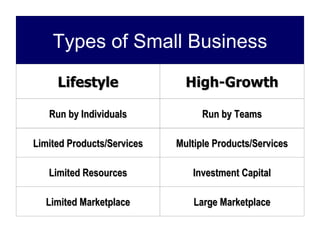
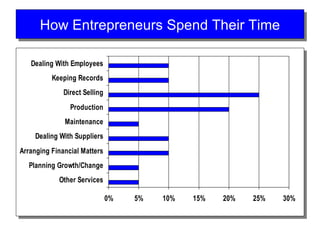
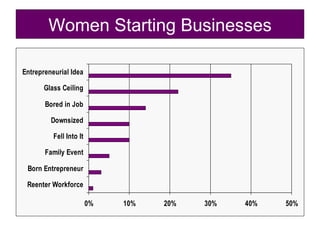
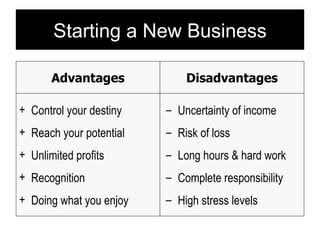
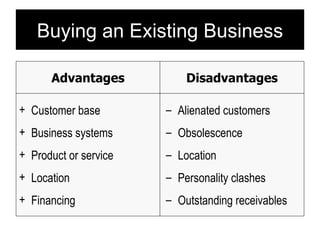
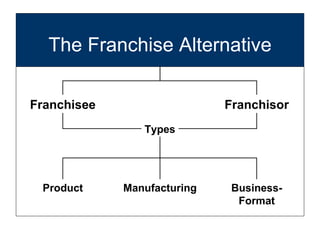
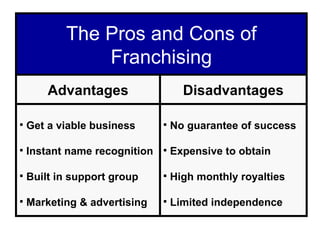
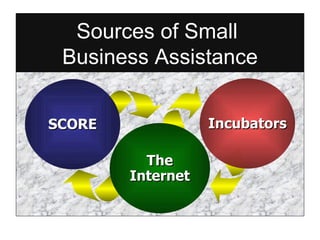
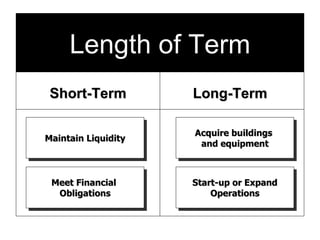
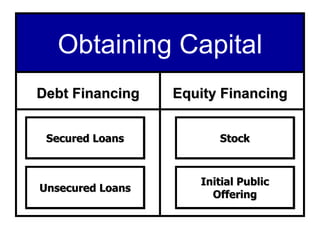
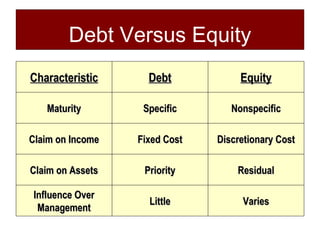
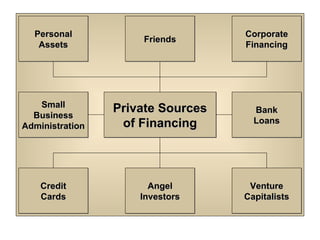
Starting and Financing a Small Business discusses the different types of small businesses including lifestyle, high-growth, and franchise businesses. It also covers how entrepreneurs spend their time, factors contributing to small business growth like technology and women/minorities, and the importance of preparing a business plan to guide operations and attract investors. The document outlines sources of financing for small businesses including debt, equity, and government assistance as well as why many new businesses fail due to issues like poor planning, funding, and management.