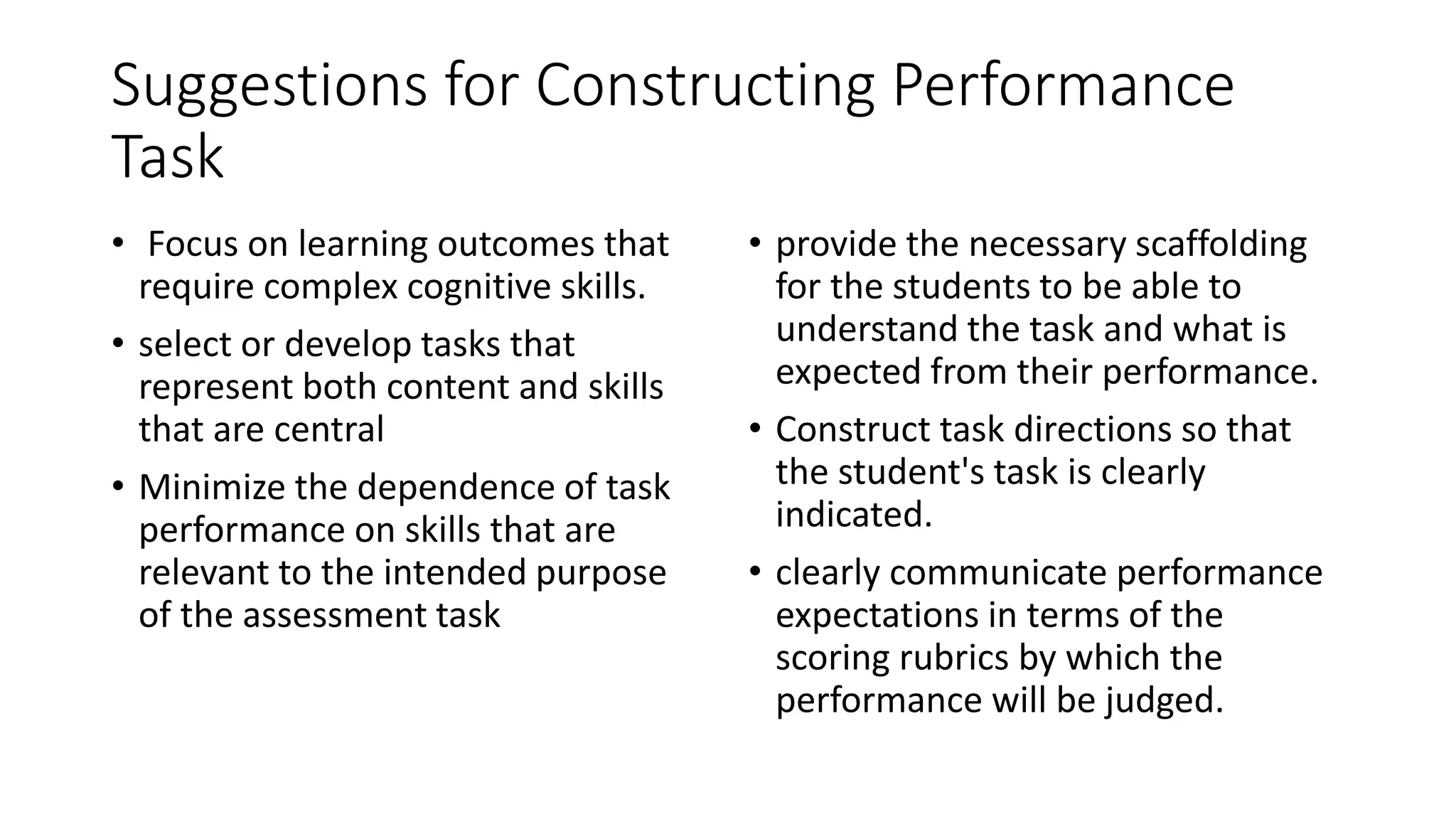
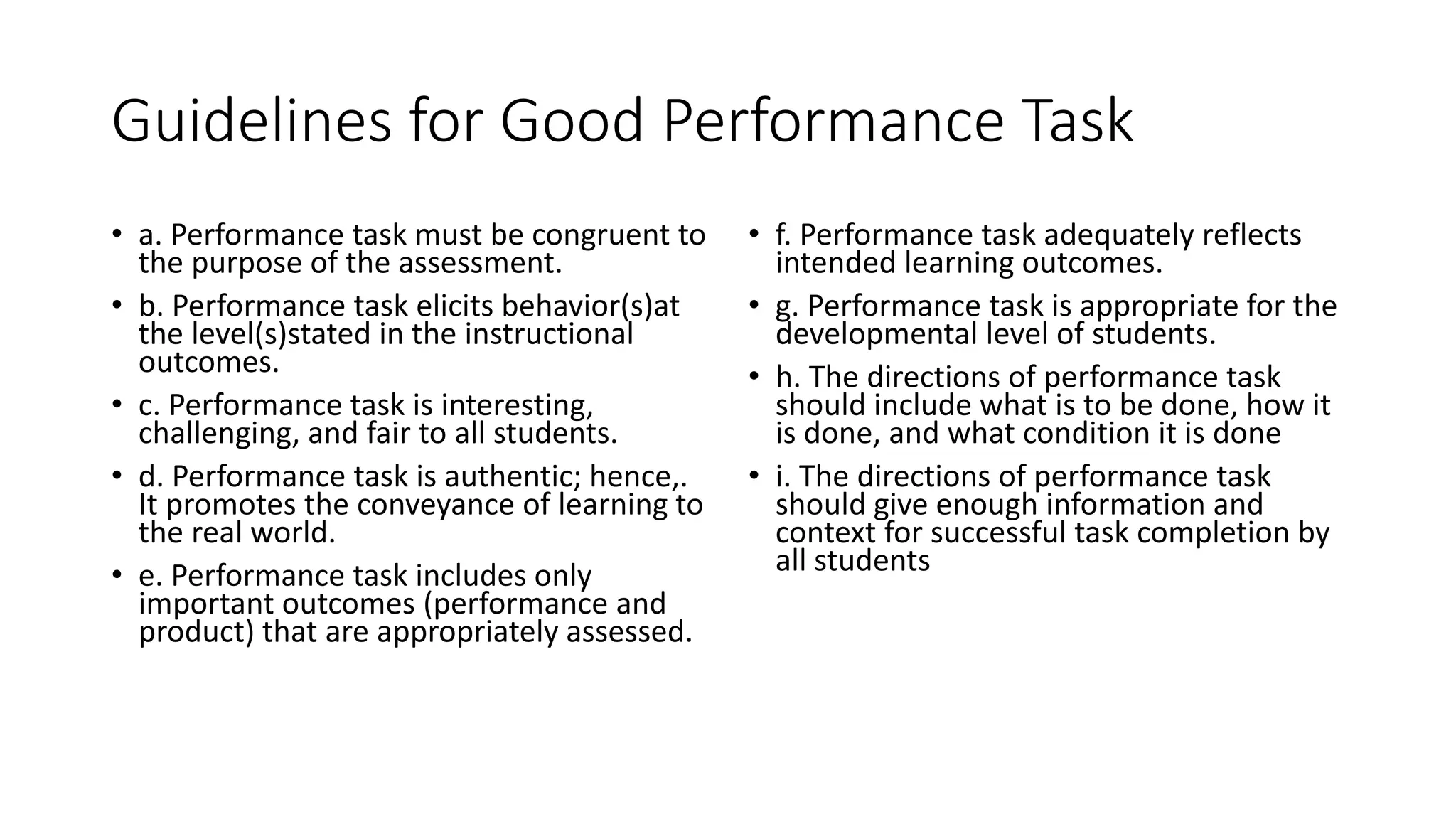
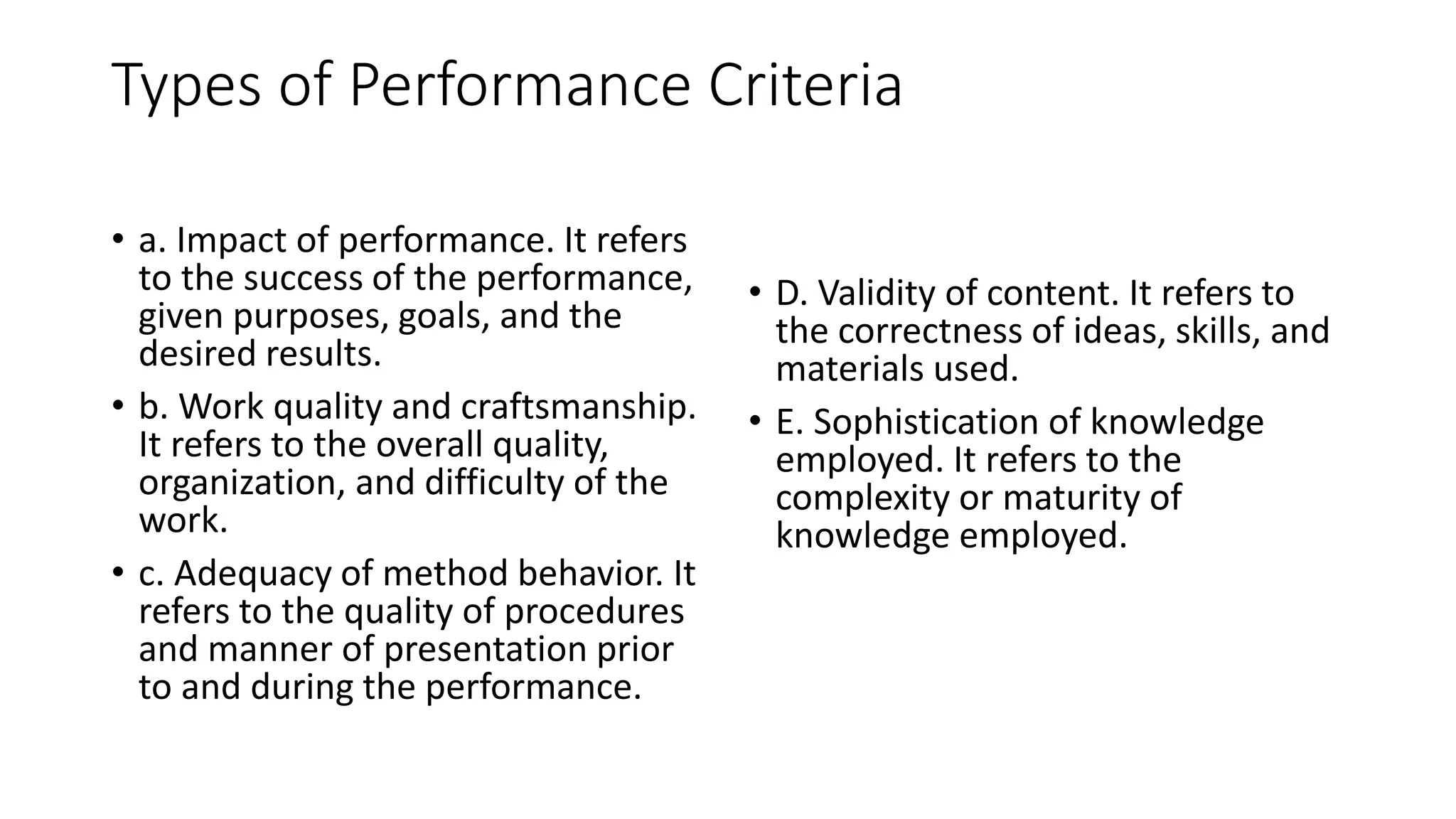
The document outlines the steps for developing performance-based assessments, focusing on how to determine assessment purposes, design effective performance tasks, and establish criteria for judging student performance. It emphasizes the significance of aligning assessments with real-life applications and higher-order thinking skills while providing guidelines for creating scoring rubrics. The document stresses the importance of clarity, engagement, and objective evaluation in the assessment process.