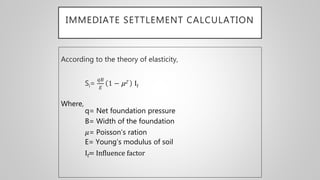
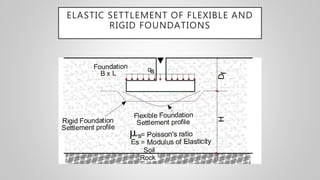
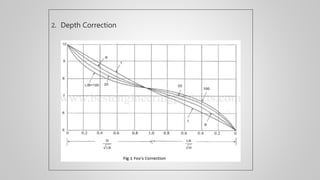
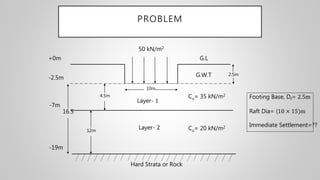
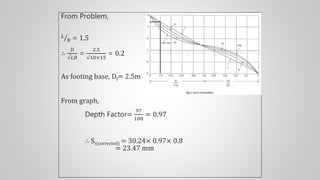
The document discusses immediate settlement in foundations, especially for shallow footings on sandy bases, and provides the formula for calculating immediate settlement using parameters such as net foundation pressure, foundation width, Poisson's ratio, and Young's modulus of soil. It explains the differences in settlement for flexible and rigid foundations, emphasizing the need to calculate the influence factor for various footing shapes. Additionally, it outlines corrections for rigidity and depth in determining settlement values.