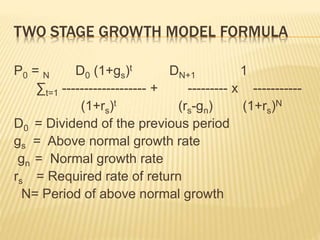
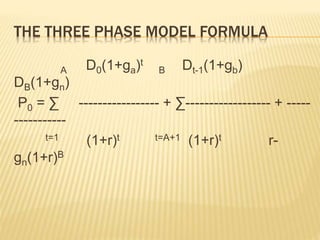
This document discusses various approaches to valuing equity shares, including accounting-based methods like book value and liquidation value, and dividend-based methods like the single-period, multi-period, and constant/variable growth dividend discount models. It also covers valuation using the price-earnings (P/E) ratio and models like Graham-Dodd and Whitbeck-Kisor that use factors like earnings, growth rates, and dividend yield to determine fair value.