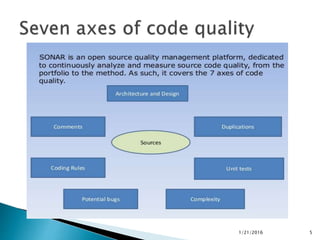
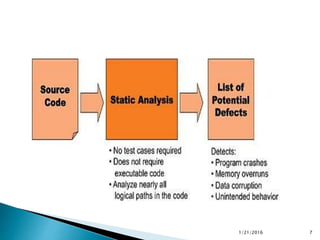
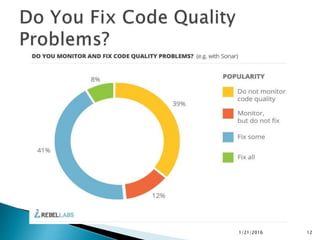
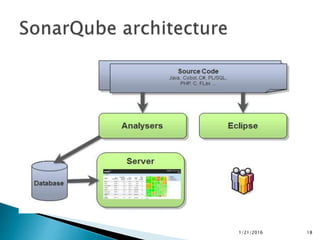
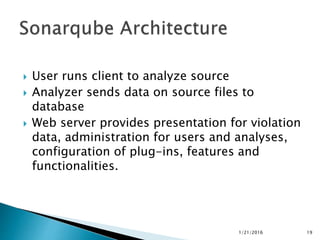
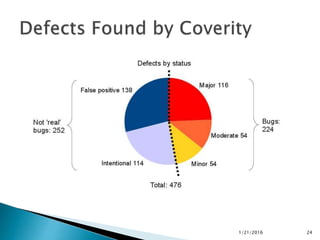
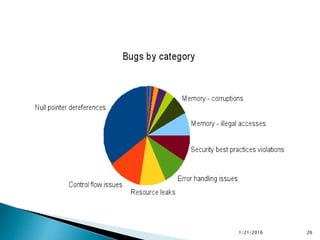
This document discusses static code analysis and tools like SonarQube and Coverity. Static code analysis examines code without executing it to find bugs. Monitoring and fixing code quality issues improves application quality and delivery. SonarQube is an open source tool that manages code quality through analysis, issues detection, and metrics. Coverity also detects defects early through static analysis of various languages. Both tools help improve code quality.