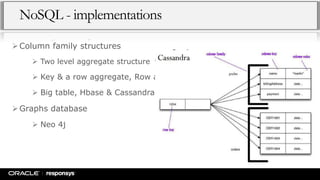
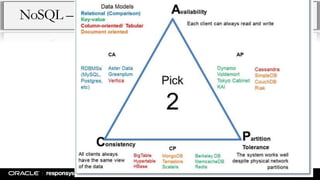
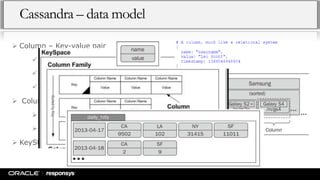
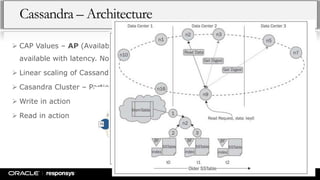
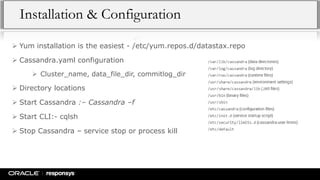
This document provides an overview of NoSQL databases and Apache Cassandra. It discusses how data and data modeling have evolved with big data. It introduces key concepts like CAP theorem and ACID vs BASE. It describes various NoSQL implementations like key-value, document, and column-oriented databases. It provides details on Cassandra's architecture, data model, and operational aspects. The document demonstrates Cassandra configuration, CQL usage, and monitoring tools.