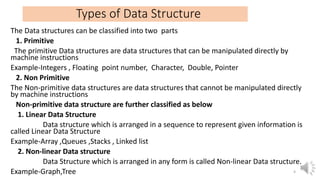
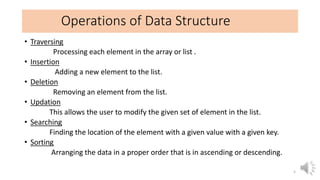
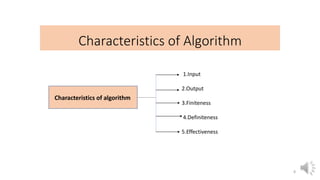
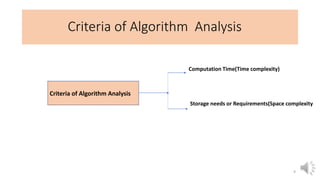
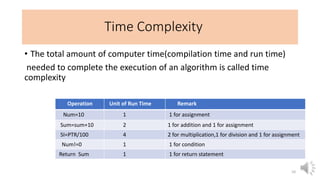
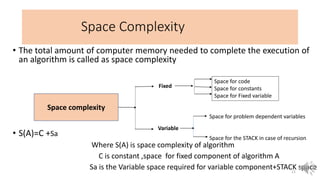
This document provides an introduction to data structures, including definitions, types, and operations. It defines a data structure as a particular way of organizing data in computer memory for effective use and retrieval. Data structures are classified as primitive (directly manipulated by machine instructions) and non-primitive (requiring machine instructions to manipulate). Non-primitive structures include linear (ordered sequences like arrays and lists) and non-linear (graphs and trees) types. Common operations on data structures include traversing, inserting, deleting, updating, searching, and sorting. The performance of algorithms that use these structures depends on their time complexity (computation time) and space complexity (memory usage). Lists and arrays are introduced as examples of linear data structures.