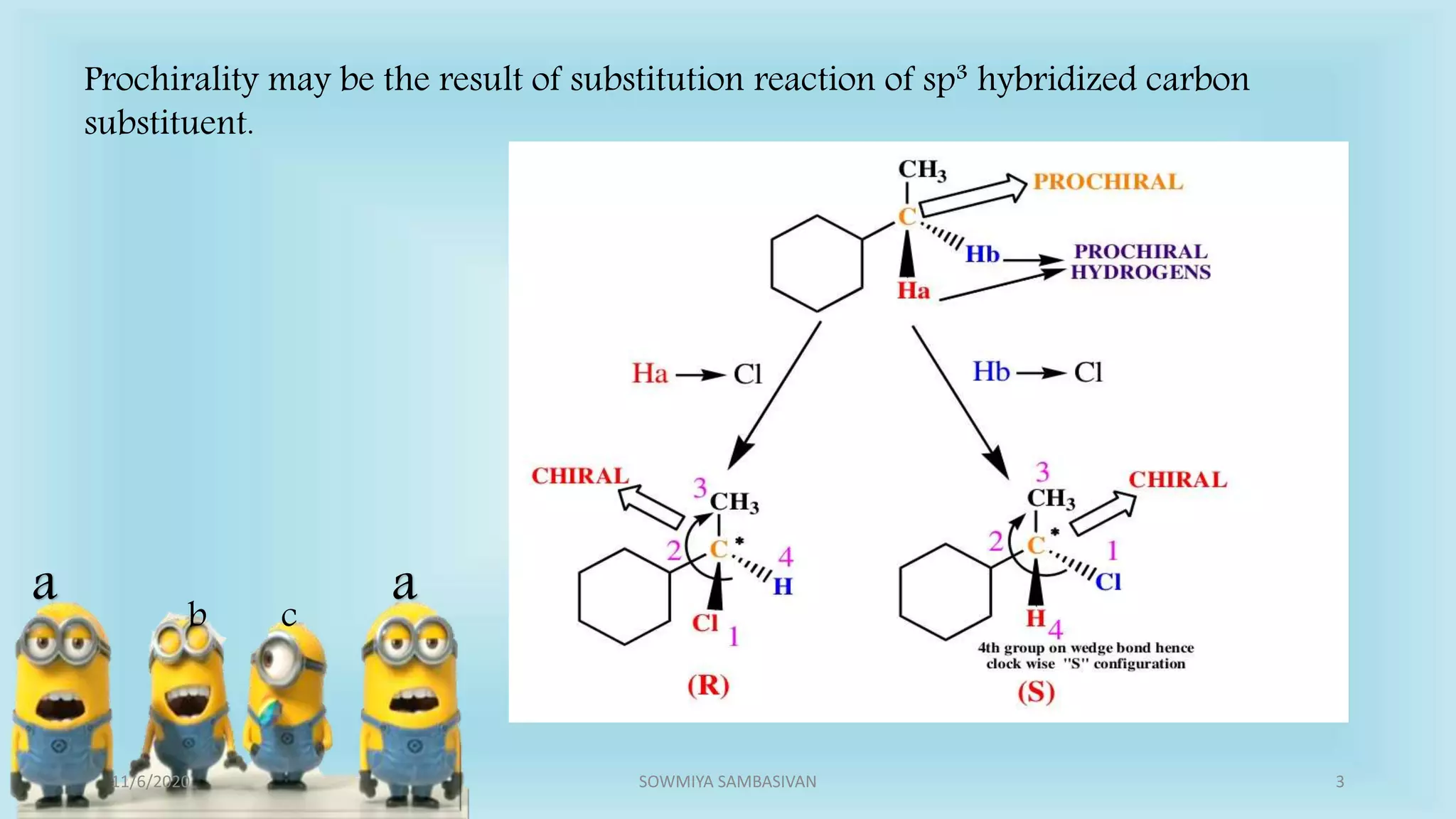
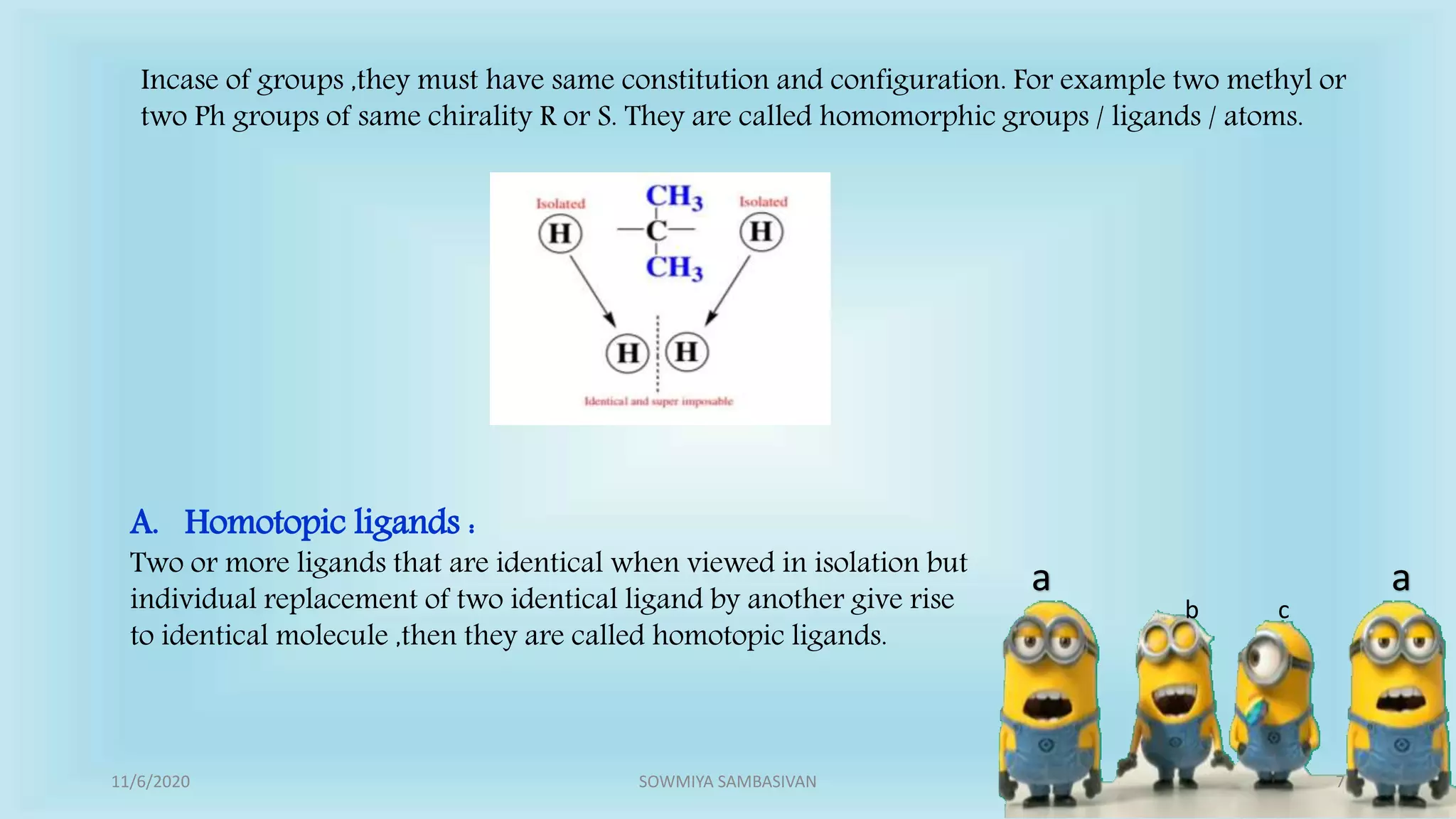
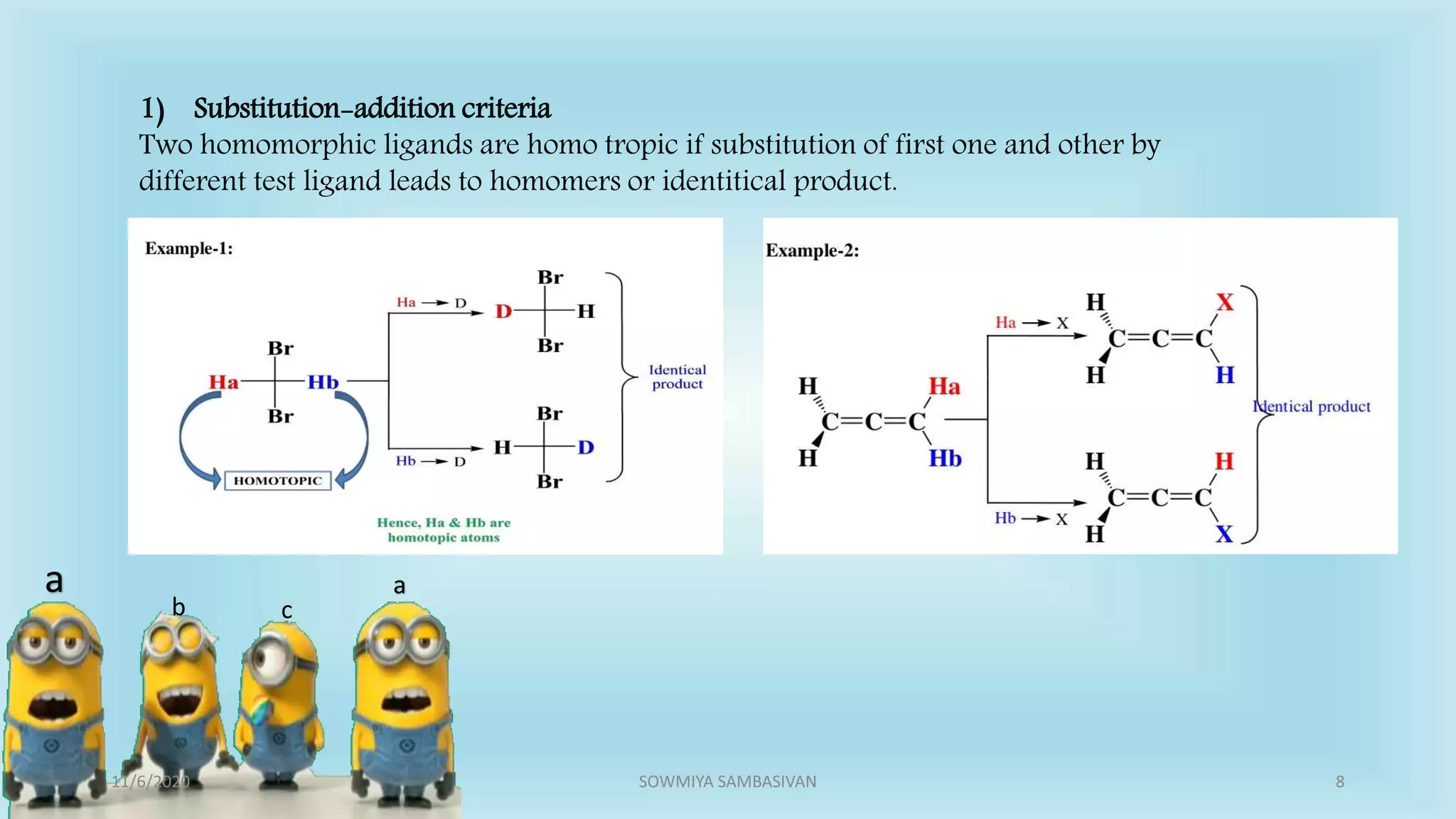
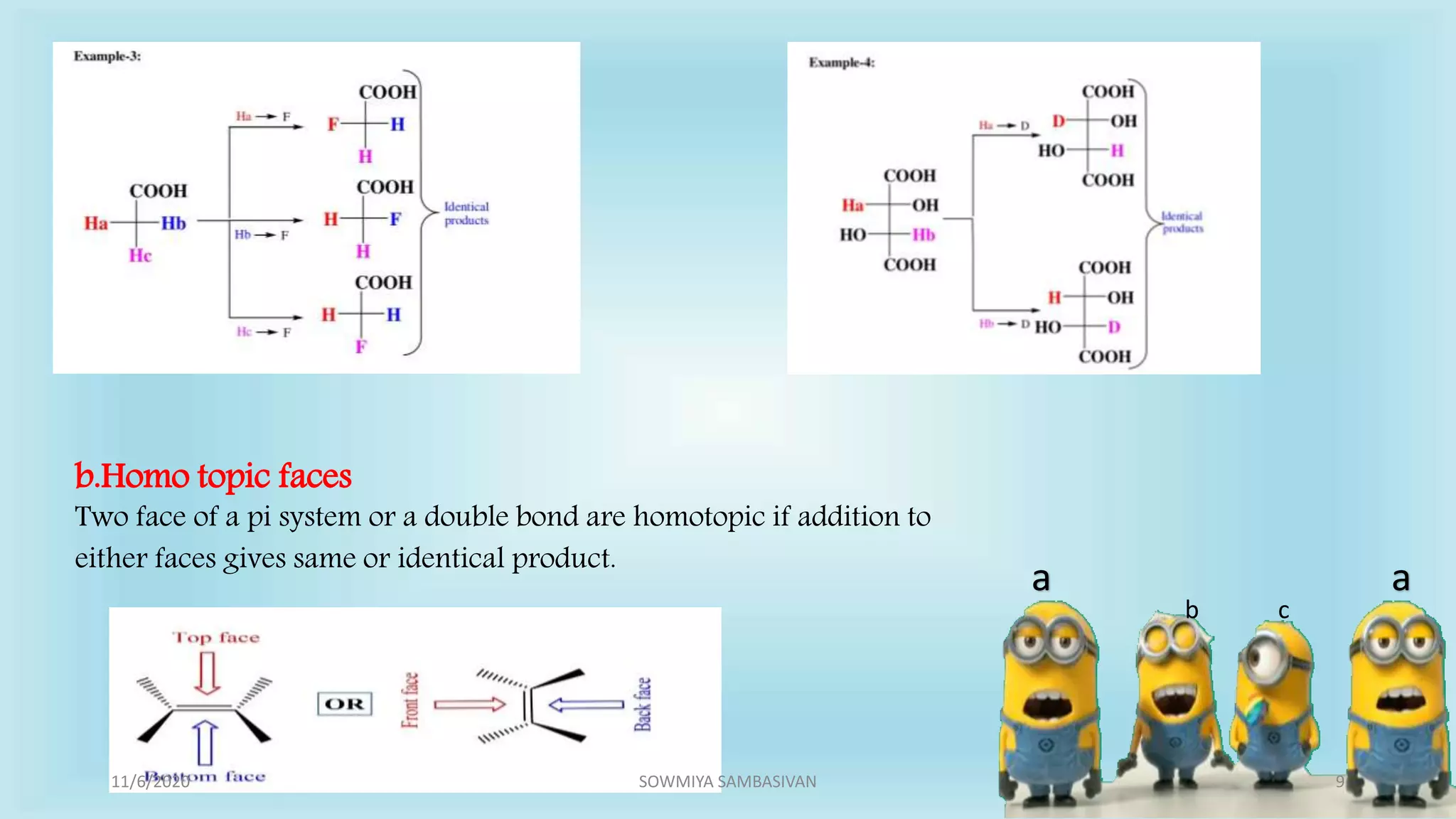
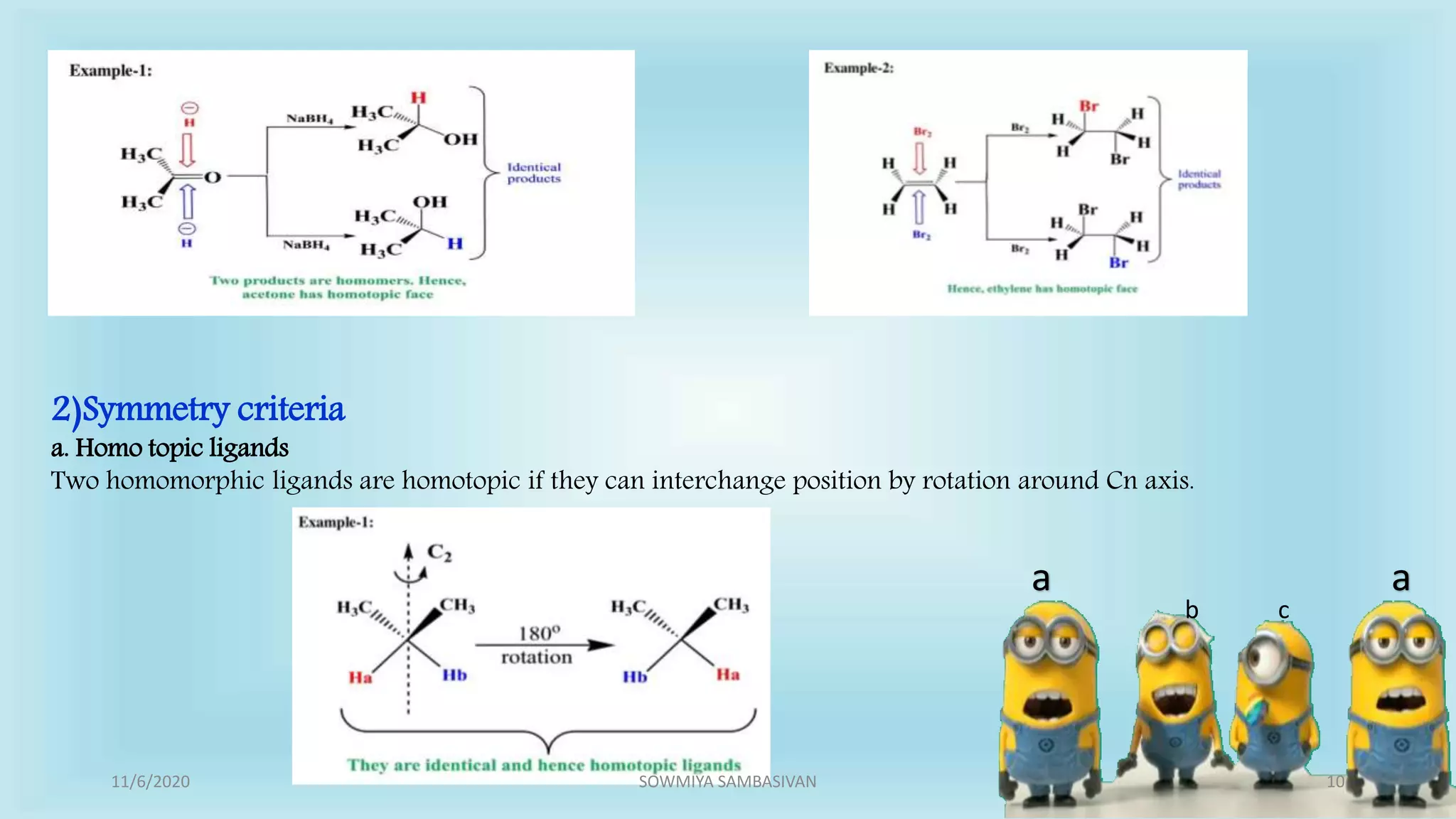
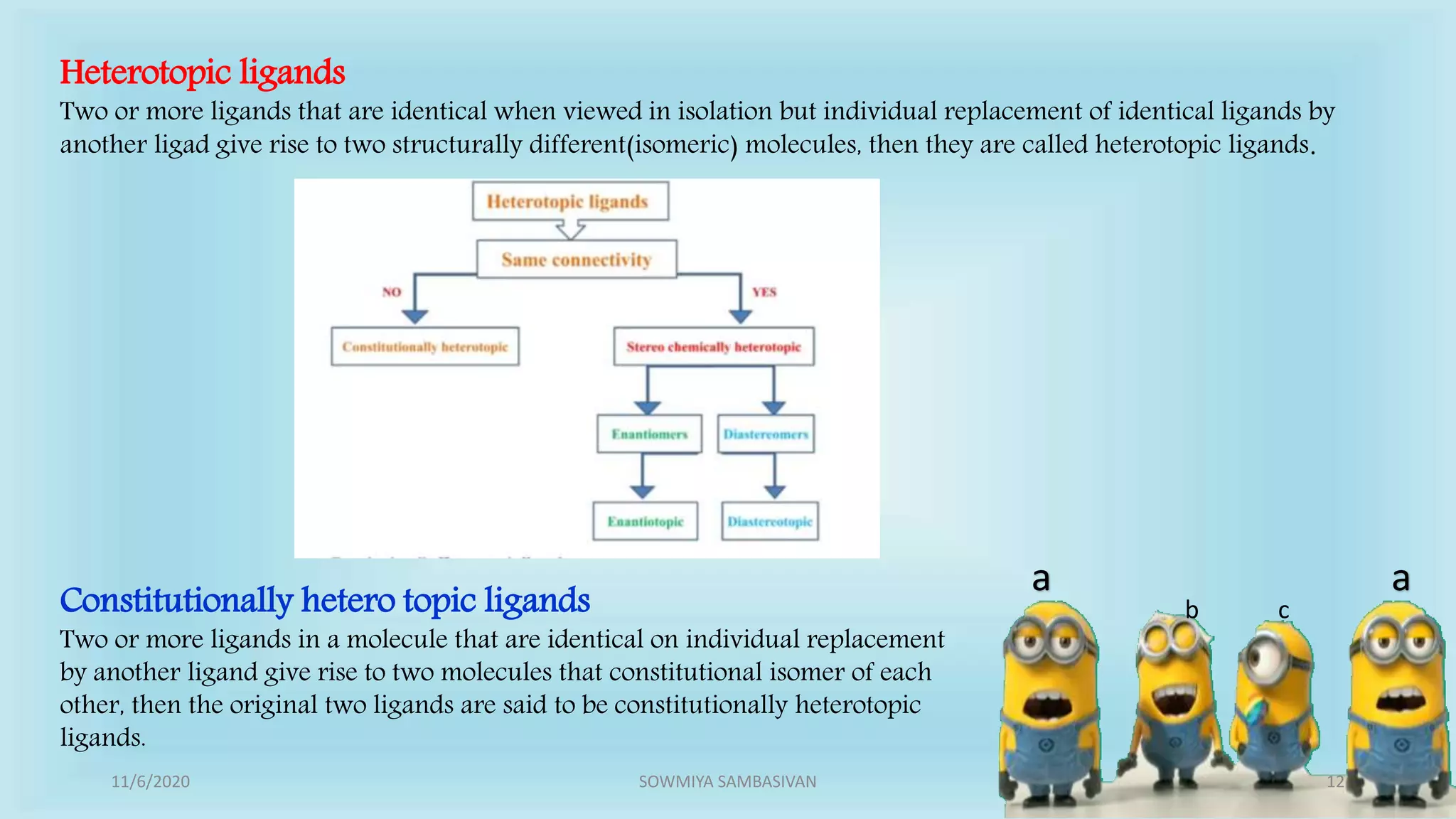
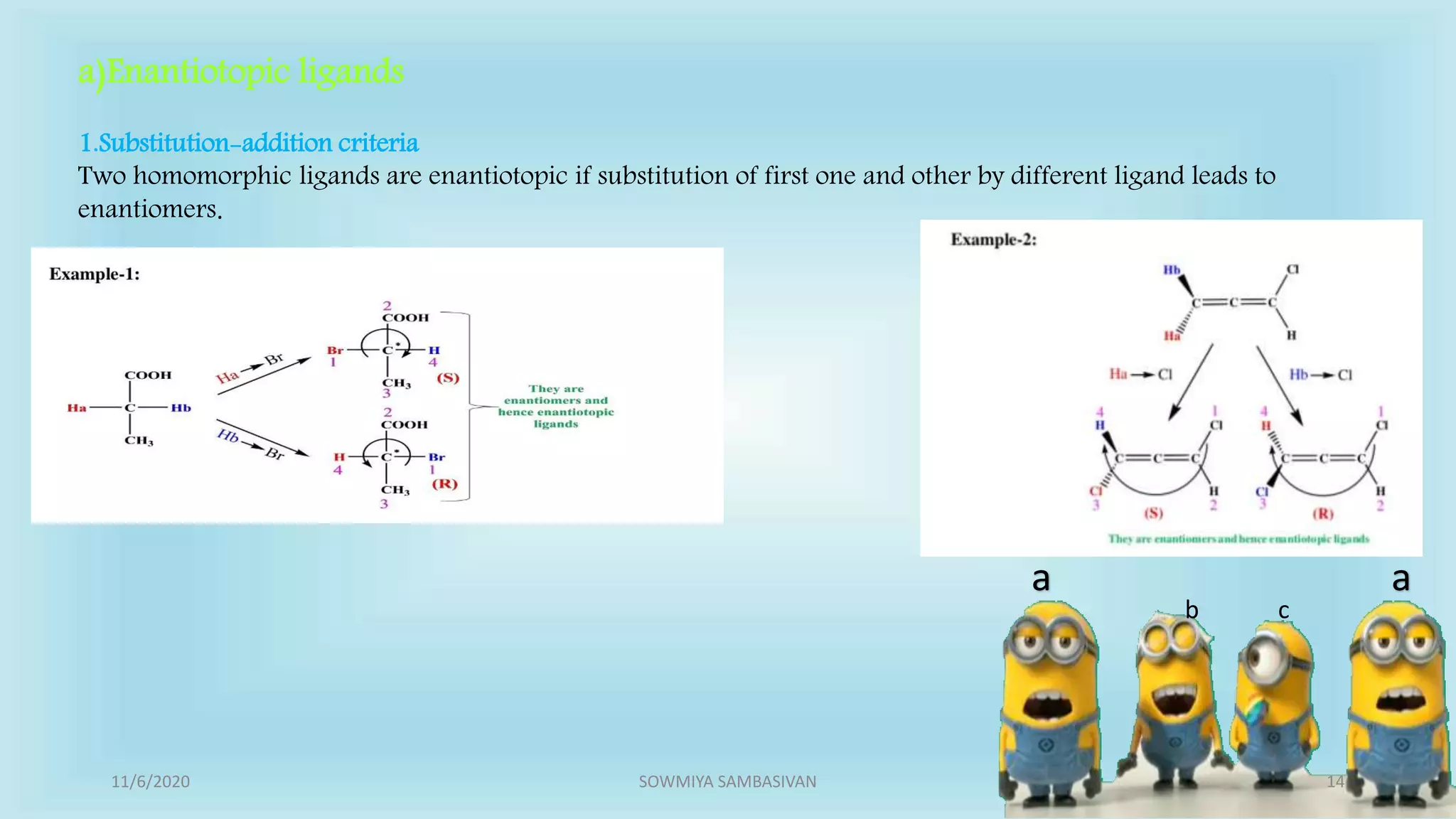
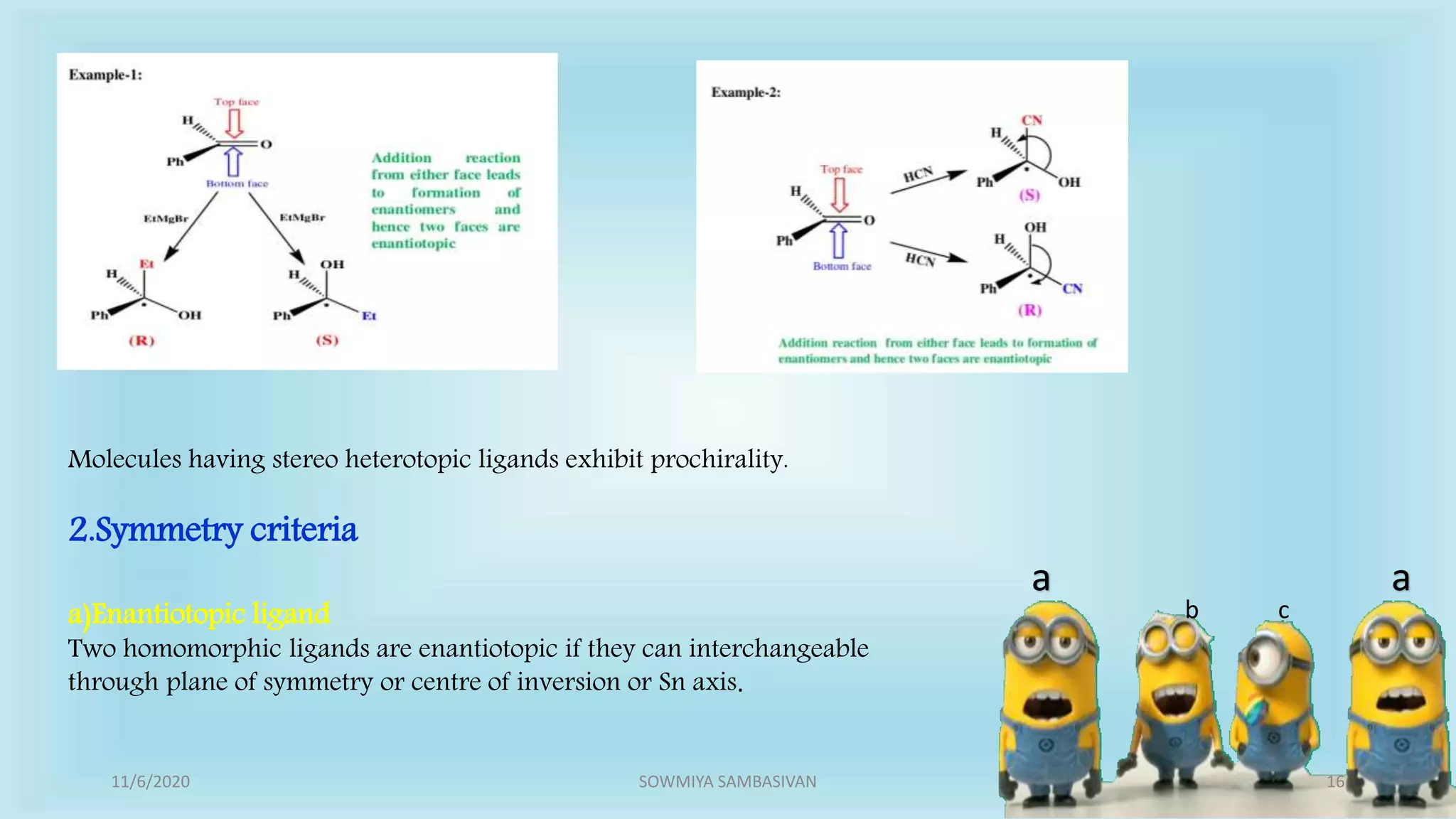
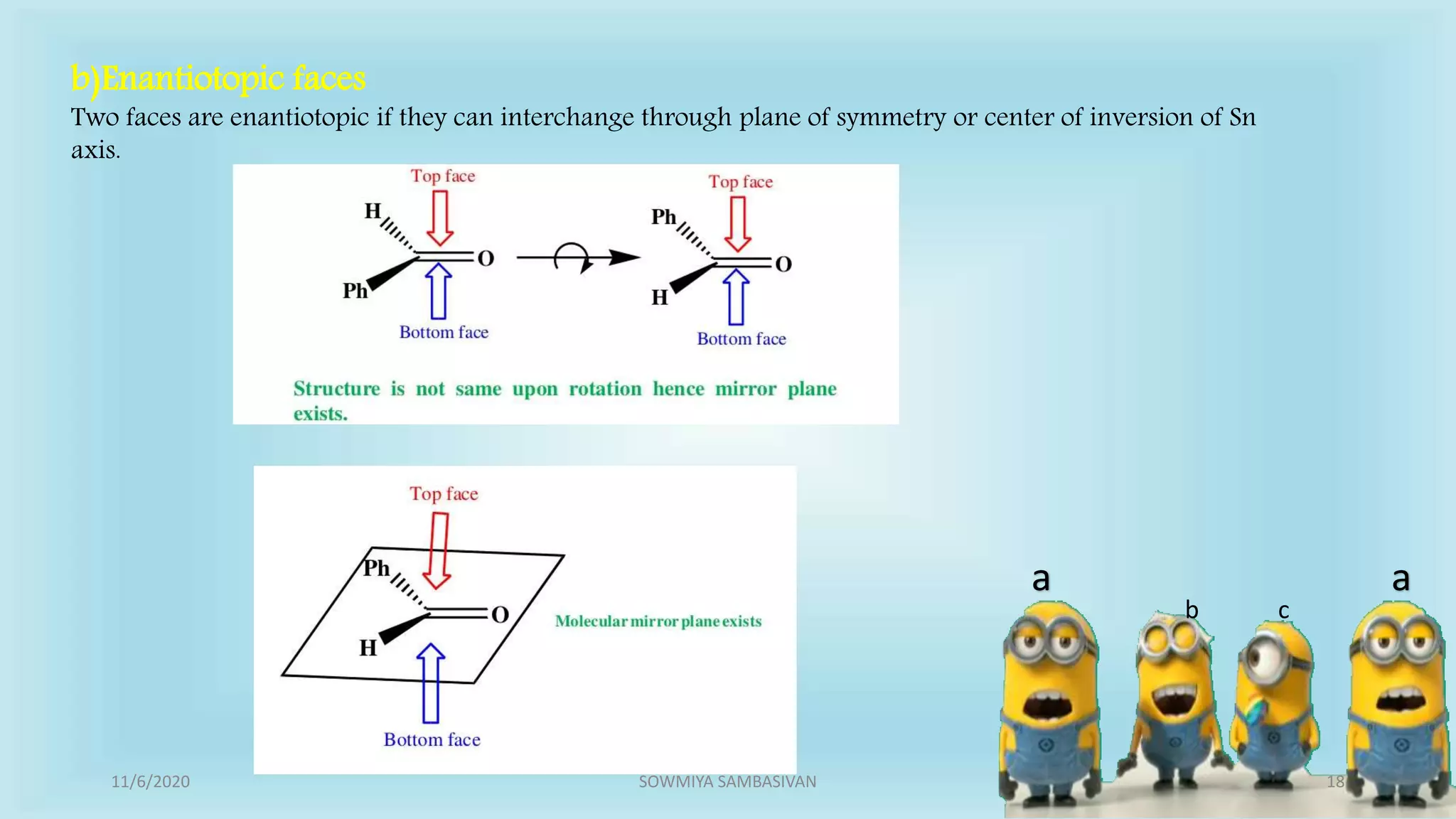
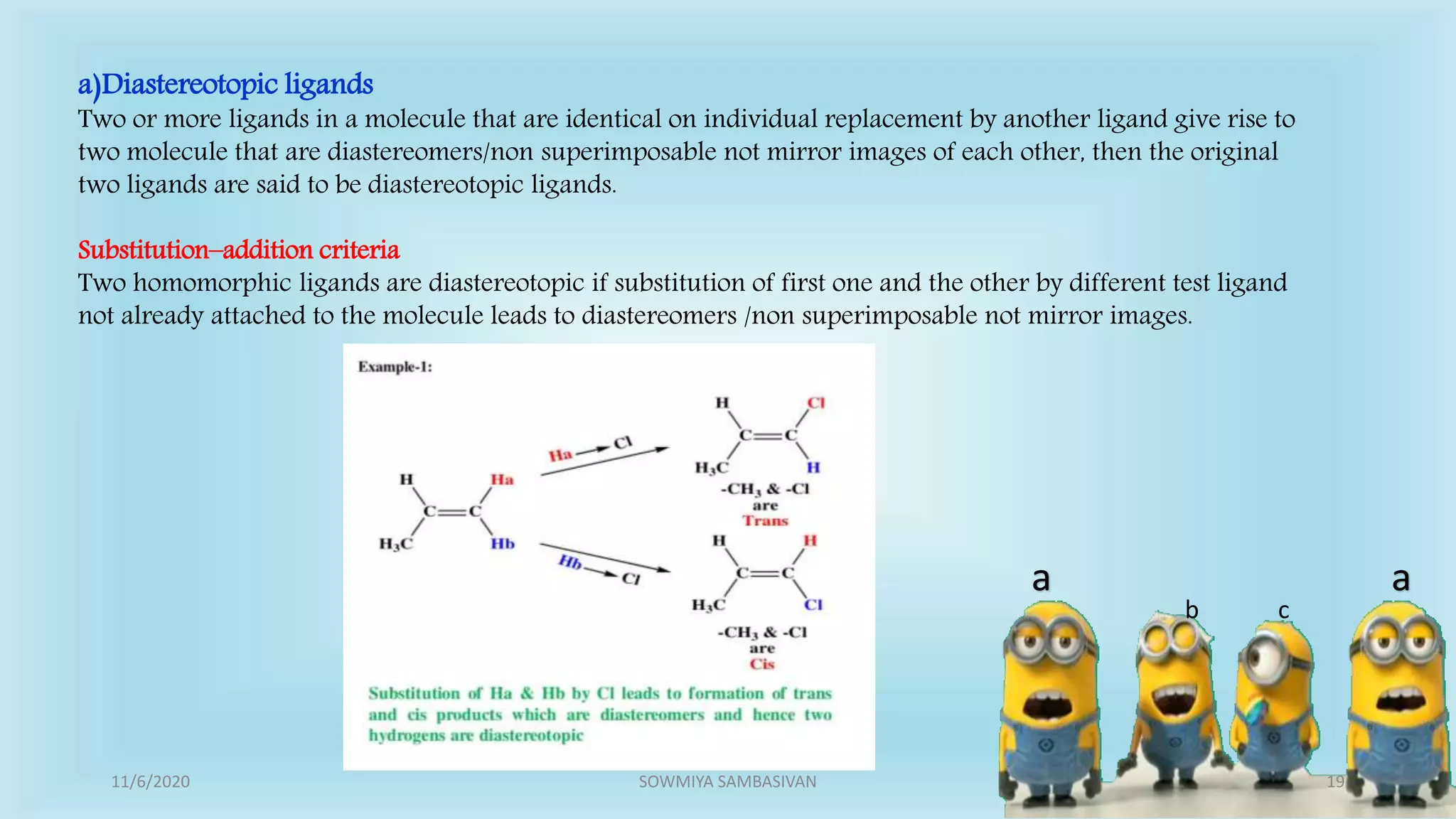
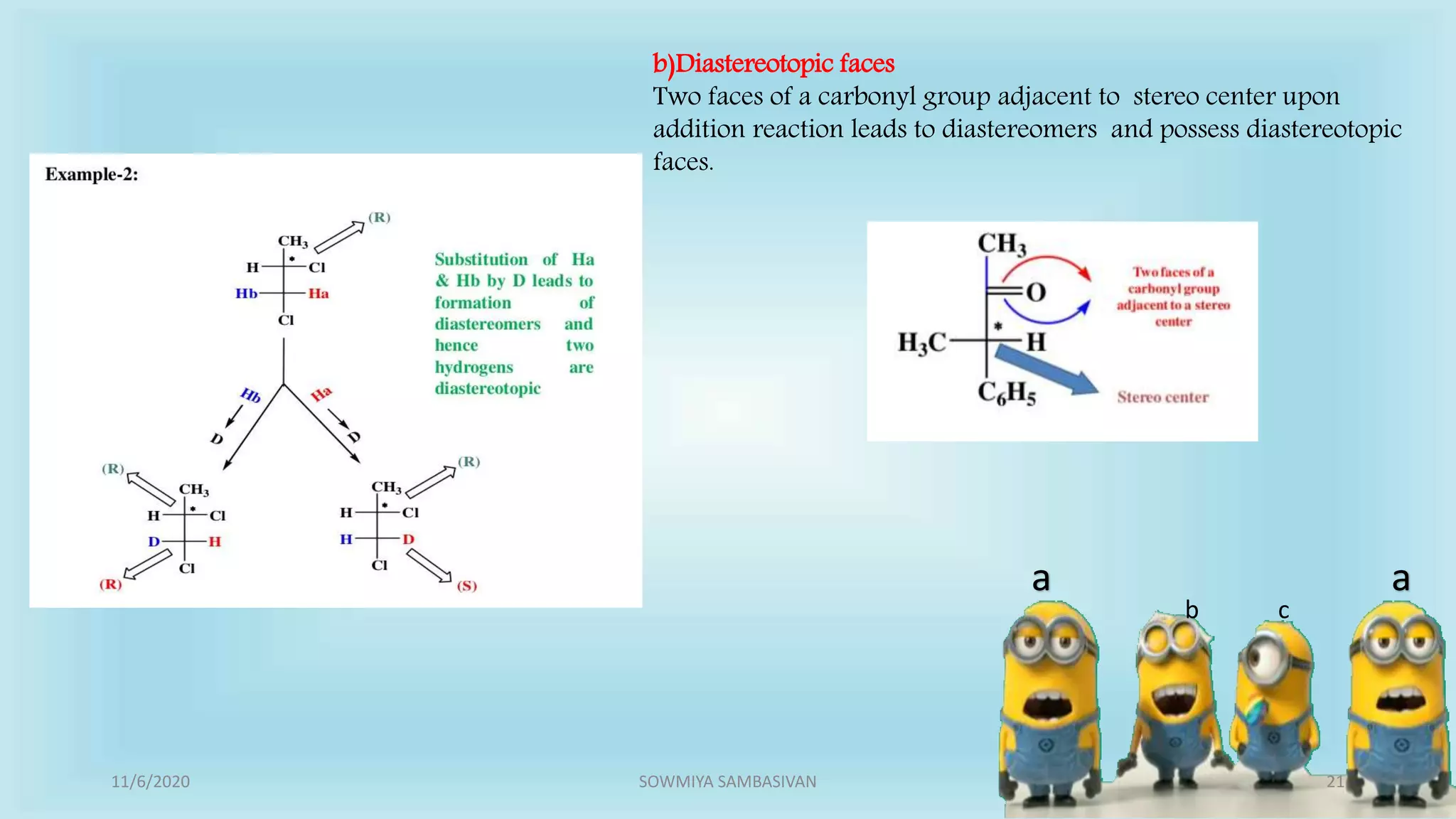
The document discusses prochirality and topicity in organic chemistry, defining prochiral molecules and various types of homomorphic ligands and their relationships. It explains the criteria for identifying homotopic, heterotopic, enantiotopic, and diastereotopic ligands based on substitution, addition reactions, and symmetry. Additionally, it covers the stereochemical aspects of these ligands and their implications in molecular structure and reactivity.