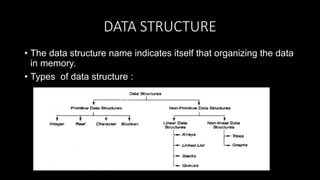
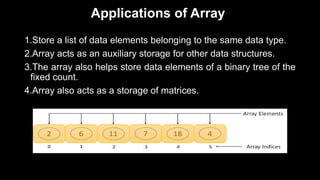
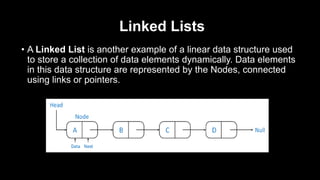
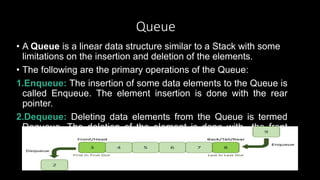
This document provides an overview of common data structures and algorithms. It discusses static and dynamic data structures, including arrays, linked lists, stacks, and queues. Arrays allow storing multiple elements of the same type and can be one-dimensional, two-dimensional, or multidimensional. Linked lists connect nodes using pointers and can be singly linked, doubly linked, or circular linked. Stacks follow LIFO principles using push and pop operations, while queues use enqueue and dequeue following FIFO order. These data structures find applications in areas like memory management, expression evaluation, job scheduling, and graph searches.