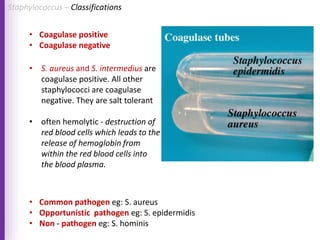
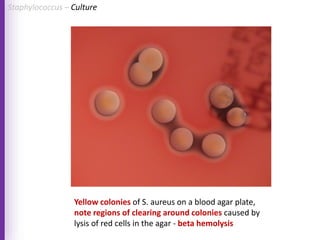
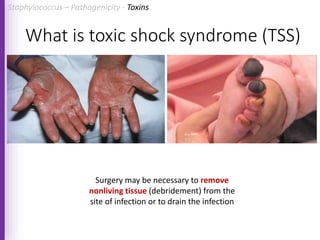
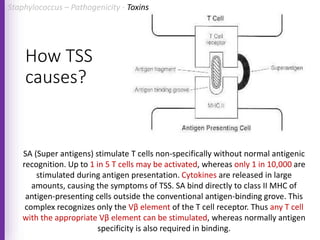
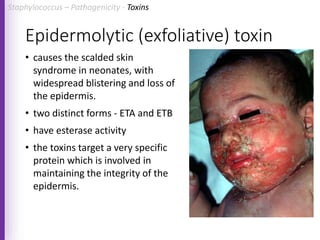
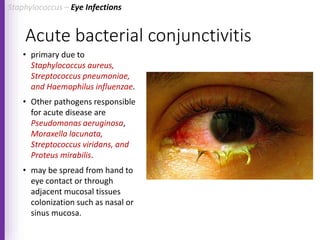
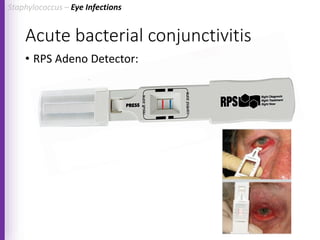
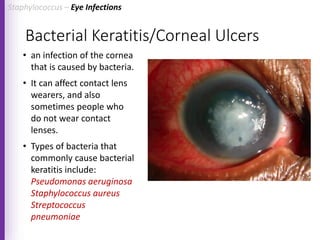
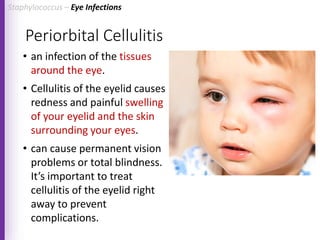
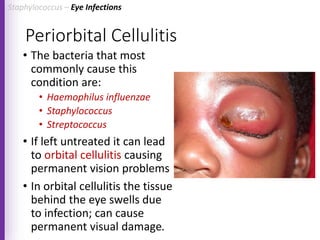
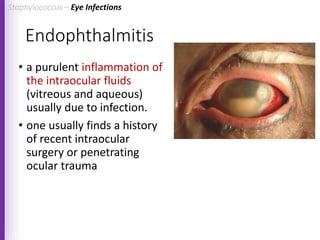
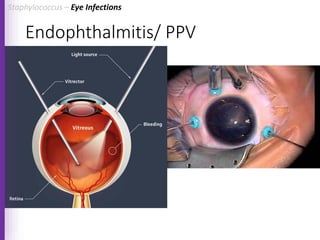
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Staphylococcus bacteria, including their classification, pathogenicity, and the infections they cause, particularly eye infections like conjunctivitis and keratitis. It details the structure, virulence factors, and toxins associated with Staphylococcus aureus and related species, as well as treatment options for various infections. Additionally, it discusses diagnostic procedures and risk factors associated with staphylococcal infections.