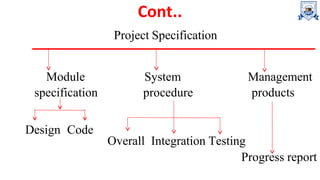
This document outlines the 10 step process for step-wise project planning for software projects. The 10 steps are: 1) identify project scope and objectives, 2) identify project infrastructure, 3) analyze project characteristics, 4) identify project products and activities, 5) estimate effort for each activity, 6) identify activity risks, 7) allocate resources, 8) review and publicize the plan, 9) execute the plan, and 10) conduct lower level planning as more details emerge. The goal of these steps is to ensure project tasks are well coordinated and meet objectives like timely completion through processes like stakeholder analysis, risk assessment, and resource planning.




![Source:-Bob Hughes & Mike Cotterell [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1-230519155700-08f7885e/85/Unit-1-2-Stepwise-Project-Planning-pdf-5-320.jpg)