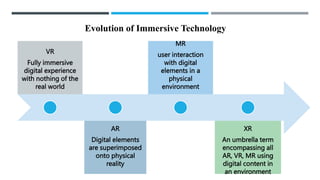
This document discusses STEM education and initiatives in India. It begins by outlining research questions on STEM education and then discusses teaching STEM through an integrated approach focusing on science, technology, engineering and mathematics. It outlines government initiatives to promote STEM like the National Education Policy 2020 and Atal Tinkering Labs. It also discusses building STEM readiness in institutions, corporate initiatives to support STEM and self-initiatives students can take to learn STEM.