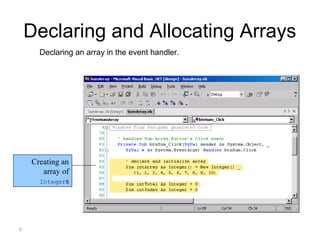
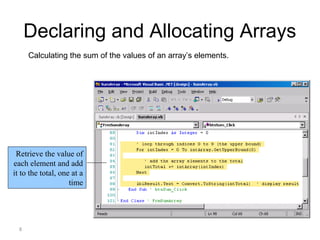
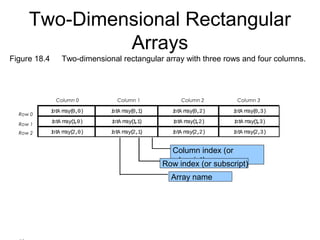
This document discusses one-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays in Visual Basic. It introduces arrays as data structures that store multiple values of the same type under a single variable name. Elements in an array are accessed via an index or position number, starting at zero. The document shows how to declare and allocate arrays, including initializing element values. It also covers retrieving an array's length and highest index. Finally, it discusses two-dimensional arrays, which require two indices to access individual elements and are often used to represent tables with rows and columns.