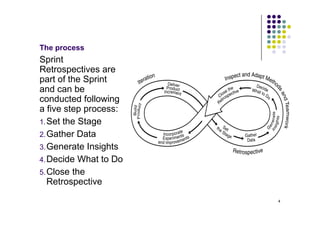
Sprint retrospectives are meetings where teams reflect on past work periods to learn and improve future sprints. The process involves setting the stage, gathering data on metrics and events, generating insights by investigating successes and failures, deciding on priority areas to improve through voting, and closing by documenting decisions and planning follow up. The goal is for teams to regularly adjust their behaviors to continuously improve effectiveness through reflection.