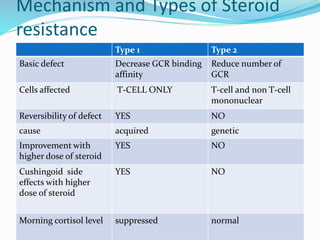
This document discusses steroid resistant asthma, which affects 5-10% of asthma patients. It defines steroid resistant asthma as less than a 15% improvement in lung function after treatment with oral steroids. The document outlines two main mechanisms of steroid resistance - type 1 involves reduced steroid receptor binding affinity while type 2 involves a reduced number of steroid receptors. It recommends a multi-step approach to diagnosing and managing steroid resistant asthma, including identifying triggers, optimizing inhaler technique, treating comorbidities, using combination therapies, and considering alternative immunomodulators if initial steps fail.