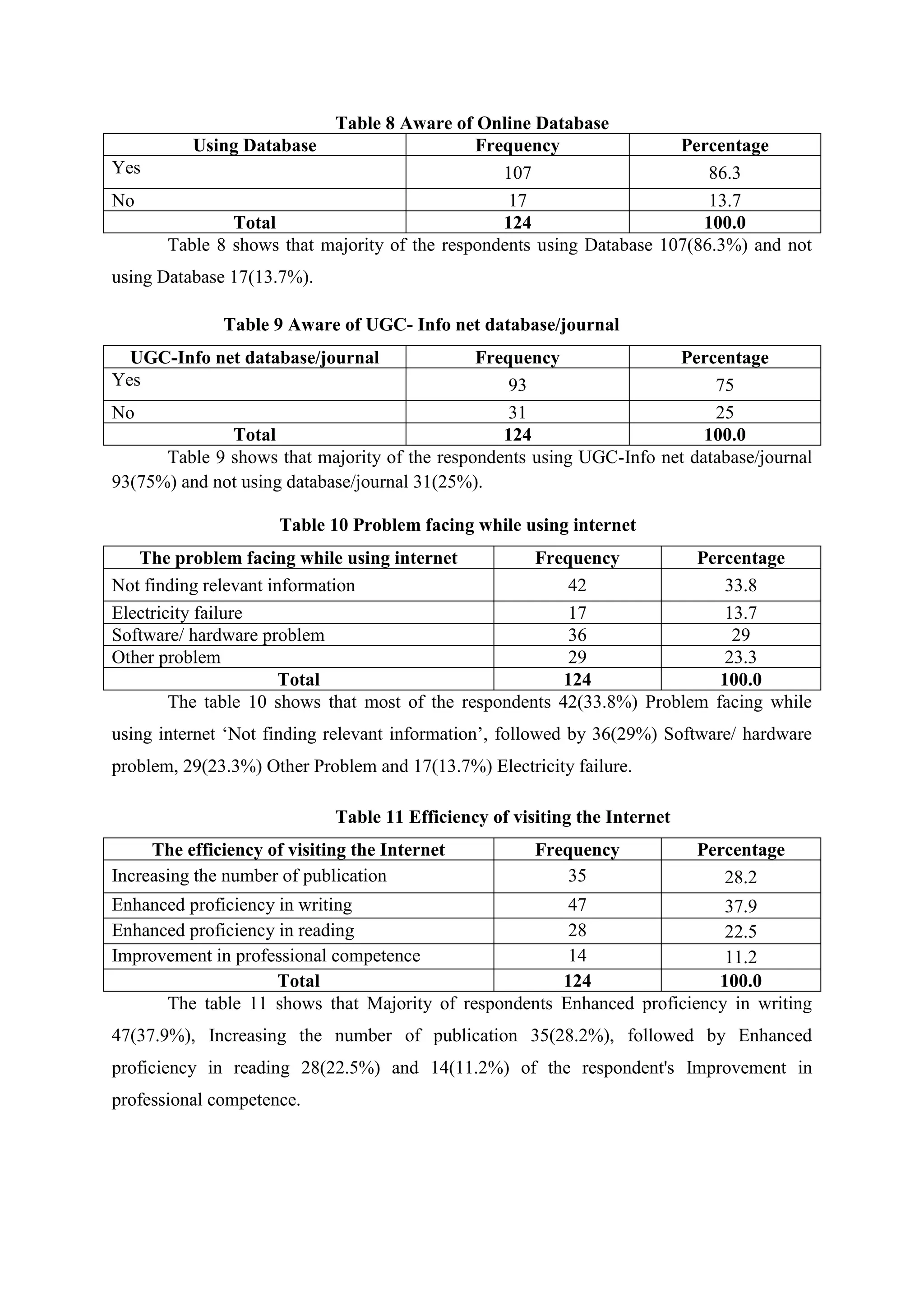
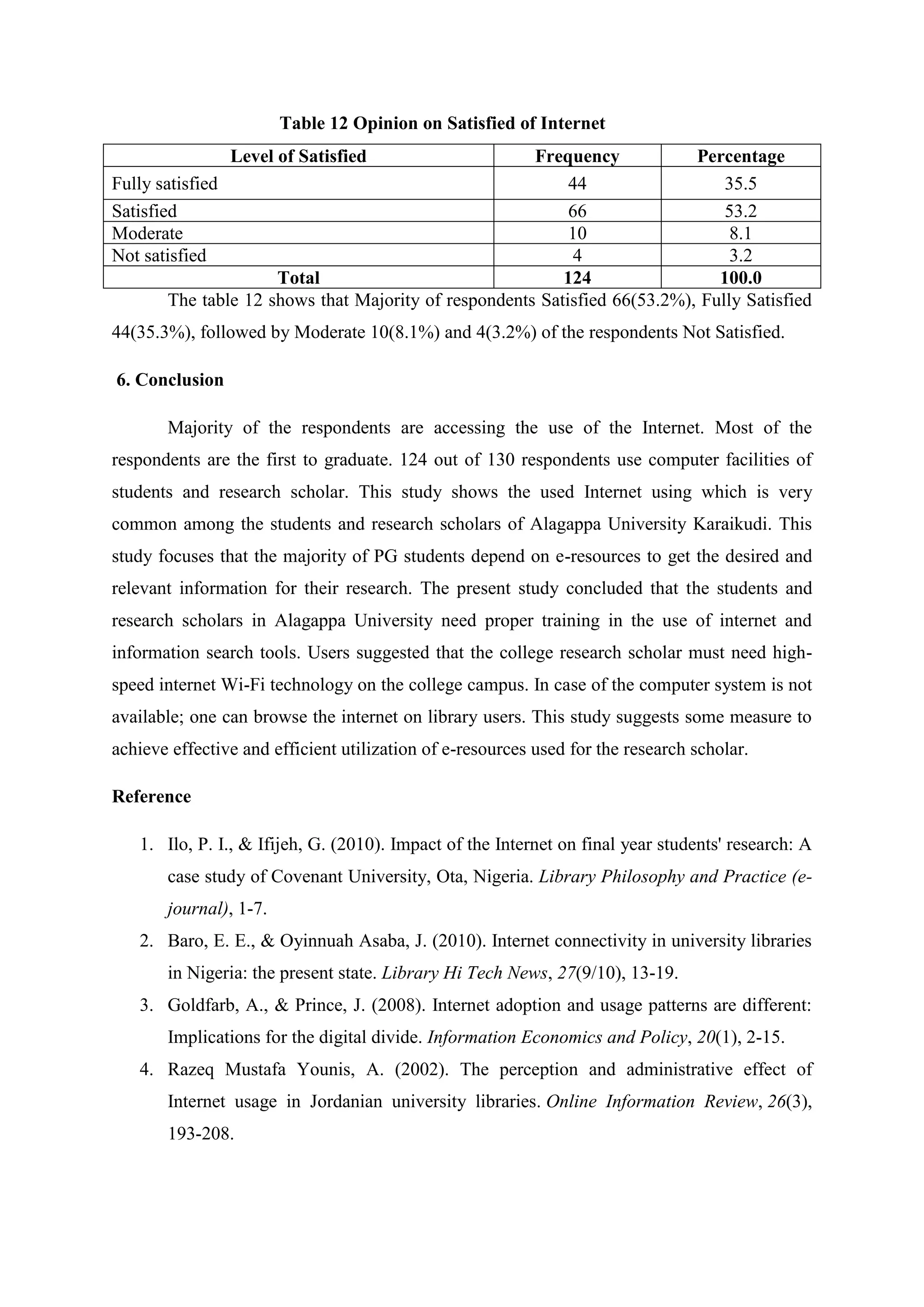
The study assesses the usage and impact of the internet among 124 library users at Alagappa University. It found high internet usage (96.8%) with users primarily utilizing it for knowledge updates and research; however, challenges like difficulty in finding relevant information were also noted. Most respondents expressed satisfaction with the internet's role in enhancing their academic work and proficiency.