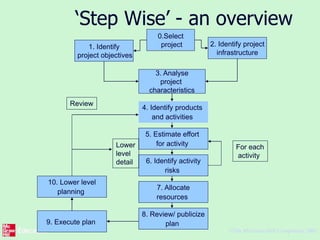
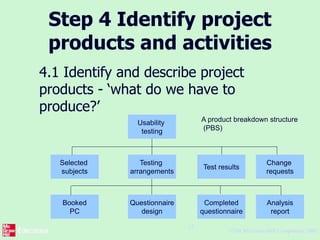
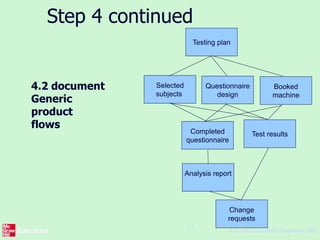
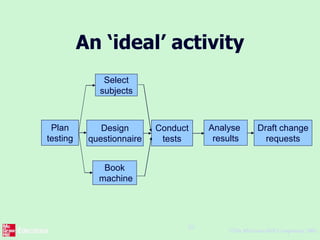
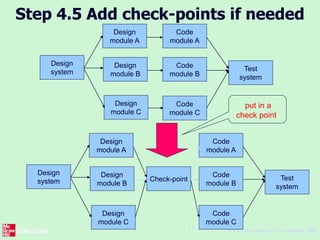
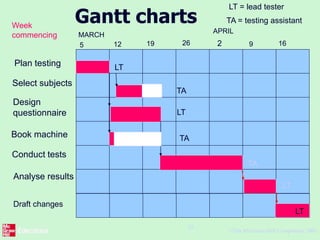
This document outlines the "Step Wise" approach to planning software projects. It describes 10 steps to develop a project plan, including establishing objectives and infrastructure, analyzing project characteristics, identifying products and activities, estimating effort, identifying risks, allocating resources, and reviewing the plan. It provides examples applying these steps to a scenario involving developing a software tool to conduct psychometric testing of employees. Key steps include determining objectives, stakeholders, and risks; identifying products like questionnaires and test results; estimating activity efforts; and allocating resources like personnel and machines.