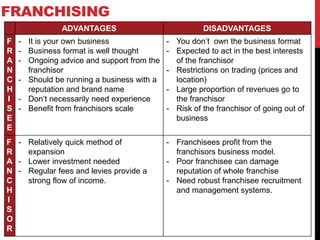
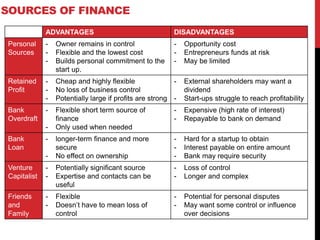
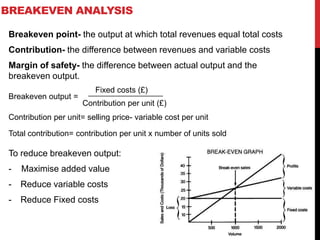
This document provides information about starting and running a business. It discusses key characteristics of successful entrepreneurs, reasons for starting a business, risks involved, and rewards. It also outlines sources of funding, choosing a business structure, employing people, calculating costs and revenues, and setting objectives. The overall content provides guidance to entrepreneurs on important business concepts to consider when launching a new venture.