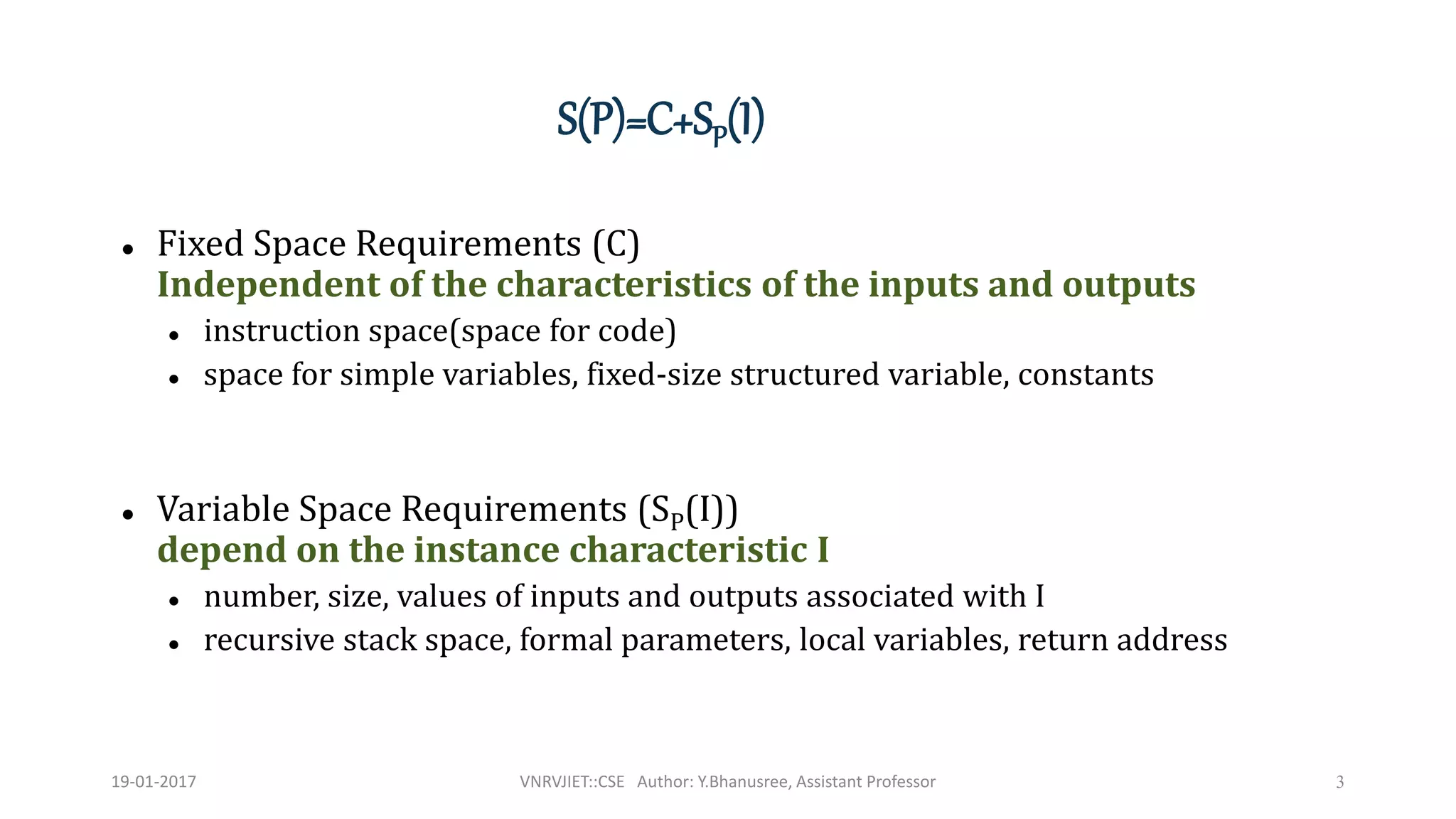
The document discusses space complexity, which is the amount of computer memory required during program execution based on input size. Space complexity includes fixed space requirements like instruction space and simple variables, as well as variable space requirements that depend on input instance characteristics like input/output size and values. It provides examples of calculating space complexity for different algorithms, showing that space complexity can be a constant plus a variable component related to input size.

![Space Complexity
Amount of computer memory that is required during program execution as a function of input
size.
OR
Space complexity is the amount of memory it needs to run to completion
Space=Fixed part +Variable part
Fixed: varies from problem to problem. Includes space needed for storing instructions
variables , constants and structured variables.[arrays , struct]
Variable: varies from program to program. Includes space needed for stack and for
structured variables that are dynamically allocated during run time.
219-01-2017 VNRVJIET::CSE Author: Y.Bhanusree, Assistant Professor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spacecomplexity-170119071255/75/Space-complexity-2-2048.jpg)
![Algorithm abc(a,b,c)
{
return a+b*c+(a-b-)/a+b+4.0
}
Algorithm Sum(a,n)
{
s:=0
for i:=1 to n do
s:=s+a[i];
return s;
}
19-01-2017 VNRVJIET::CSE Author: Y.Bhanusree, Assistant Professor 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spacecomplexity-170119071255/75/Space-complexity-4-2048.jpg)
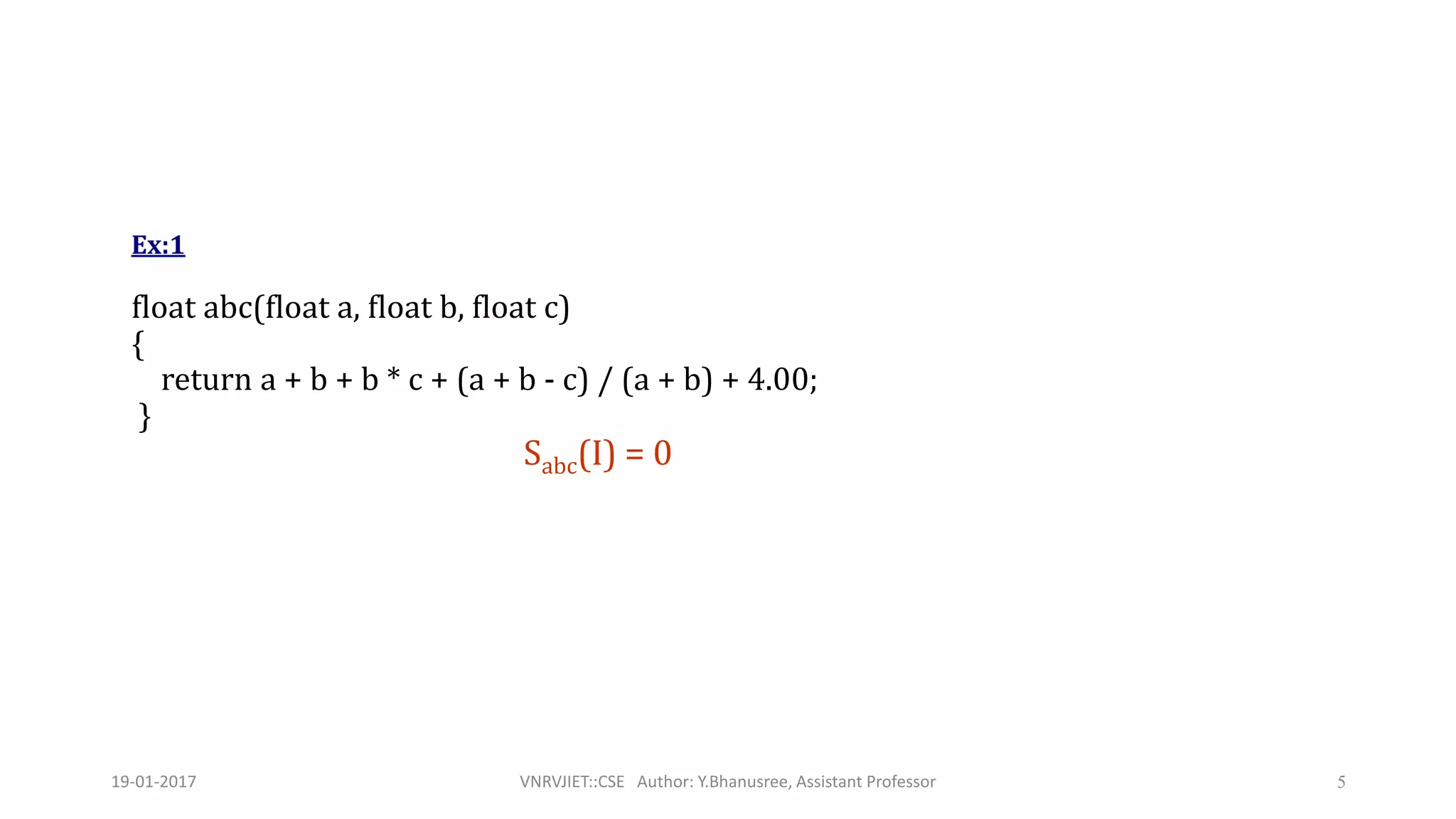
![Ex:2
float sum(float list[ ], int n)
{
float tempsum = 0;
int i;
for (i = 0; i<n; i++)
tempsum += list [i];
return tempsum;
}
Ssum(I) = 0
19-01-2017 VNRVJIET::CSE Author: Y.Bhanusree, Assistant Professor 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spacecomplexity-170119071255/75/Space-complexity-6-2048.jpg)
![Ex:3 Recursive function for summing a list of numbers
float sum(float list[ ], int n)
{
if (n)
return sum(list, n-1) + list[n];
else
return 0;
}
8
Type Name Number of bytes
parameter: float
parameter: integer
return address:(used internally)
list [ ]
n
4
2
2(unless a far address)
TOTAL per recursive call 8
Ssum(I)=Ssum(n)=8n
19-01-2017 VNRVJIET::CSE Author: Y.Bhanusree, Assistant Professor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spacecomplexity-170119071255/75/Space-complexity-8-2048.jpg)