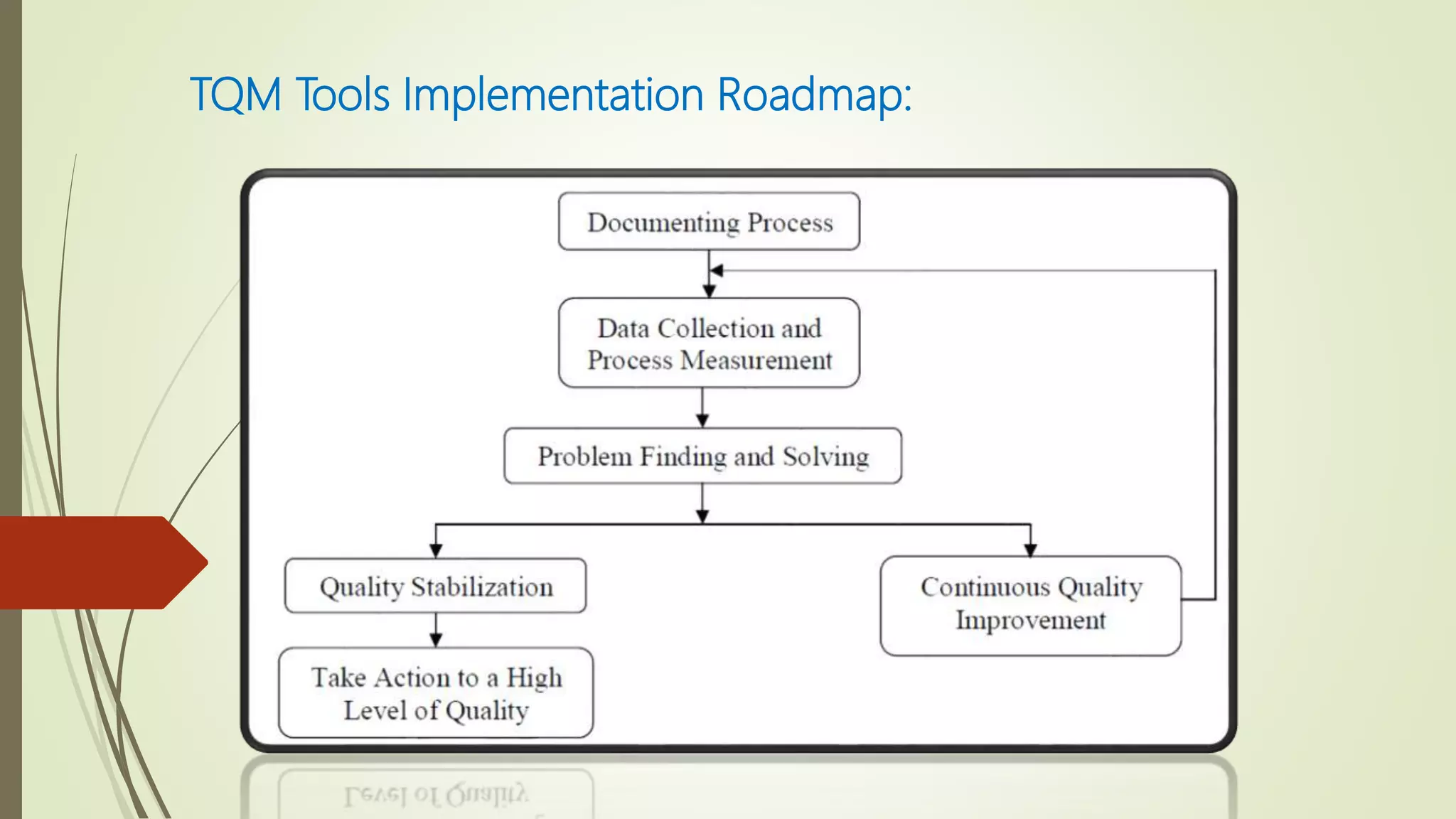
This document outlines the steps to implement Total Quality Management (TQM) in organizations, emphasizing its importance in enhancing customer satisfaction through improved quality and workforce motivation. TQM is described as a comprehensive approach that involves all levels of the organization and aims for continuous improvement while maintaining a focus on customer needs. The text details the historical evolution, objectives, significance, and tools associated with TQM, along with potential challenges in implementation and reasons for failure.