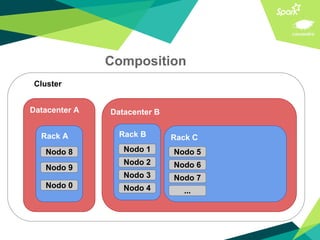
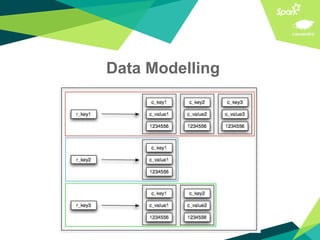
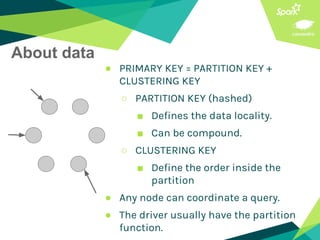
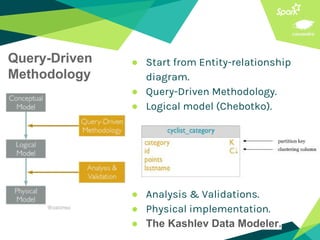
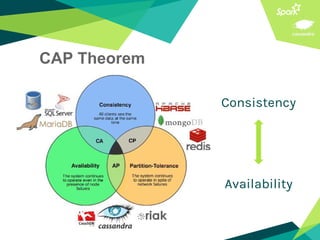
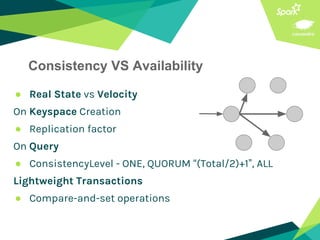
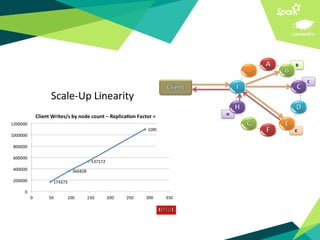
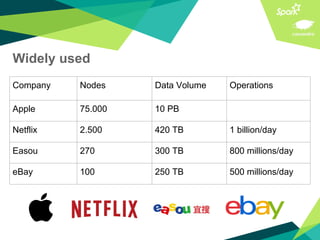
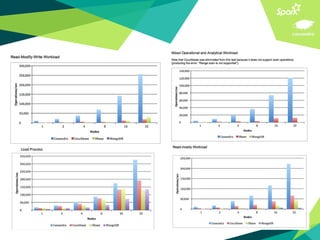
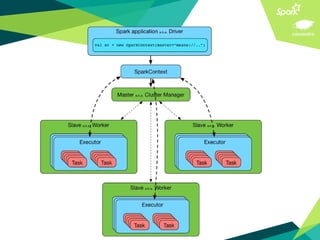
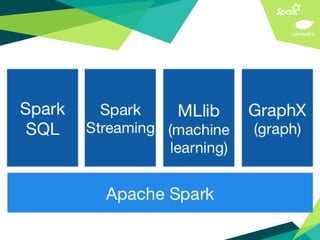
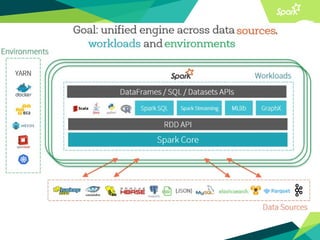
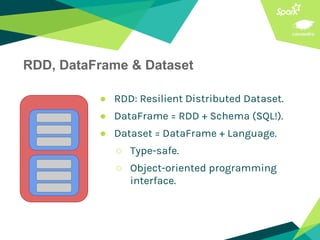
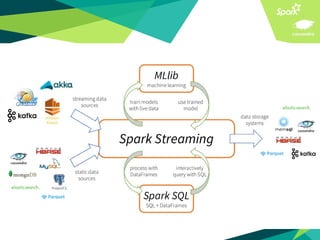
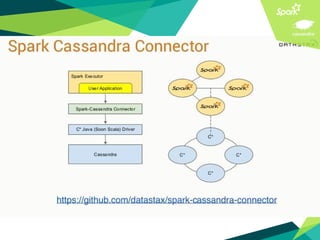
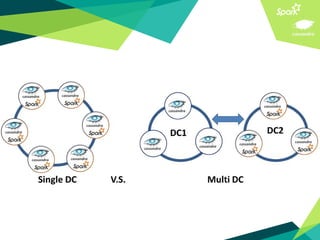
This document presents a discussion on Apache Cassandra and Apache Spark, highlighting their complementary nature for analytics and data processing. It emphasizes the importance of query-driven methodology and careful data modeling while detailing features like linear scalability, fault tolerance, and integration capabilities. Conclusions drawn include both advantages, such as faster performance than Hadoop and challenges with query flexibility and secondary indexing.