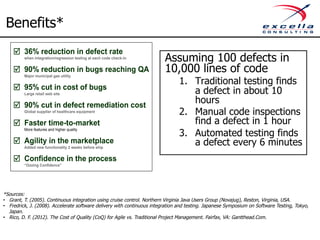
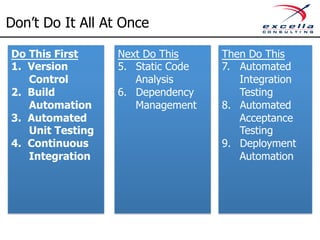
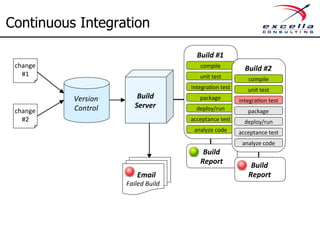
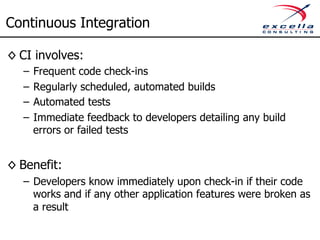
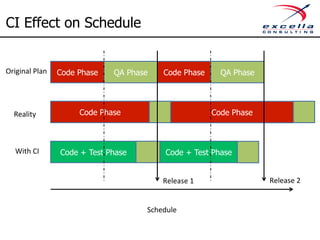
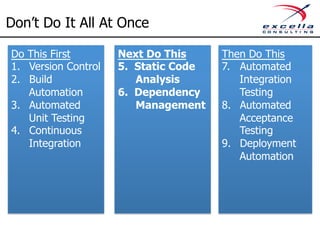
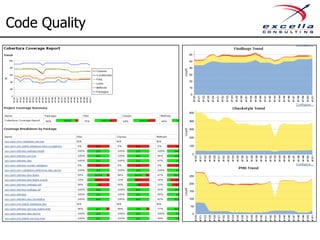
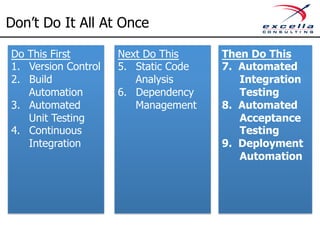
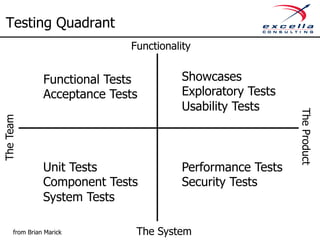
The document outlines best practices for implementing quality and agile methodologies in software development, emphasizing the importance of tools such as version control, automated testing, and continuous integration. It details the sequential steps to establish a robust agile workflow, highlighting significant improvements in defect rates and cost reductions achieved through automation and early testing. Additionally, it includes insights on team member's rights and references to further literature on agile practices.