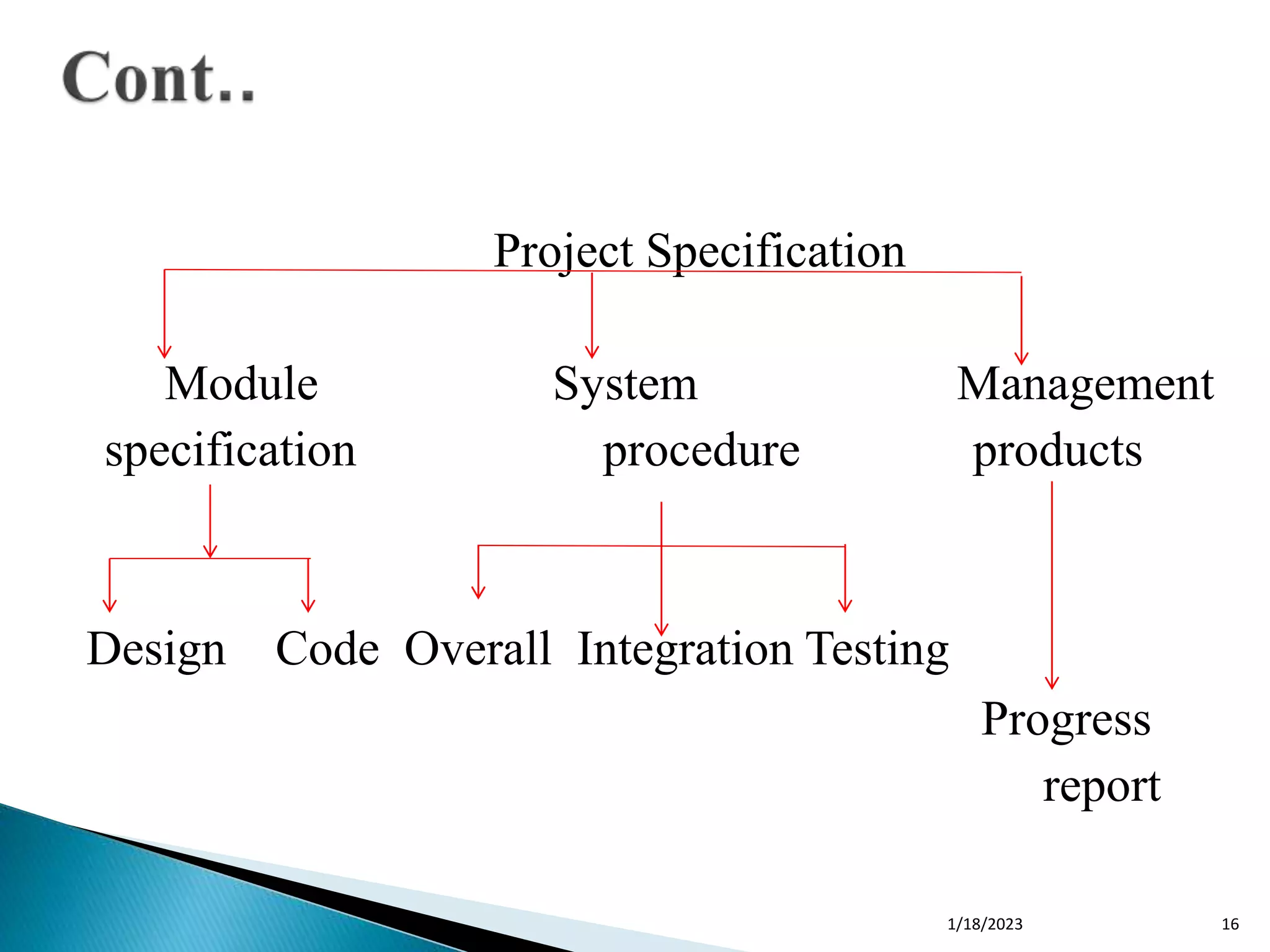
PRINCE2 is a structured project management methodology used widely in the UK. It covers the planning stage of projects with 10 defined steps: (1) select the project, (2) identify scope and objectives, (3) analyze characteristics, (4) identify products and activities, (5) estimate effort, (6) identify risks, (7) allocate resources, (8) review the plan, (9) execute the plan, and (10) conduct lower-level planning as needed. The document then provides details on each of the 10 planning steps and how to implement them for effective project management.