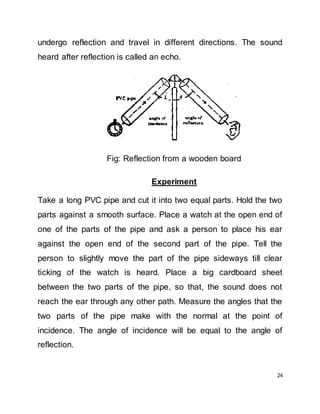
Sound is produced by vibrating objects and travels as compressional waves through a medium such as air, which are sensed by the human ear. For sound to be produced, three things are required: a vibrating body, a medium such as air, and a receiver like the ear. Sound waves can be recorded and played back by converting vibrations to electrical signals that are stored and then used to recreate the original sound waves. The human ear can detect sounds between frequencies of 20-20,000 Hz.