The static keyword in Java is used for memory management. Static can be applied to variables, methods, blocks, and nested classes. Static members belong to the class rather than objects of the class. Static variables and methods are used for properties and behaviors that are common to all objects. A static nested class can access static members of the outer class without creating an instance of the outer class.








![class MathApplication
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
float a=MathOperation.mul(4.0,5.0);
float b=MathOperation.divide(a,2.0);
System.out.println("b="+b);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticmembers-java-230604145207-e63f9798/85/Static-Members-Java-pptx-9-320.jpg)

![class StudentsInfomethod
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Student.change()
Student s1=new Student(501,“Pavan”);
Student s2=new Student(502,“Kalyani”);
Student s3=new Student(503,“Vignesh”);
s1.display();
s2.display();
s3.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticmembers-java-230604145207-e63f9798/85/Static-Members-Java-pptx-11-320.jpg)

![Example:
class Test
{
static
{
System.out.println("static block");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println("main block");
}
}
Output:
Static block
main block](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticmembers-java-230604145207-e63f9798/85/Static-Members-Java-pptx-13-320.jpg)




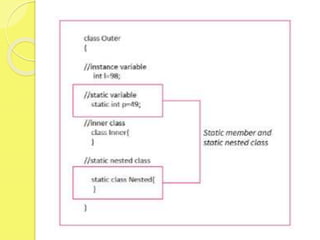

![public static void main(String args[]) {
Outer.Nested obj = new Outer.Nested();
//creating an object of nested
// class without creating an object
// of the outer class.
obj.fun();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticmembers-java-230604145207-e63f9798/85/Static-Members-Java-pptx-20-320.jpg)
![Example 2:
class TestOuter1{
static int data=30;
static class Inner{
void msg()
{
System.out.println("data is "+data);}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
TestOuter1.Inner obj=new TestOuter1.Inner
();
obj.msg();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticmembers-java-230604145207-e63f9798/85/Static-Members-Java-pptx-21-320.jpg)
