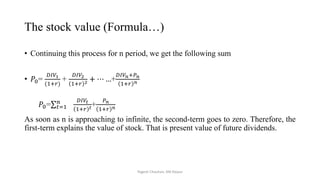
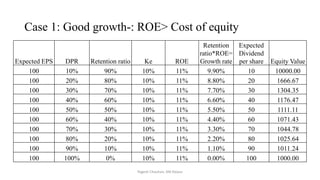
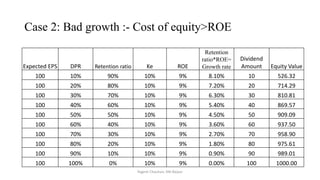
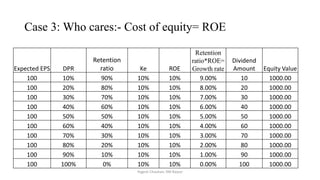
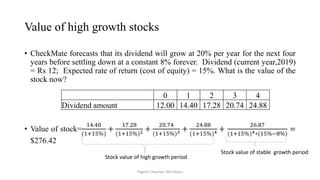
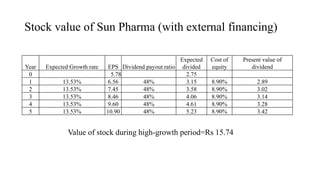
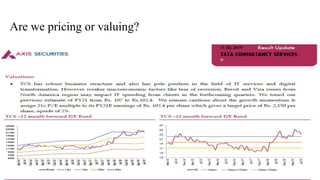
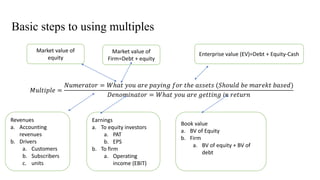
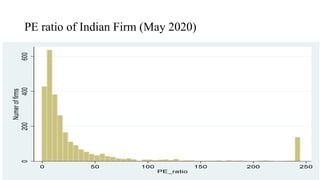
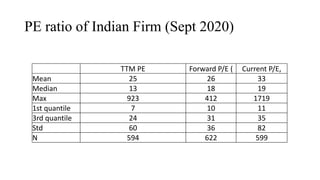
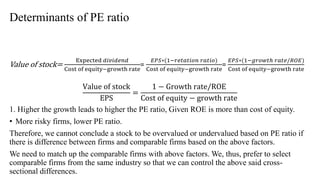
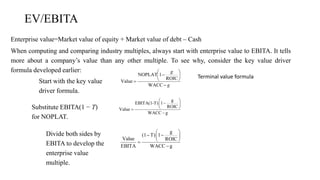
The document discusses valuation of stocks using the dividend discount model. It explains that under this model, the value of a stock is equal to the present value of all expected future dividend payments. The document then provides formulas for valuing stocks in different scenarios, such as when dividends are expected to remain constant forever, or grow at a constant rate. It also discusses how a company's reinvestment rate and return on equity determine its long-term growth rate.