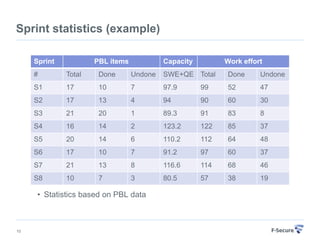
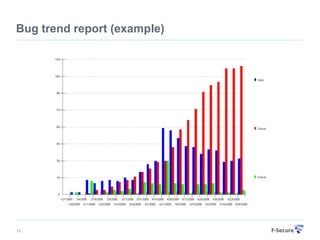
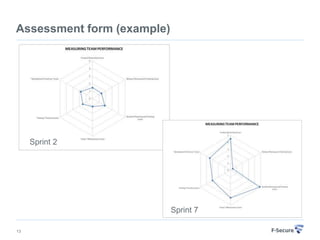
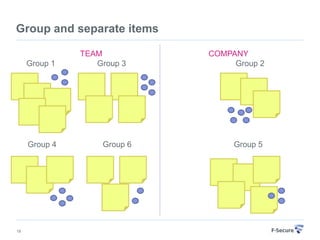
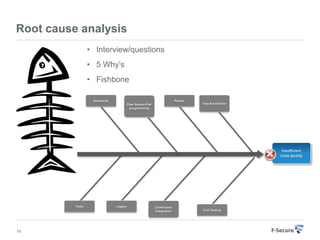
This document discusses agile retrospectives, including why they are important, what they involve, and how to conduct them successfully. Retrospectives allow teams to continuously improve by reflecting on what went well and what could be improved in the last sprint or iteration. The key aspects covered are preparing an agenda and materials, gathering feedback from the team, analyzing the feedback to select a few key items to action, and planning follow-ups to ensure improvements are implemented. Conducting regular retrospectives helps teams enhance their processes and productivity over time.