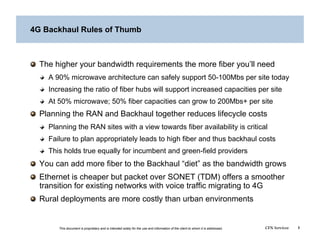
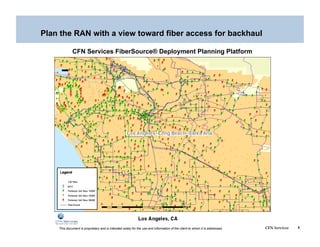
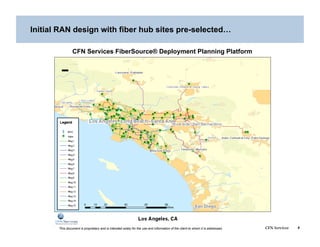
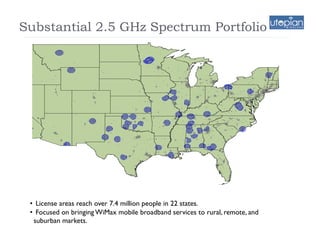
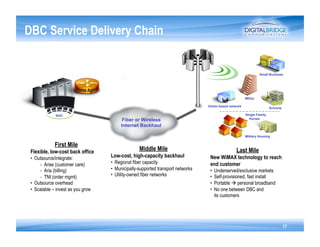
This document addresses the optimization of wireless transport networks, focusing on the challenges of 4G backhaul solutions, such as the need for increased fiber and microwave infrastructure to meet varying bandwidth demands. It discusses key planning considerations, including the economic viability of fiber access, and emphasizes the importance of integrating radio access network (RAN) design with backhaul planning to lower lifecycle costs. Additionally, the document outlines various backhaul technologies and best practices for deploying them effectively in rural and urban markets.