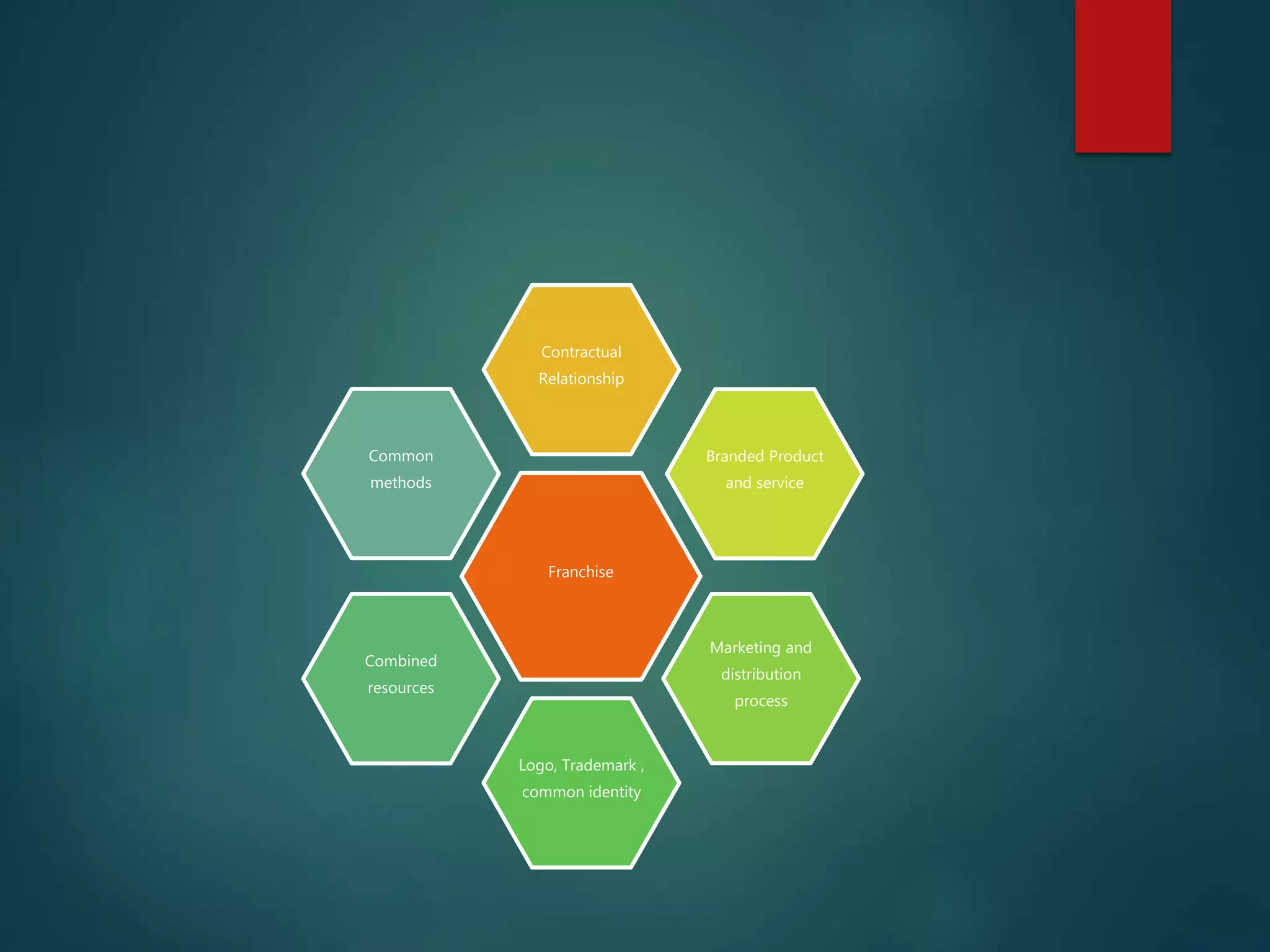
There are several options for starting a new venture as an entrepreneur, including buying an existing business, starting a new business, or franchising. When buying an existing business, some advantages are reducing risks and obtaining an established customer base, while disadvantages can include needing modernization or inaccurate financial records. Important factors to consider include business finances, assets/liabilities, location, and reasons for sale. Starting a new business requires entrepreneurial skills, but allows more freedom and control. Franchising provides an established brand but less independence, with advantages and disadvantages for both franchisors and franchisees. The two main types are product distribution and business format franchising.