Start up seminar-a
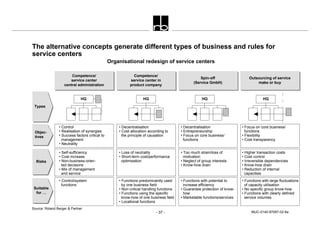
- 1. - 37 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a Organisational redesign of service centers The alternative concepts generate different types of business and rules for service centers Types Objec- tives Risks Suitable for … Competence/ service center central administration Competence/ service center in product company Spin-off (Service GmbH) Outsourcing of service make or buy HQ HQ HQ • Control • Realisation of synergies • Success factors critical to management • Neutrality • Decentralisation • Cost allocation according to the principle of causation • Decentralisation • Entrepreneurship • Focus on core business/ functions • Focus on core business/ functions • Flexibility • Cost transparency • Self-sufficiency • Cost increase • Non-business-orien- ted decisions • Mix of management and service • Loss of neutrality • Short-term cost/performance optimisation • Too much strain/loss of motivation • Neglect of group interests • Know-how drain • Higher transaction costs • Cost control • Irreversible dependencies • Know-how drain • Reduction of internal capacities • Control/system functions • Functions predominantly used by one business field • Non-critical handling functions • Functions using the specific know-how of one business field • Locational functions • Functions with potential to increase efficiency • Guarantee protection of know- how • Marketable functions/services • Functions with large fluctuations of capacity utilisation • No specific group know-how • Functions with clearly defined service volumes HQ Source: Roland Berger & Partner
- 2. - 36 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a Allocation of optional central functions Allocation alternative Sample companies Reallocated functions Spin-off (Service GmbH) HQ • KHD • Krupp • Mannesmann • Hoesch • Springer • AGROB • Klöckner-Werke AG • Daimler Benz • AEG • Hardware and software • Auditing • Licensed sales/handling • Personnel management • Central research • Insurances • Training and seminars • Real estate/housing • Forwarding/dispatch • Travel agency Competence/ service center in business field HQ • MBB • VOEST Alpine • Hoesch • Dornier • Freudenberg • AEG • Accounting • Data processing (primarily hardware) • Locational services (security, canteen etc.) • Purchasing • Training • Payroll accounting • Pensions Div. Focus on • Org/DP • Accounting functions • Consulting • Locational services Outsourcing of service HQ In practice, there are typical, time-honoured concepts for the organisational redesign of service functions Source: Roland Berger & Partner
- 3. - 35 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a 1.5 Service center
- 4. - 34 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a The holding company's typical core functions are the result of the type of management pursued Financial management Operative management • Operative controlling/budgeting • Central administrative functions/systems • Coordination of product development/centralised functions • Coordination of distribution/central functions Management functions required Staff dimensioning Type of management Increasing number of functions Strategic management Typical core functions of a holding company • Group strategy/ROI participation portfolio • Allocation of resources, finance • Financial management/treasuring • Participation management (reporting) • Investment guidance/monitoring/strategic planning • Strategic group planning/controlling • Programme planning • Participation planning/M+A projects • Synergy management via committees and central functions • Target coordination of operative plans • Basic issues regarding personnel/management development • Central services/facilities, if applicable Staffing of central administration Source: Roland Berger & Partner Example
- 5. - 33 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a Entrepreneurial vision and objective Determinants and characteristics of the holding company's organisation Type of management pursued by partners Type of holding • Financial • Strategic • Operative Functions • Core functions • Optional functions • Service functions Staff dimensioning Management concept and management situation Management system and vertical collaboration Business/participation portfolio Strategic and operative management demand The type of management pursued thus forms the basis for the detailed design of the holding company Source: Roland Berger & Partner
- 6. - 32 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a The management focus can lead to three specific types of holding companies regarding management objectives and central functions Typical central functions Management objectives • Maximum return on equity - no matter in which business • Dividend/return on capital • High company values • Strategic optimisation of resource utilisation • Management of synergies • Management of "white spots" • Industrial management company • Strategic and operative result optimisation using all business fields • Operative control/optimisation of business fields/functions • Market shares, ROI, growth • Finance/Treasuring • Legal/tax • Group accounting • Participation management • Finance • Group controlling • Strategic planning • Executive development • Distribution/sales coordination • Group marketing • Group services Optional: • Central research • Group distribution • Management staff e. g. • Finance/accounting • Central distribution • Central development • Works organisation Types of holding companies Financial holding co. Strategic management holding co. Services Operative management holding co. Central busi- ness units Source: Roland Berger & Partner
- 7. - 31 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a Decentralisation and establishment of management holding companies are the general organisational trends for group organisations General strategic/organisational trends Increasing significance of takeovers, mergers and strategic alliances within the framework of international division of labour and globalisation Rediscovery of small, flexible, decentralised business units with own entrepreneurship to deconcentrate large companies and utilisation of business potentials Decentralisation of DP into functions and flexible structure-independent management/communication systems "From hierarchy to expertocraty" as structural characteristic of large companies, i. e. flat structures and new management requirements • Necessary business orientation of organisation by way of business field segmentation • Decentral management and organisational concepts under a minimum of superior structures (as a framework for values, vision and synergies) • Often extreme re-thinking in the companies due to loss of core business dominance in structures, qualification and culture Management holding organisation Source: Roland Berger & Partner
- 8. - 30 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a 1.4 Holding concept
- 9. - 29 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a • Personification of inte- gration is necessary • Multipliers must come from both companies/ become firmly anchored in the other one Initiator • Start of communication process with six core issues Contents • Most important target group during 1st phase are executives • Executives need to commu- nicate/support integration top-down • Information of responsible executives at Ruther group Target group • Focus on existing media • Supplemented by ad hoc transition media later to be integrated into the overall concept Media • Reduction of individual interpretations/insecuri- ties • Speeding up top- down information Effect Who says what to whom using which media pursuing which goal? 1. Historical development from point zero to present 2. Strategy 3. Process of integration 4. Intercultural collaboration 5. Structure/organisation 6. Results of transition teams • CEO of both companies • Executives from both companies Total number of contacts (Nov./Dec. 94) 20.253 (Executives + staff) • XY actual • AB today • Company newsletter of integrated company • Management summaries • Segment-internal jour fixe • Achievement of common base of information Activities during the start phase The project phases' individual parameters of communication are designed in great detail Example PMI Source: Roland Berger & Partner
- 10. - 28 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a A requirement for successful communication during a PMI-Project is a comparable level of information of all those involved Start: Communication of decision-making process Turning point: Objective: Communication of integration/success and focus on business process/ day-to-day business Phase Communication of progress/success/ decisions in the integration process 1. 2. 3. Process Communication Objective • Creation of a common basis of information • First step towards common convictions/opinions • Modification/adjustment of communication • Anchoring and acceptance of common values, standards and objectives Tools Media, e. g. • xy actual • Company newsletter To be supplemented by: • Personal communication (e. g. social contacts) • Feedback (e. g. survey, workshops) • Management tools (e. g. training/ preparation for rotation) Closed concept • Top-down • Bottom-up Information Information Feedback Sender Recei- ver Communication concept Example PMI Source: Roland Berger & Partner
- 11. - 27 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a 1.3 Communication concept (KK)
- 12. - 26 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a The results of the cultural audit cover the major factors of corporate management • Strategic success factors • Characteristics of the company • Structure • Working methods • Staff/executive qualification • Incentive systems • Motivation • Personnel management • Career development • Information/communication • Management style • Working atmosphere • Flexibility/readiness to change • Innovation orientation • Behaviour towards staff/trust • Work processes • Decision-making processes • Openness/transparency/ communication competence • Entrepreneurship • Internationalisation Result areas Questionnaire relating to individual questions relating to several questions • ––––––––––– • ––––––––––– • ––––––––––– Source: Roland Berger & Partner
- 13. - 25 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a The cultural audit is performed in three steps using standardised tools Pilot phase • Approx. five to ten interviews/explo- rations with executives and participants in the project to determine focus issues • Adjustment of standardised questionnaire by integrating the company's specific situation • Coordination of questionnaire action • Design of sample/selection of target persons Collection phase • Mailing of questionnaires to executives/ staff (incl. explanation of objectives and procedure) • Monitoring of questionnaire-return and evaluation of responses • Interpretation of responses • Development of recommendations for action/measures Communication of results • Presentation (Board/executives) • Management workshops – Detailed discussion of results – Expansion/coordination of recommen- dations for action • Internal communication in the company 1 2 3 Steps of cultural audit-approach Source: Roland Berger & Partner
- 14. - 24 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a The cultural audit identifies weaknesses in the collaboration between a company's staff and its executives Cultural audit • Identification of disruptive factors • Weighted evaluation of identified disruptive factors Objectives • Personal interviews – Executives – Staff • Questionnaires – Executive survey – Staff survey • Workshops with executives – Guarantee/expansion analysis – Conceptualisation of target culture Tools Source: Roland Berger & Partner
- 15. - 23 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a 1.2 Cultural audit (CA)
- 16. - 22 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a The critical project phase is the deduction of organisational consequences from business system and strategy Source: Roland Berger & Partner • Concept development • Workshop • Presentation Development of design concepts and alternatives • Management concept/structure • Organisational structure Detailed design of target organisation incl. actual/target transition models Strategy audit • Identification of strategic position, opportunities/risks, orientation and strategies • Business field segmentation incl. business system and success factors • Deduction of strategic and organisational requirements for management, structure and systems • Expert interviews (internal) • Secondary data • Workshops Pilot interviews Familiarisation with business, problem structure and focuses of the survey • Top management/ shareholder interviews Step 4 Step 5 Step 2 Step 1 Step 3 Organisational assessment • Actual organisation and distribution of functions • Strengths and weaknesses • Company image and management concept • Executive discussions (1st - 3rd level) • Secondary data
- 17. - 21 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a SBO: From business system to strategy-oriented group structure Source: Roland Berger & Partner Functional, divisional service relations Management concept Actual Business position/ strategies Actual target Corporate organisation/ culture Actual Model/targets/vision of partners and top management Controlled management concept central/decentral Business field identifi- cation Business affinities/ synergies Business field strategies Business system/ success factors Manage- ment system/ potential Strengths/ weak- nesses Strategic evaluation of functions • Core functions for the management of a business field • Optional functions • Superior control functions Formation of busi- ness units • Bundling of core function into manage- ment areas (business units) • Formation of cen- tralised functions and service areas • Organisational structures Detailed design of target organisation • Management struc- ture of business units • Management structure of superior control/ synergy utilisation • Horizontal and vertical management system • Management requirements Manage- ment require- ments Analysis Manage ment require- ment Corporate culture Deduction Design SBO-approach
- 18. - 20 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a Strategy-based Organisation: How to establish business-oriented organisational structures Optional functions Market Business activities Business needs Core functions Deduction of strategic business needs Identification of core functions Creation of business units Design of overall management structure Adjustment of management systems Segmentation of business activities Management Advisory boards Central functions Commit- tees Service- Center Business units Optional functions Line functions? Service functions? Make or buy? Subsi- diaries Internal structure Source: Roland Berger & Partner
- 19. - 19 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a 1.1 Strategy-based organisation (SBO)
- 20. - 18 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a Examples of existing consulting programs 1. Strategy-based organisation (SBO) 2. Cultural audit (CA) 3. Communication concept (KK) 4. Holding concept 5. Service center Source: Roland Berger & Partner
- 21. - 17 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a 1. Classical issues and tools of CC Organisation
- 22. - 16 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a Newly developed or currently being developed Consulting programs, tools and new concepts of CC Organisation – an overview Products/programs Instruments/tools Industry know-how Marketing tools (Issue papers) Basic studies/ organisational concepts • Benefit for public image/ competence references • Project modules • Accessibility/ up-to-dateness • Marketability • Standardisation (manual) • Internal training module • Marketing/acquisition base • Innovation for new programmes • Marketability • Defined client benefit • Science/practice links • Internal training • Basic expertise/know-how• Value for publication• Standard approach • Documentation (AA)EDP-supported process analyses: Supplement process cost analysis (SGS)Strategic reduction of overhead/structural adjustment (FKD)Functional ratios file (HDD)Holding benchmarking/ documentation (PA)Personnel structure analysis (ÖHD)Public sector documentation (CA)Cultural audit Management systems: Adjustment to divisional requirements (KA)Cost structure analysis (BRD)Organisational documentation by industry (CCP)Cultural change programme Lean management/ Business reengineering (KK)Communication concept (FA)EDP-supported function analysis (OGK)Operative reduction of overhead Study on European management culture Holding concepts Family-owned businesses (PAD)Personnel structures file (SBO)Strategy-based organisation (PMI)Post Merger Integration • CC Marketing Model for transnational company management incl. practical examples (TUF) Virtual corporation concept (RL)Implementation guidelines Networking Source: Roland Berger & Partner
- 23. - 15 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a B. Tools and concepts of CC Organisation
- 24. - 14 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a The WDR example shows that interactive projects are more costly, but can achieve better results Source: Roland Berger & Partner 9 3 6 12Time Cost 2$ 5$ 2$ 5$1$5$ Quality Errors t Results • Reduction of processing times by up to 80 %, e. g. fee calculation and remuneration of freelancers from three weeks to three days • A minimum of DM 18 million direct cost reduction • Establishment of internal customer/supplier relations reduces error rates and increases customer satisfaction Example
- 25. - 13 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a This approach counts on a continuously increasing employee participation in the course of the project Active and passive participation of employees in the change process 10% 100% Anchoring, contin- uous improvement DisseminationPilot implementation Actual analysis, target forecast Kick-off Communication and off-and-on participation Work in the changed organisation Process/project teams Employees Source: Roland Berger & Partner Example
- 26. - 12 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a The pilot implementation forms an integral part of the interactive bottom-up project work at WDR Selection of process Actual analysis Concept and measures Pilot implementation Dissemination Anchoring • Workshops • Individual tasks • Basis teams • Cooperation with divisions concerned T C Q • Pilot region • Set targets • Training • … Source: Roland Berger & Partner Steps of project work at WDRExample
- 27. - 11 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a Top-down approach Objectives defined by the Board Desk research/ benchmarks Interviews at manager level Target concept (discussion) Implementation Consultant as expert, little interaction Source: Roland Berger & Partner Steps of project work at Deutz Motor GmbHExample
- 28. - 10 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a The decision for a consulting approach depends on the objectives pursued Consulting approach RB&P consulting programs Client objectives Company development Bottom-up Starting with the employee Restructuring Top-down Starting with the business system Source: Roland Berger & Partner Alternative consulting approaches
- 29. - 9 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a 2. What is the proceeding in organisational projects?
- 30. - 8 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a Fields of application for organisational consulting • Horizontal and vertical structuring • Functional and object orientation • Centralised – decentralised • Staff line Structures • Division of labour – integration of functions • One piece flow • Coordinative mechanisms Processes and cooperation • Operative and strategic controlling • Management systems, forums • Incentive systems Systems • Thinking in terms of divisions • Value added/customer orientation • Exchange of information Culture Management Source: Roland Berger & Partner Five fields of potential change have to be worked on
- 31. - 7 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a The main objective of organisational consulting is to improve efficiency and effectiveness of an organisation External factors Internal factors Time, cost and quality as competitive factors Activities in the world market Technological progress Product/market diversity Complex structures Size • Reduced product life cycles and market cycles • Delivery time and flexibility of delivery • Eastern Europe • Globalisation • Competitive/cost pressure • High demand for capital and know-how • New technologies as success factor • Diversity of business • High coordination expenses • High degree of division of labour • Many hierarchical levels • Staffs • Turnover • Employees • Countries • Increase flexibility • Strengthen innovative power • Improve ability to cooperate • Manage core competences Objectives of organisational consulting Source: Roland Berger & Partner Determinants and objectives of organisational consulting
- 32. - 6 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a International organisational structures – an overview
- 33. - 5 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a 1. What is organisational consulting?
- 34. - 4 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a A. Object and approach of CC Organisation
- 35. - 3 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a
- 36. - 2 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a A. Object and approach of Organisation 4 1. What is organisational consulting? 5 2. What is the proceeding in organisational projects? 9 B. Tools and concepts of CC Organisation 15 1. Classical issues and tools of CC Organisation 17 2. New consulting programs 38 C. Structure and tasks of CC Organisation 44 Index Page
- 37. - 1 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a Roland Berger & Partner GmbH – International Management Consultants Barcelona – Beijing – Berlin – Brussels – Bucharest – Budapest – Buenos Aires – Düsseldorf – Frankfurt – Hamburg – Helsinki – Hong Kong – Kiev – Lisbon – London Madrid – Milan – Moscow – Munich – New York – Paris – Prague – Riga – Rome – São Paulo – Shanghai – Stockholm – Stuttgart – Tel Aviv – Tokyo – Vienna Start-up Seminar – Organisation – Roland Berger & Partner GmbH International Management Consultants Munich, August 1997
- 38. - 0 - MUC-0140-97097-02-6a MUC-0140-97097-02-06 6 0140/Dr. Simon x 58 0 58 58 0 0 0 0 1 1 4 0 Remarks: Doc.Controlling:Doc.Controlling:Doc.Controlling: Client: Project number: Project title: Project start: Branch office: Partner/Competence Center: Documentation title: Type of document (e.g. workshop): Date of issue/of presentation: Place where hard copy is filed: Resp. for preparation: Resp. for graphic: document INFOrmationdocument INFOrmation One-doc. Seiten: Korrekturen: Planung: Arbeitstage … Doc.Code No.: Cost centre + Project manager: KW ja nein ange- meldet neu erstellt alte über- nommen ver- wendet KDL neue Seiten KDL KDL nach Präs. Korrekt. zeit (Min.) zw. Anmeld. + Abgabe zw. Fertig- stell. + Präs. Produk- tion Verzugs- zeit (Min.) Automatische Trennung: Dokument zu- letzt geöffnet am: 06.05.199916:04 Uhr "Ein" "Aus" Vorlagen: gut schlecht Fax mittel Controlling in Sammelliste eingegeben Intern A 97000 140 97 MUC Dr. Simon/Orga Einführungsseminar Workshop Februar ‘97 Fr. Ruff Hr. Padberg Hr. Böhm Textfeld x x