The document outlines the Math/Science/Technology (MST) K-5 teacher preparation program at The College of New Jersey, emphasizing its goals to improve integrated STEM education in elementary classrooms. It discusses the historical context, structure, challenges faced, and impacts of the MST program, highlighting significant improvements in mathematics and science knowledge among graduates, as well as gender representation in the field. The program aims to create a well-trained cohort of teachers equipped to facilitate STEM learning, addressing both education policies and student performance metrics.


![TCNJ School of Engineering
K-12 13-16 16-20+
Biomedical
Civil
Computer
Electrical
Mechanical
Technology/
pre-engineering
education [K-12]
MST [K-5(8)]
MAT
Active UG Research
30% graduates go
onto graduate or
prof. school
Future Prof. Dev.
Opportunities
Supports K-20+ Engineering Education Pipeline
Ctr for Excel. In STEM Ed.
3
~50
160
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-3-320.jpg)


![i-STEM Definition / Thoughts
Very important to define i-STEM well
Many studies cite lowered National performance in M & S [T&E?]
Big impact on economic & social processes
“STEM” has become to mean S or T or E or M
Has lead to the acronym becoming less useful, perhaps harmful
Government officials: “ … more support for M & S”
Lose “interconnectedness”
Need a better acronym: “integrated-STEM” is a good step
Why?
S M E T Separate silos with
perhaps M:S and T:E
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-6-320.jpg)
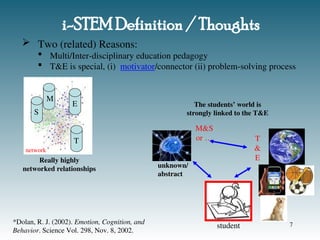
![i-STEM Definition
Possible Def’n: Integration of 2 or more of the 4 STEM
content area with each other into a teaching/learning
experience with purposeful intent of deepening learning.
Common Ex.: M + S
Does not include non-STEM integrations [Soc. St. + M, or … etc.]
Does not account for context/motivation capability of the T&E
Modified Def’n: Integration of 1 or more STEM contents into
A teaching/learning experience, with purposeful intent of
deepening learning.
Ex.’s: M + T/E, S + M, Soc. St. + T/E, or Lang. Arts + S
Due to context-setting and problem-solving process of T&E,
our preference is integrating T&E to other subjects. [Note: E
M&S]
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-8-320.jpg)



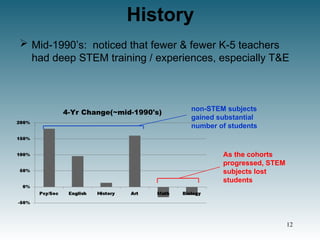
![History
Technology recognized as one of 13 General Ed goals
Society, Ethics, and Technology (1990).
New Jersey Systemic Statewide Initiative director (STEM)
Dr. J. Karsnitz (Chair) convenes study group (1995),
[School of Ed. and Arts & Sciences] ...
MST approved as a new major by TCNJ and NJ Higher
Education governance system (1998).
MST approved as academic major by NJ DOE (2000).
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-13-320.jpg)


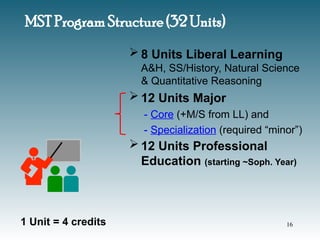
![MST Major Courses
CORE** – 8 units
Mathematics – 1 units
Technology – 2 units
Science – 2 units
MST Electives (M or S or T&E) – 2 units
i-STEM [TED460] – 1 unit
SPECIALIZATION (“Minor”) – 4 units
M, S or T (equal to a minor in discipline)
1 Unit = 4 credits
**Creative Design &
Calculus-I are contained
in Liberal Learning
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-17-320.jpg)
![Specializations
~100% of graduates satisfy requirements for Middle School
endorsements in M or S. [4 courses in M or S … etc.]
A large majority (70-90%) satisfy requirements for Middle School
endorsements in both M or S [4 courses in both M & S … etc.]
~40% of graduates satisfy requirements for K-12 Technology
Education endorsement
1) Technology
2) Mathematics
3) Science (Bio, Chemistry or Physics)
For a total of 5 possible specializations
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-18-320.jpg)
![• Calculus-I*
• MAT105* Mathematical Structures & Algorithms for Educators-I
• MTT202* Teaching Mathematics in the Early Childhood & Elementary
Classroom {Methodology / Pedagogy}
• Engineering (applied) Math
[~85% take this and will likely become required]
• MAT106 Mathematical Structures & Algorithms for Educators-II
• Calc-II
• STA115/215
Required / Typical Math Courses
* Required 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-19-320.jpg)
![• MST202* Methods of Teaching Science, Health and
Technology
• SCI103 Physical, Earth, and Space Sciences
• SCI104 Genes, Cancer and the Environment
• PHY120 Introduction to Geology
• PHY161 Introduction to Astronomy
• PHY171 Introduction to Meteorology
Typical Sci. Courses
No specific Science Content courses are required
EXCEPT for Science Specialization MST [Bio., Physics, Chemistry]
* Required 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-20-320.jpg)

![• Creative Design*
• Multimedia Design (2D)*
• Structures & Mechanisms*
• Integrated-STEM for Child/Adoles. Learner* {Method. / Pedagogy}
• Engineering (applied) Math
[~85% take this and will likely become required]
• BioTech
• Facilities
• Arch. & Civil
Required / Typical T&E Courses
* Required 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-22-320.jpg)
![ Teaching as a Design Process*
Young ages:
Key for setting STEM affect / self-efficacy
Capable age group [Age-appropriate bias]
Girls & minorities
Dev. a deeper understanding of i-STEM and be able to
defend it
Research in field
Plan and implement i-STEM lessons [Purposeful intent]
Physical nature of learning environment
Integrating T&E into K-5
i-STEM Course Overview
23
*Hiebert, J. et. al: Preparing teachers to learn from teaching [J. Teacher Ed. (2007)] and
Learning to learn to teach an “experimental” model for teaching and teacher preparation in
mathematics [J. of Mathematics Teacher Ed. (2003)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-23-320.jpg)


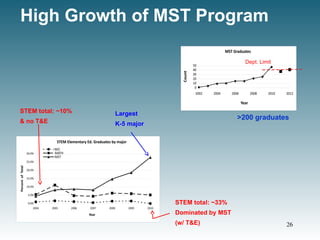
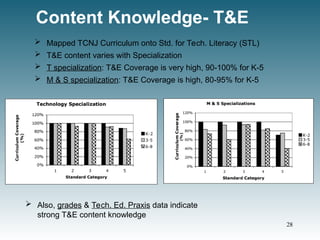
![Content Knowledge- M & S
ETS PraxisTM
test #0014
Relative results by subscore subject
t-test results: [95% Conf.; NMST=59, Nnon-MST=346]
• Math: p = 0.004; Science: p = 0.001
(Example: for math the MST population scored 5.5%
higher than the non-MST population.)
MST graduates relative to non-MST graduates.
Statistically significant higher
M & S performance
Statistically equivalent
performance on non-STEM
subjects !
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-27-320.jpg)
![Math Anxiety
Non-STEM vs. STEM
High anxiety (top quartile)
1:3
1:5
1:4
1:14
SAT (Math) Scores
TCNJ
Non-STEM [602]
MST [643]
K-5 Math [638]
- - - - - - - - - - - - -
National Ave.
Sch. of Ed. [483]
Sch. of Engin. [579]
Math [614]
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-30-320.jpg)
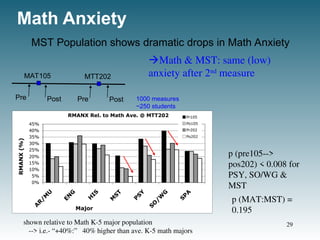
![Math Anxiety [MST Spec.’n]
RMANX: MST (Po202) RMANX: Tech. Spec.
N Ave SD N Ave SD
T&E 21 64.6 10.3 Pr105 11 76.8 15.9
Math 21 69.3 15.7 Po105 10 71 13.6
Sci 8 73.5 15.1 Pr202 18 67.2 8
Po202 21 64.6 10.3
Effects of T&E curriculum ?
Anxiety for T&E Special.z’n subpopulation drops dramatically
T&E has less M & S but more T&E courses
Substantial context, applications (applied math)
I II
Continuing Data Collection:
Double #’s within 1 year. 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-31-320.jpg)
![Gender Benefits
Historically, a high level of MST graduates are male [15-20% ]
• TCNJ K-5 average is ~5%, independent of major
• National average for K-5 teachers is ~9% (2001) {1981: 18%}
80+% MST graduates are female
Research strongly indicates these graduates will be
effective role models for female K-5(8) students,
halting the gender “gap” in STEM
Continue?? 32
Female
Male
!!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-32-320.jpg)

![Overall Lessons Learned
“Teachers as Designers:” good Teach. Prep. Model
Design Process applies to T&L environment …
ID Problem Ideate . . . Assess … Loop
Mixing Elementary with Secondary students, all in the
School of Eng., are really good
T&E courses having Content & Pedagogy is good
Gender benefits:
STEM-capable female teachers [Big !]
Perhaps attract more male K-5 teachers
Math/Quant. literacy is a problem
T&E content likely helping math / science anxiety.
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-34-320.jpg)



![Enablers and Challenges for
other Schools
~5 Universities have inquired about our i-STEM program as part of their
effort to establish i-STEM in their K-5
Obstacles:
Entrenched & “packed” K-5 programs / Faculty Loading / Economy
No Stds/State Policies for T&E or i-STEM in K-5 (or even 6-12)
PA: (i) K-5 K-2 & 3-8, (ii) Increase in field experience time
MD: Counterpoint, Strong State-wide Effort in i-STEM
[Stds, Teacher Prep, Assessment … etc.]
CN: perhaps a strong Govern.-driven effort starting … ?
Leaders / Visionaries in K-5 Faculty / Chairs
38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-38-320.jpg)

![Important Questions
– Affect
– Anxiety/S. Eff.
– Content
– Problem-solving/
21st
-Cent. skills
Students
– Affect
– Anxiety/S. Eff.
– Content/Methods
– Problem-solving/
21st
-Cent. skills
Teachers
– Impact others?
[Teachers, Admin.,
Policy, State … ]
– i-STEM Curr. Dev.?
– Expanding i-STEM
activities/methods?
T&L
Environ.
Perhaps 3 categories of important research questions:
Teacher Prep
Long- and short-term Impacts, not simply Pre vs. Post
PBL is our ally and challenge here
[i-STEM approaches vs. Conventional]
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-40-320.jpg)
![Questions for Teacher Prep
What aspects of i-STEM are needed / preferred in (i) K-
5(8) and (ii) Teacher Prep.?
T&E (i-STEM content/benefits)
PBL
Pre- vs. in-service
Systemic change vs. speed
How to promote both?
In-service data promote systemic change
Committee could also refer to output from ASEE’s
Workshop on Eng. Ed. in K-5 (@NCSU) [2009]
41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-41-320.jpg)
![Foundation Funded i-STEM …
Acquired Foundation Funding to promote i-STEM
curriculum [$100K Year-1, building over successive years]
New NJ standards on 21st
Century skills
New NJ policy on Prof. Learning Communities
PD i-STEM w/ EbDTM
curriculum
o EbD is inexpensive and very flexible
o EbD onlline enables large data collection
Key Goals:
Successful PD for i-STEM curriculum (w/ EbD & TCNJ data
collection)
o 20 Districts in Year-1
Pursue a few research questions (per previous slides)
Have PD become financially self-sustaining
Common curriculum / common dialog
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obrienfinal-240918184718-fccfc1cd/85/Obrien-FINAL-Chapter-5-and-chapter-6-ppt-42-320.jpg)
