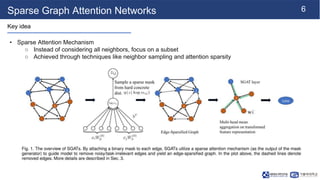
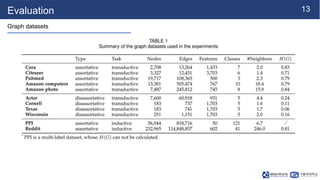
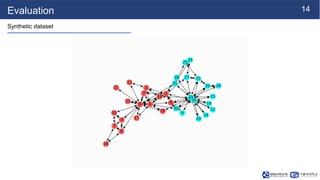
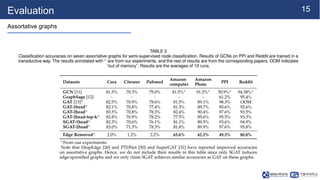
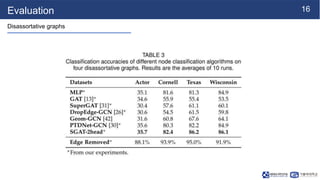
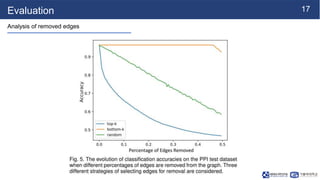
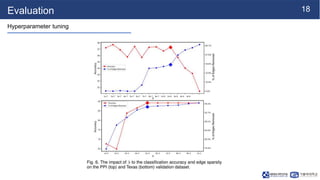
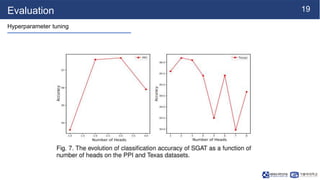
This document summarizes a research paper on sparse graph attention networks (SGATs). SGATs apply an attention mechanism to only a subset of neighbors for each node to improve the scalability and memory efficiency of graph attention networks. The key ideas are a sparse attention mechanism using techniques like neighbor sampling and a binary gate attached to each edge. SGATs show advantages in scalability, memory usage, and performance on disassortative graphs by removing up to 80% of edges while maintaining classification accuracy. Evaluation on synthetic and real-world graphs demonstrates SGATs can identify and remove noisy edges.