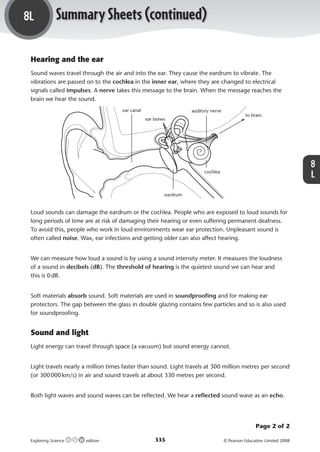
Sound is a form of energy that is created by vibrations and travels through materials as vibrations passed between particles. The speed of sound is faster in materials where the particles are closer together, allowing for easier transfer of vibrations. Sound waves can be characterized by their frequency, wavelength, and amplitude. Loud sounds can damage the ear, while softer materials are better for absorbing sound.