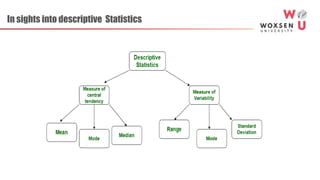
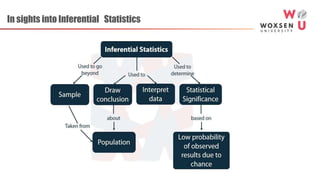
This document provides an introduction to business statistics by Prof. Venkat Reddy Yasa. It defines statistics as the science of decision making with calculated risks in the face of uncertainty or the collection, presentation and interpretation of data. The history and origin of statistics is discussed from the 18th century where it referred to state data collection to the 19th century where systematic data collection and analysis emerged. Modern statistics plays a key role in business, industry, science, economics, and other fields through data analysis. Descriptive and inferential statistics are introduced along with common statistical software used for analysis. Limitations of statistics are also noted.