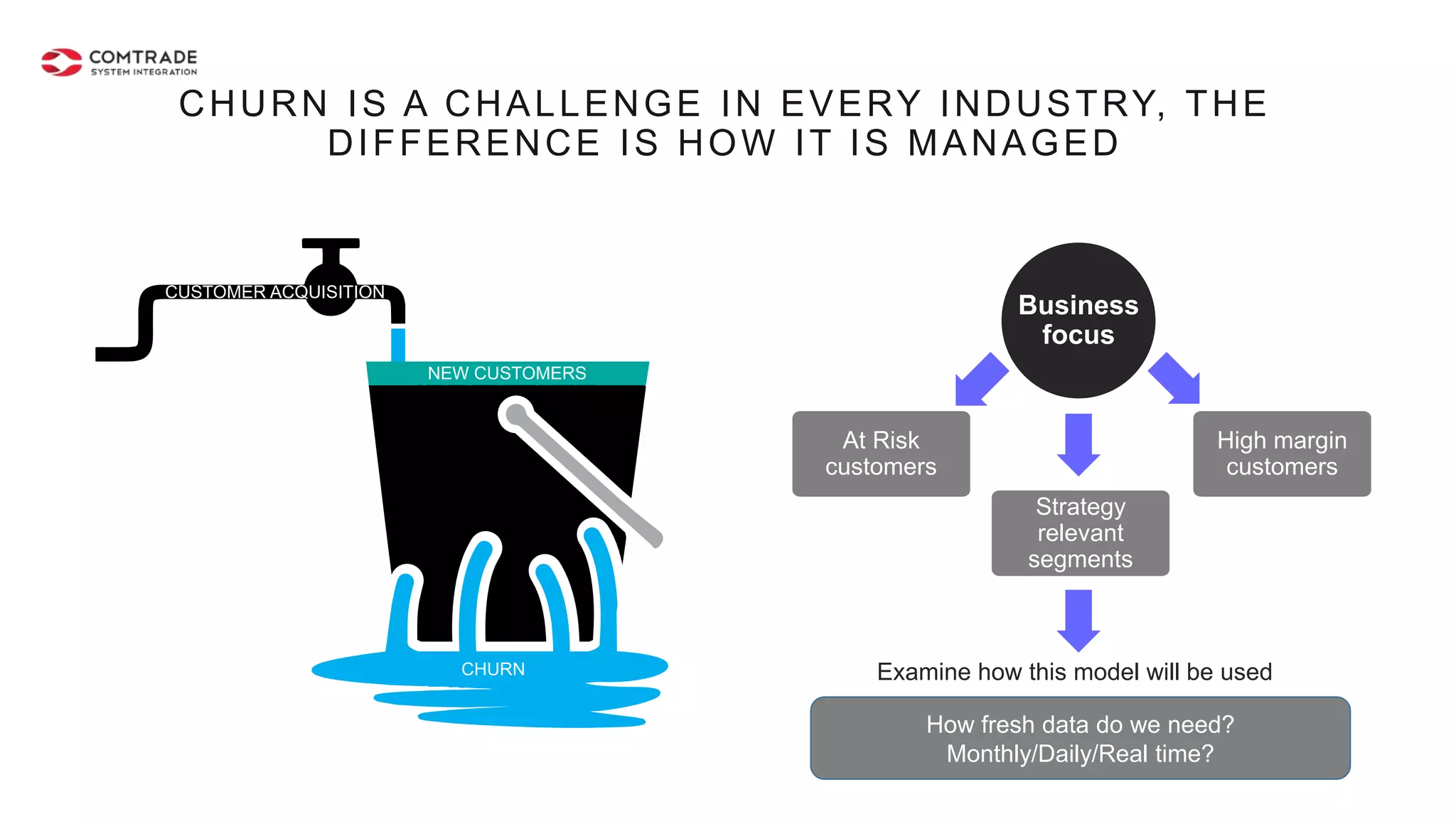
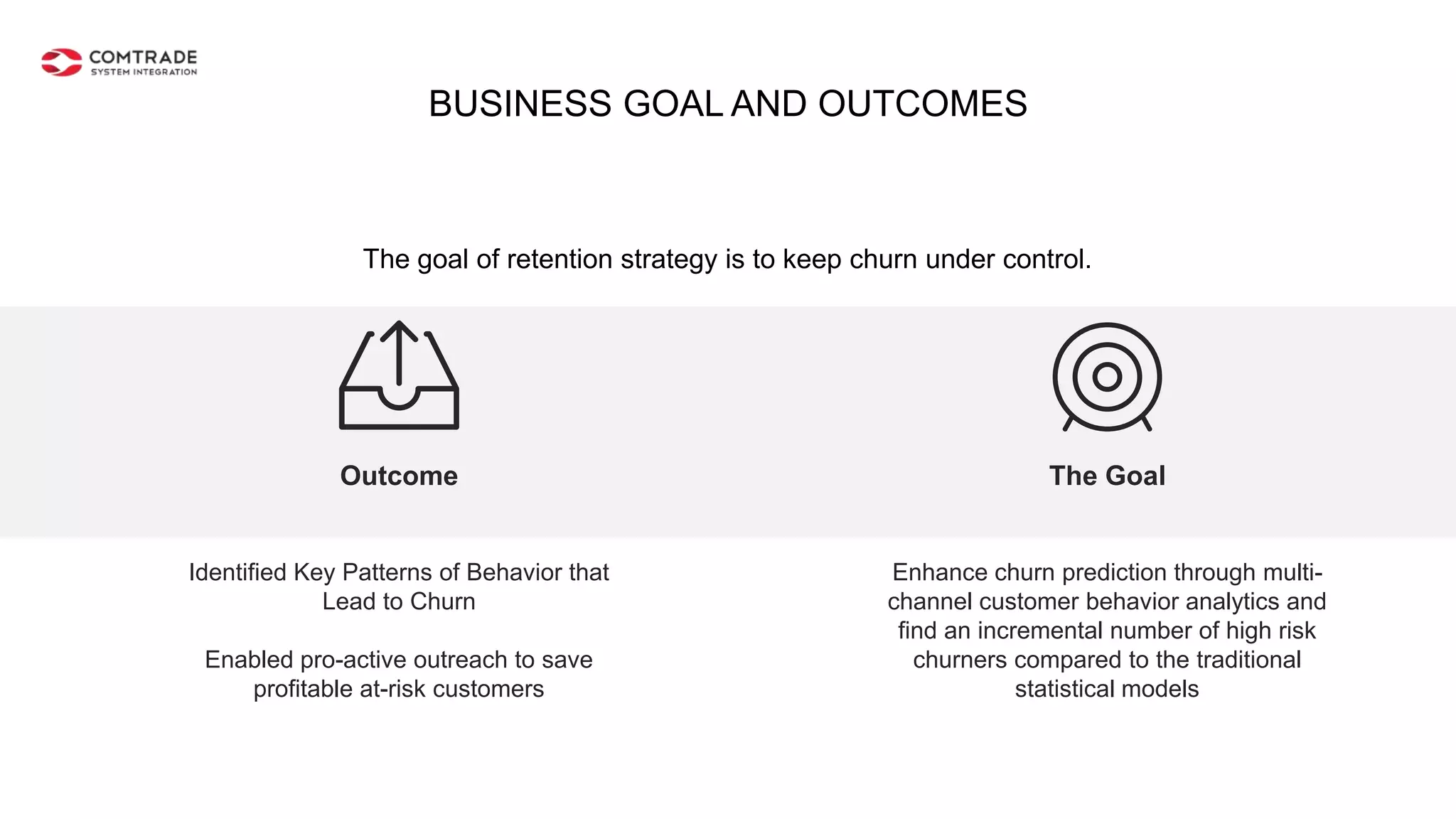
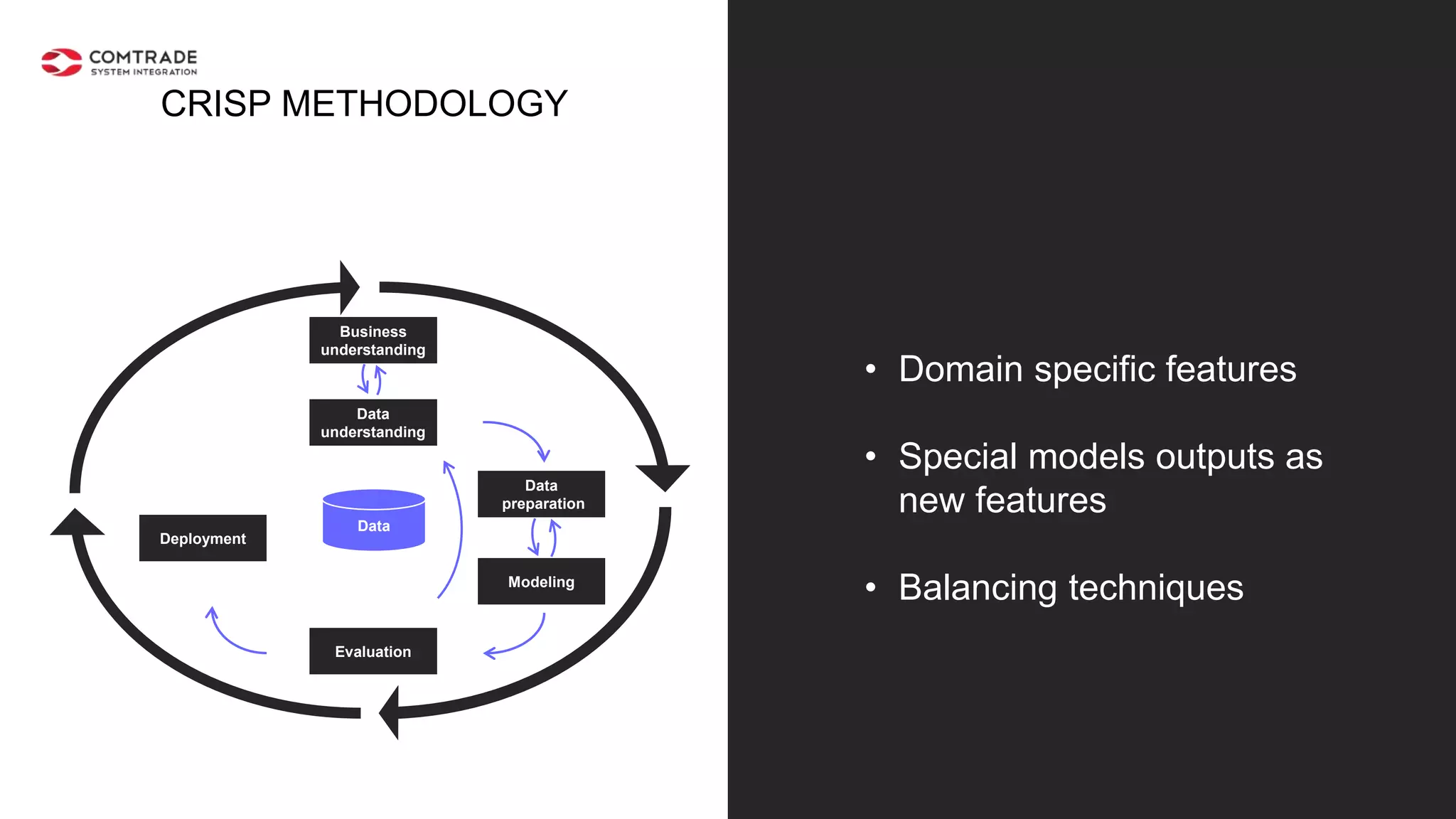
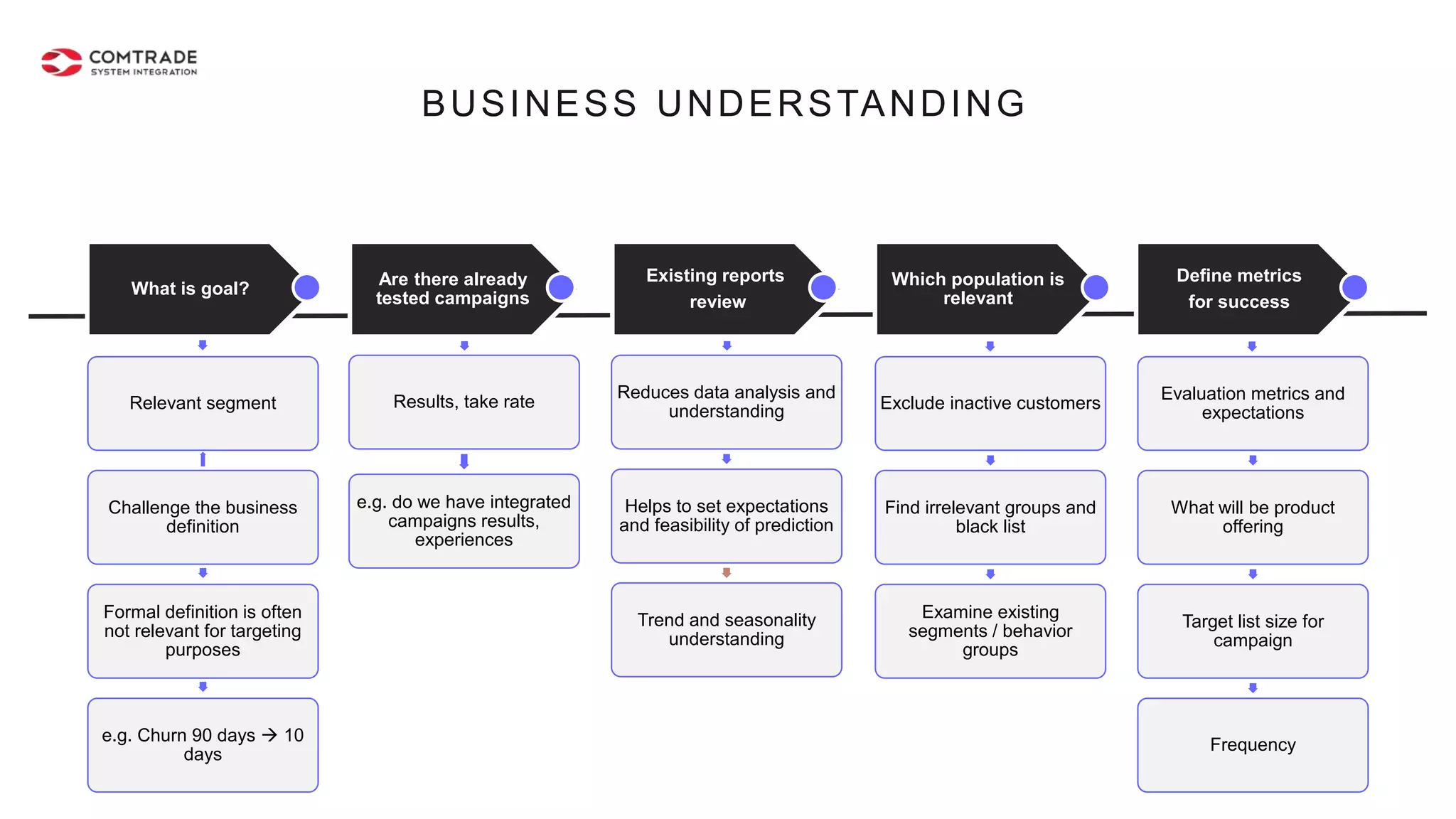
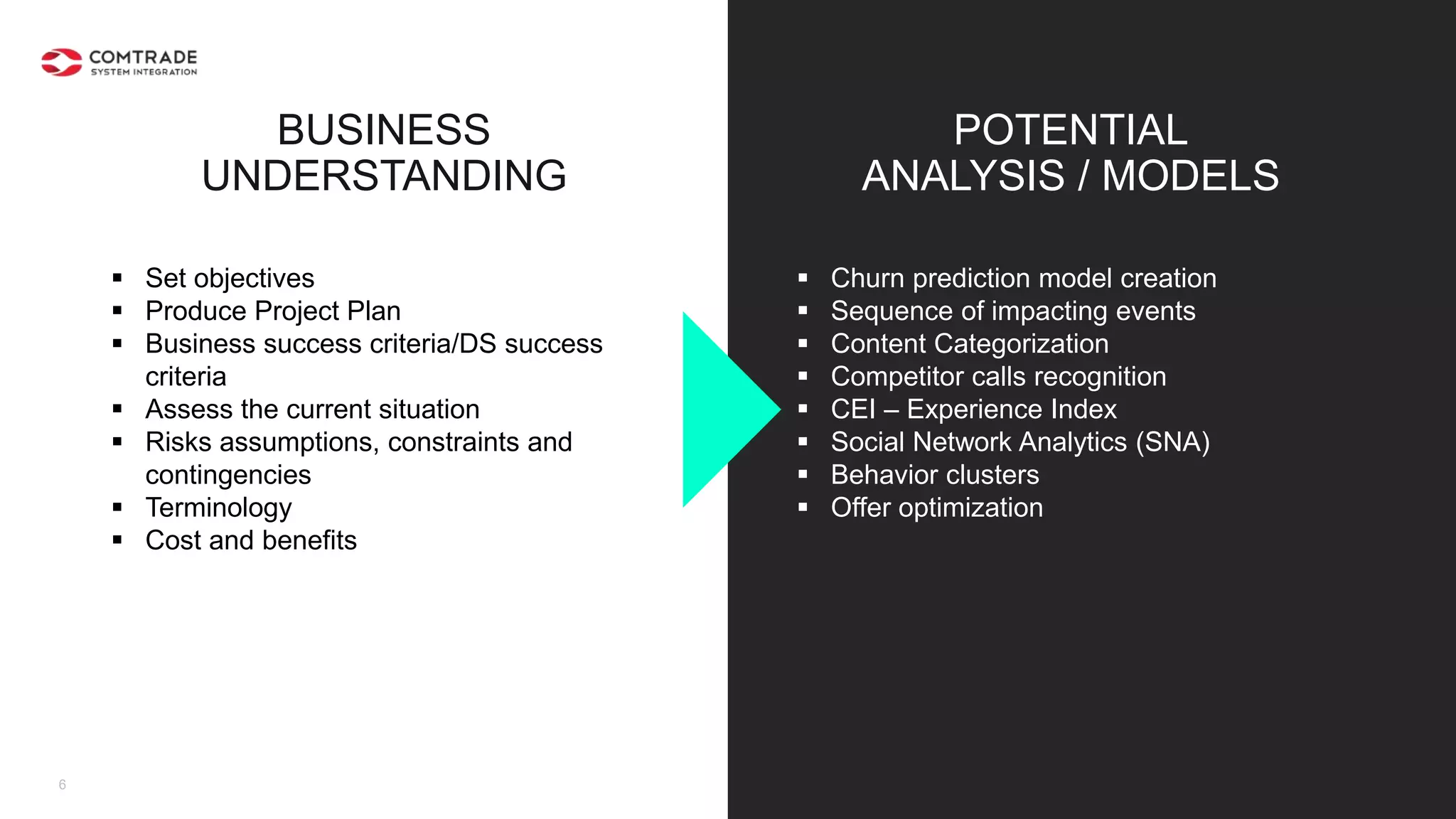
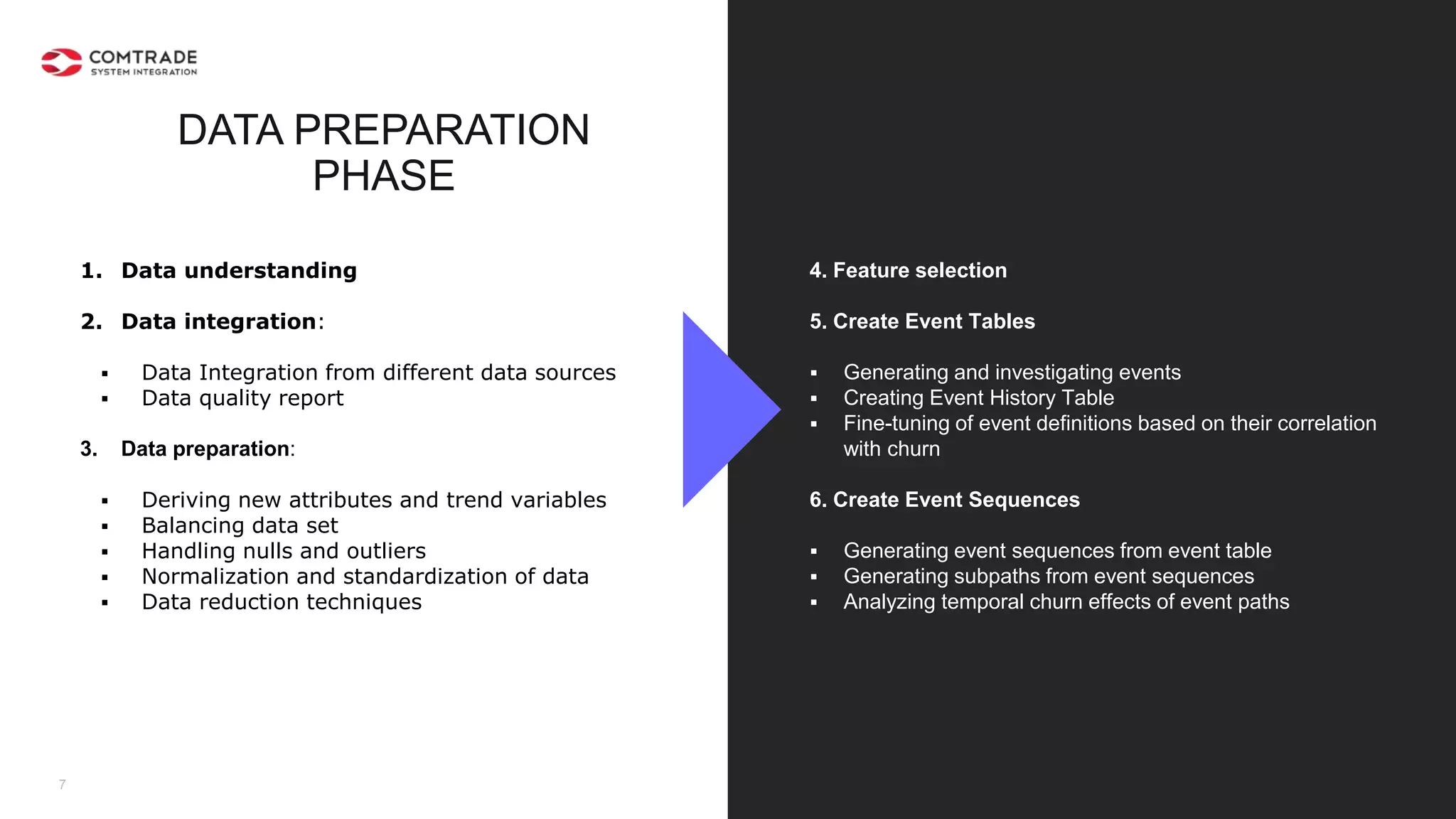
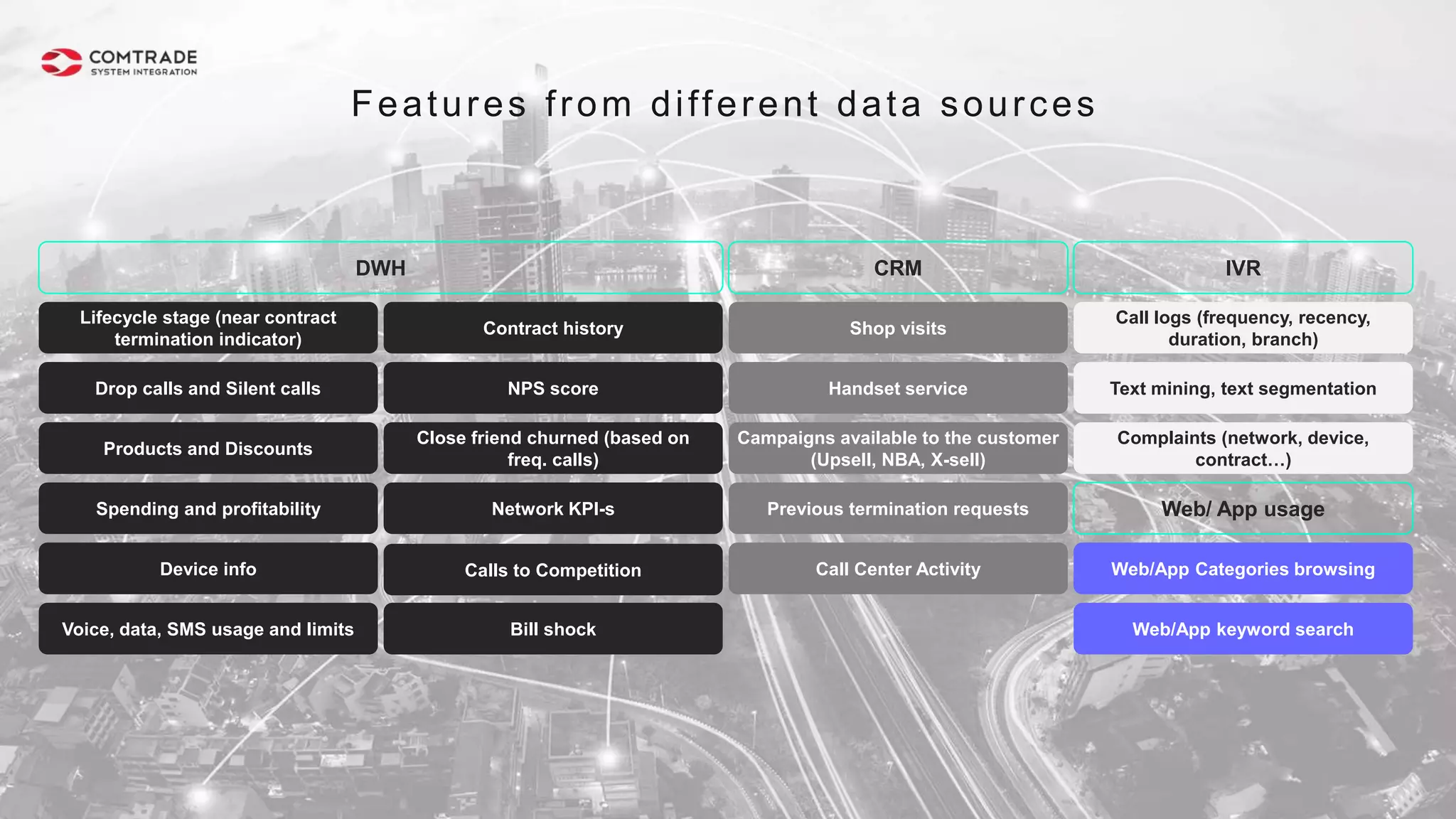
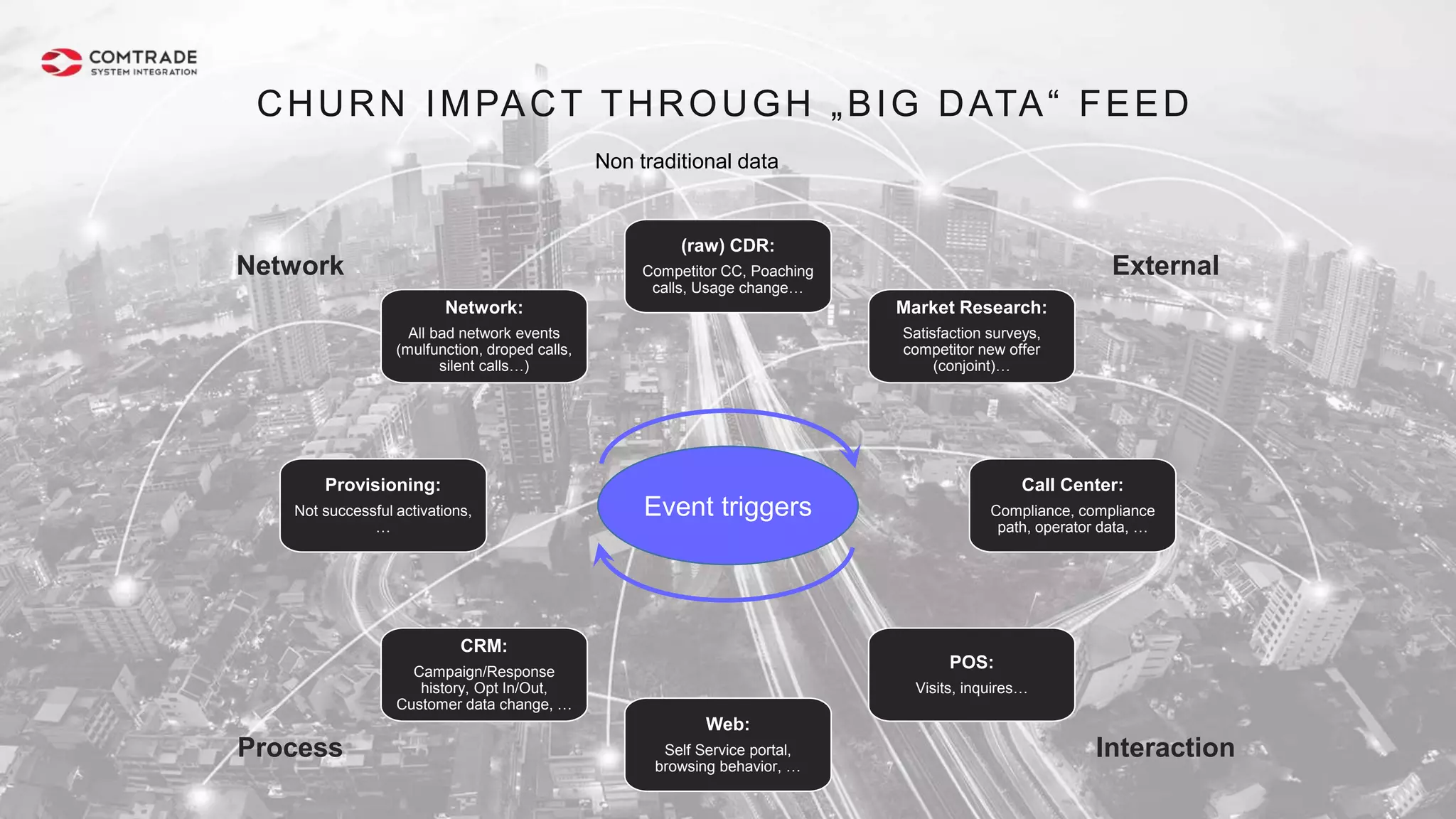
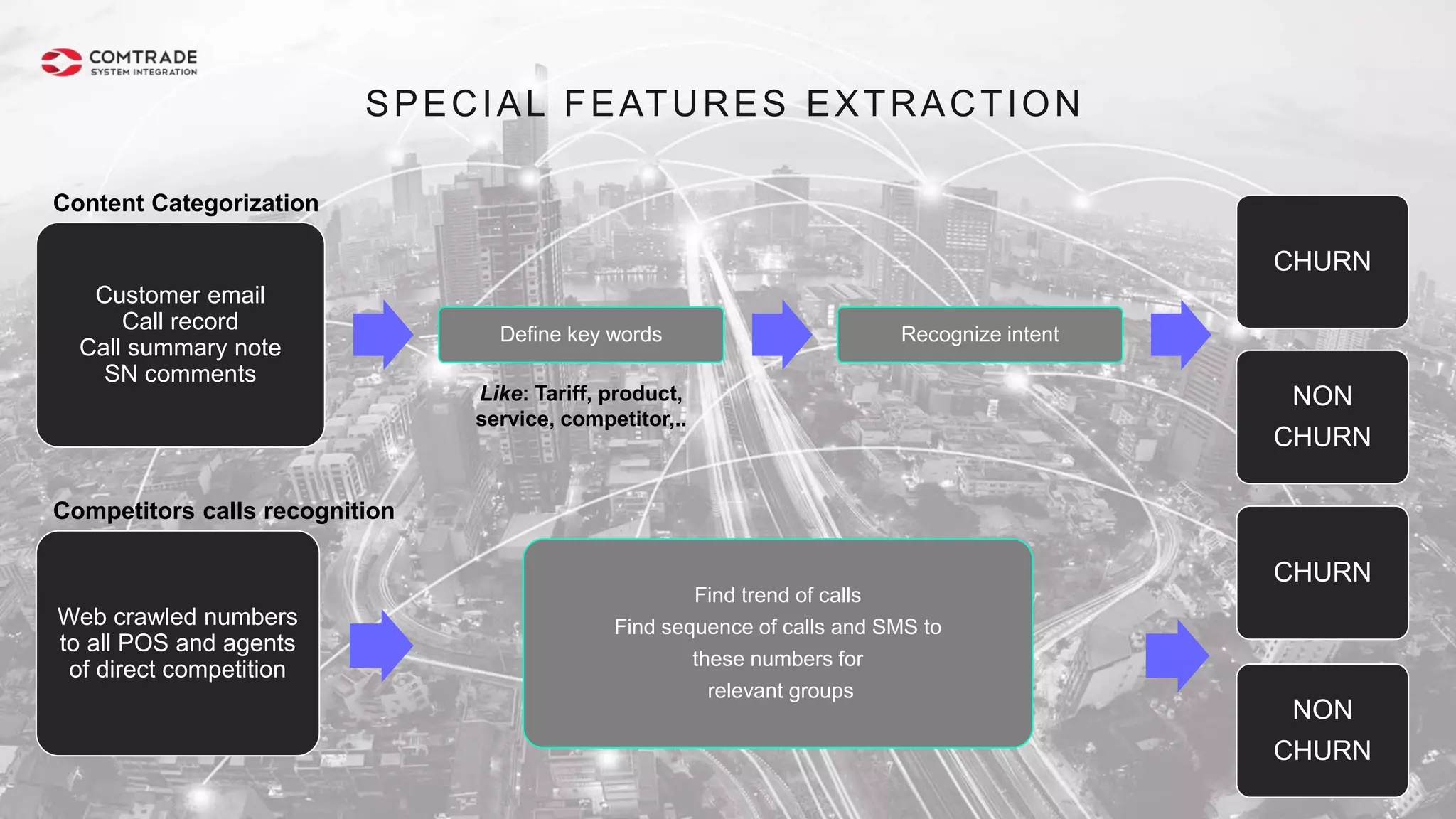
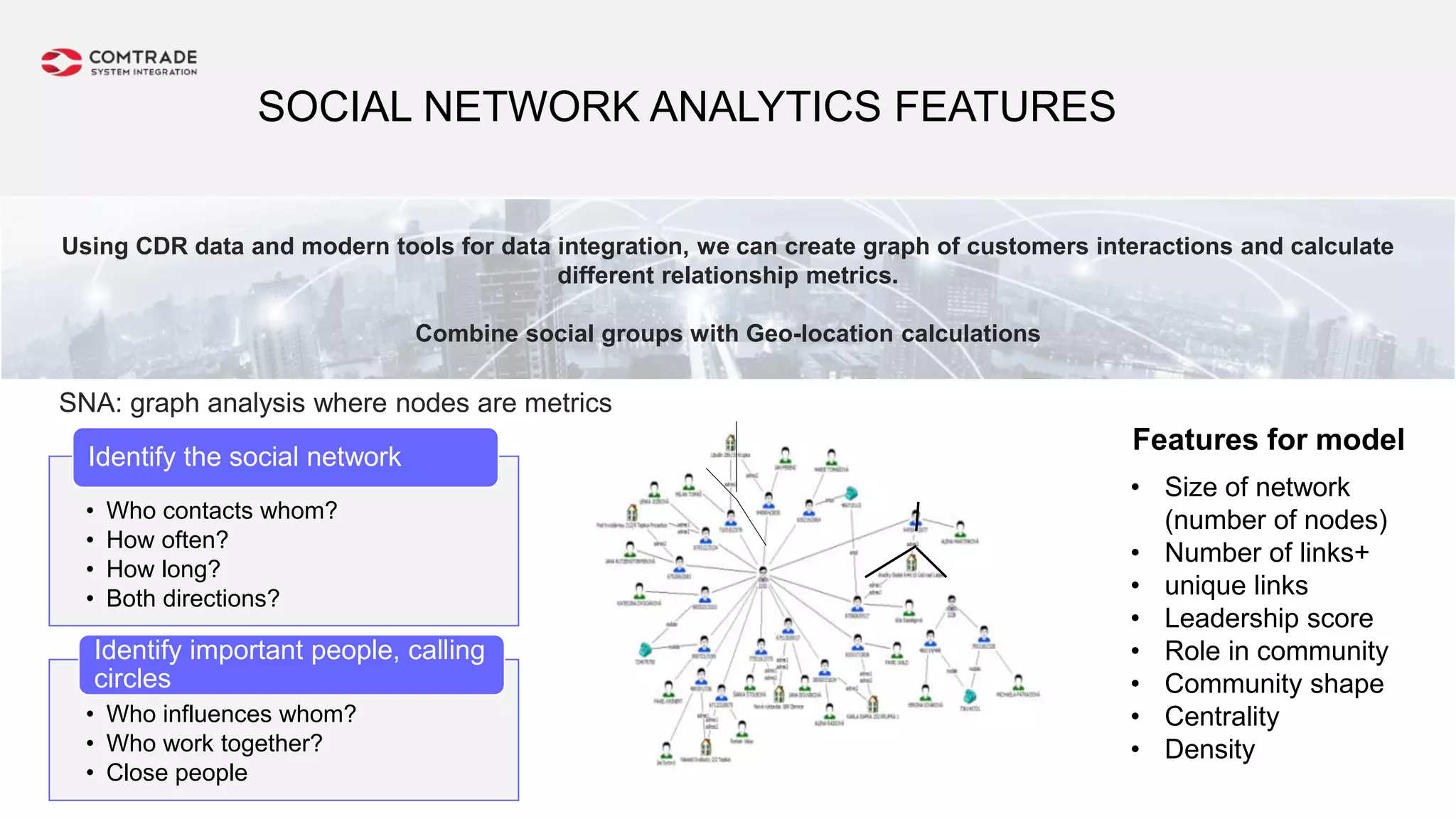
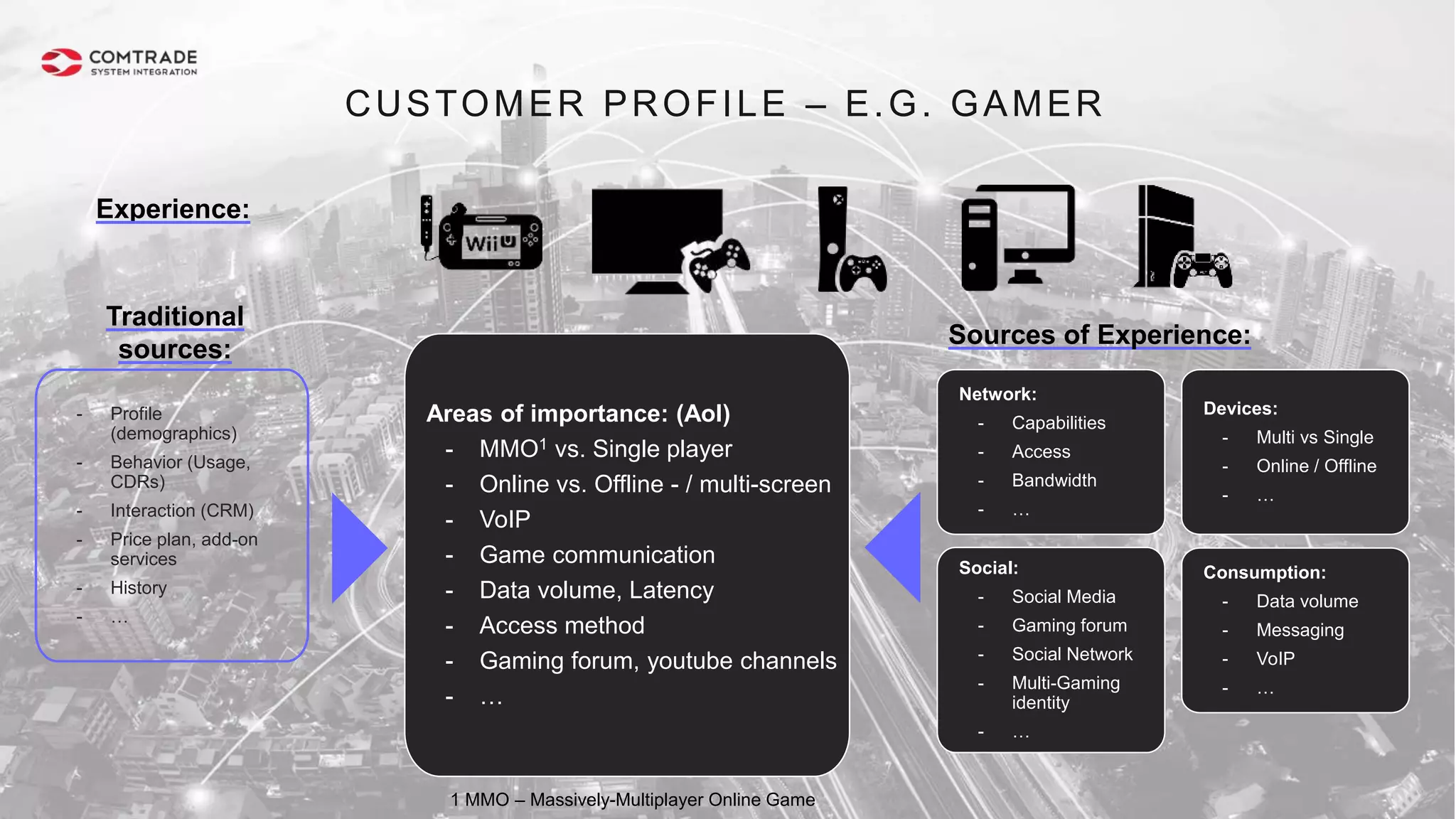
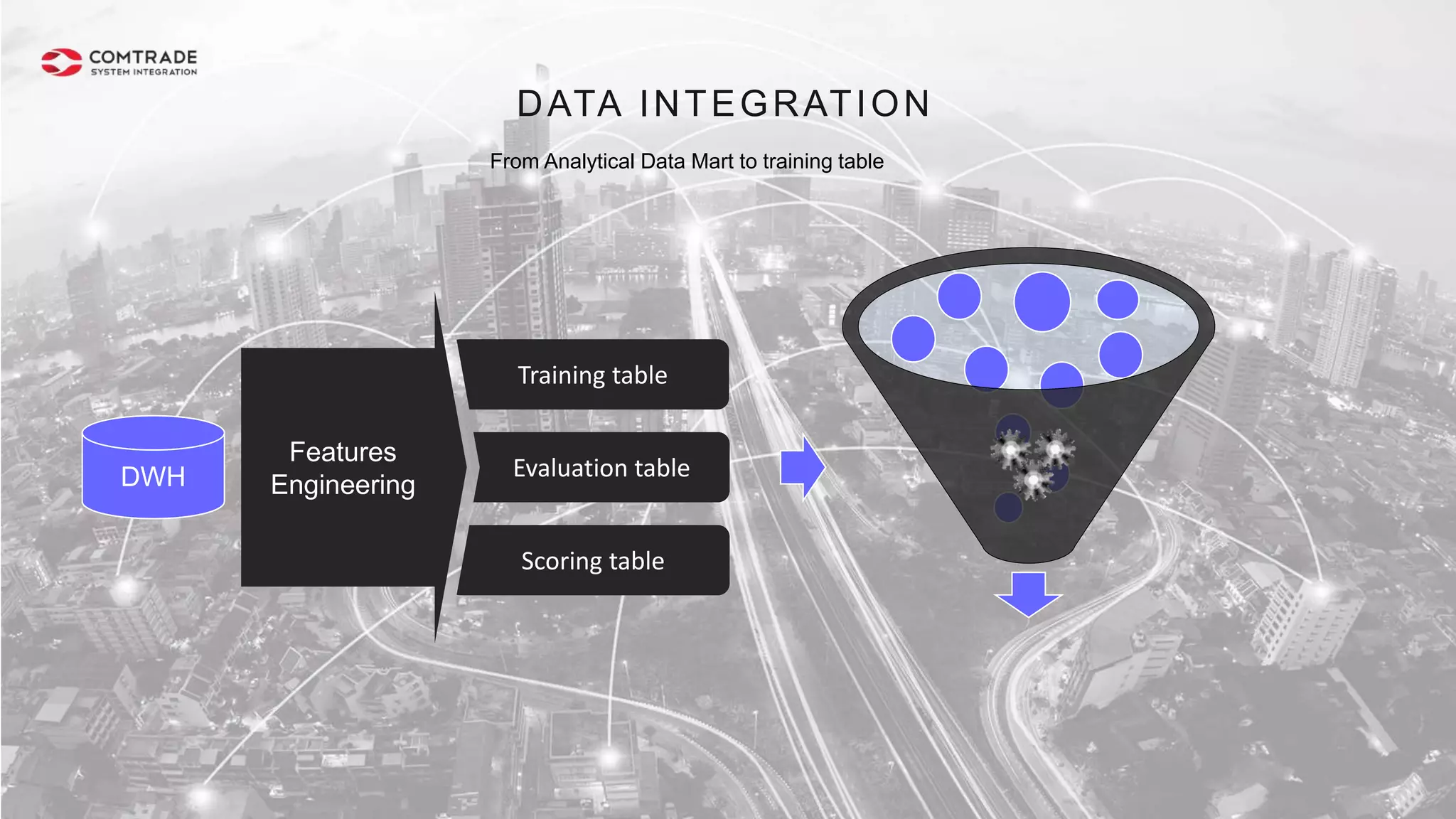
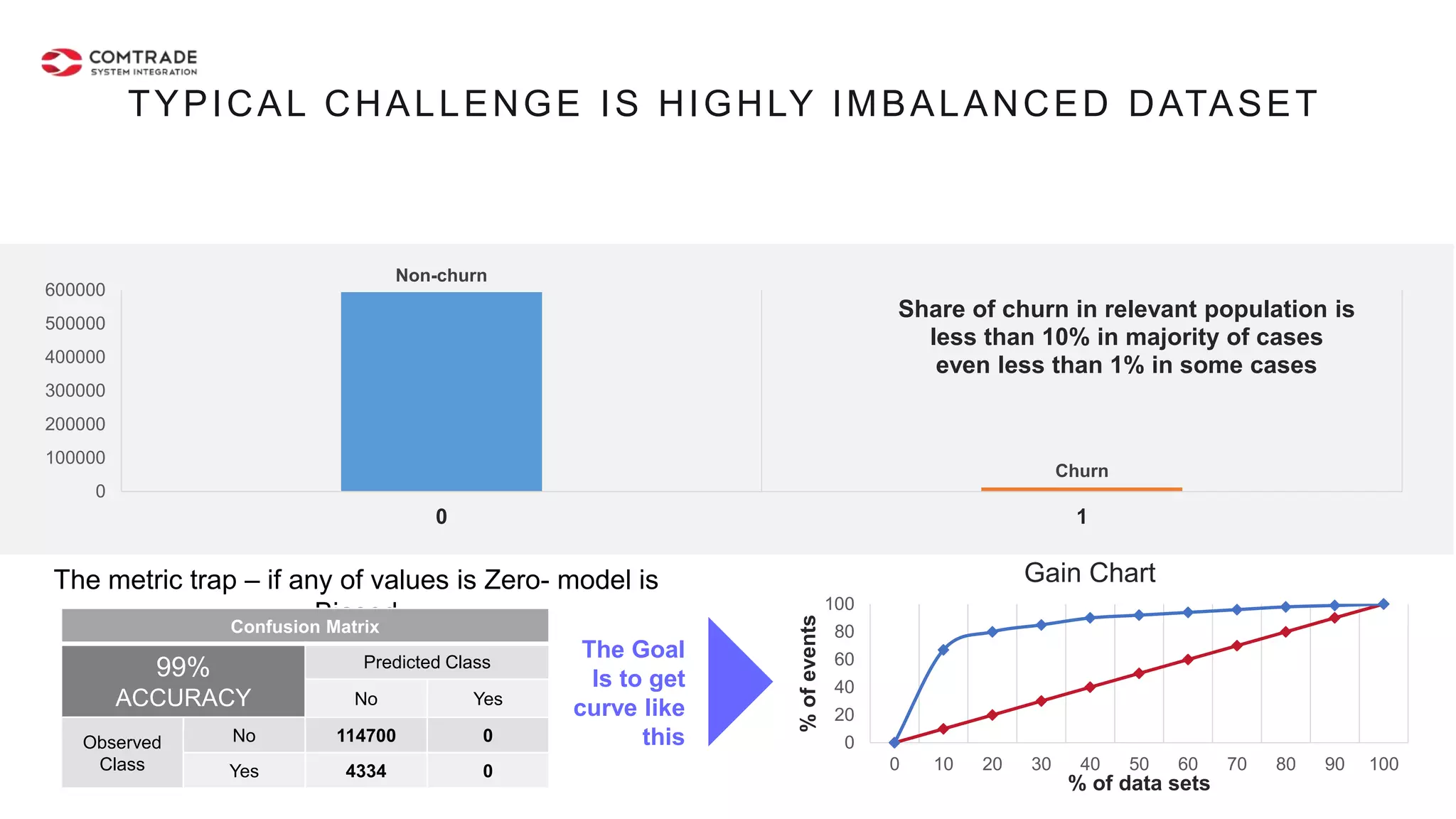
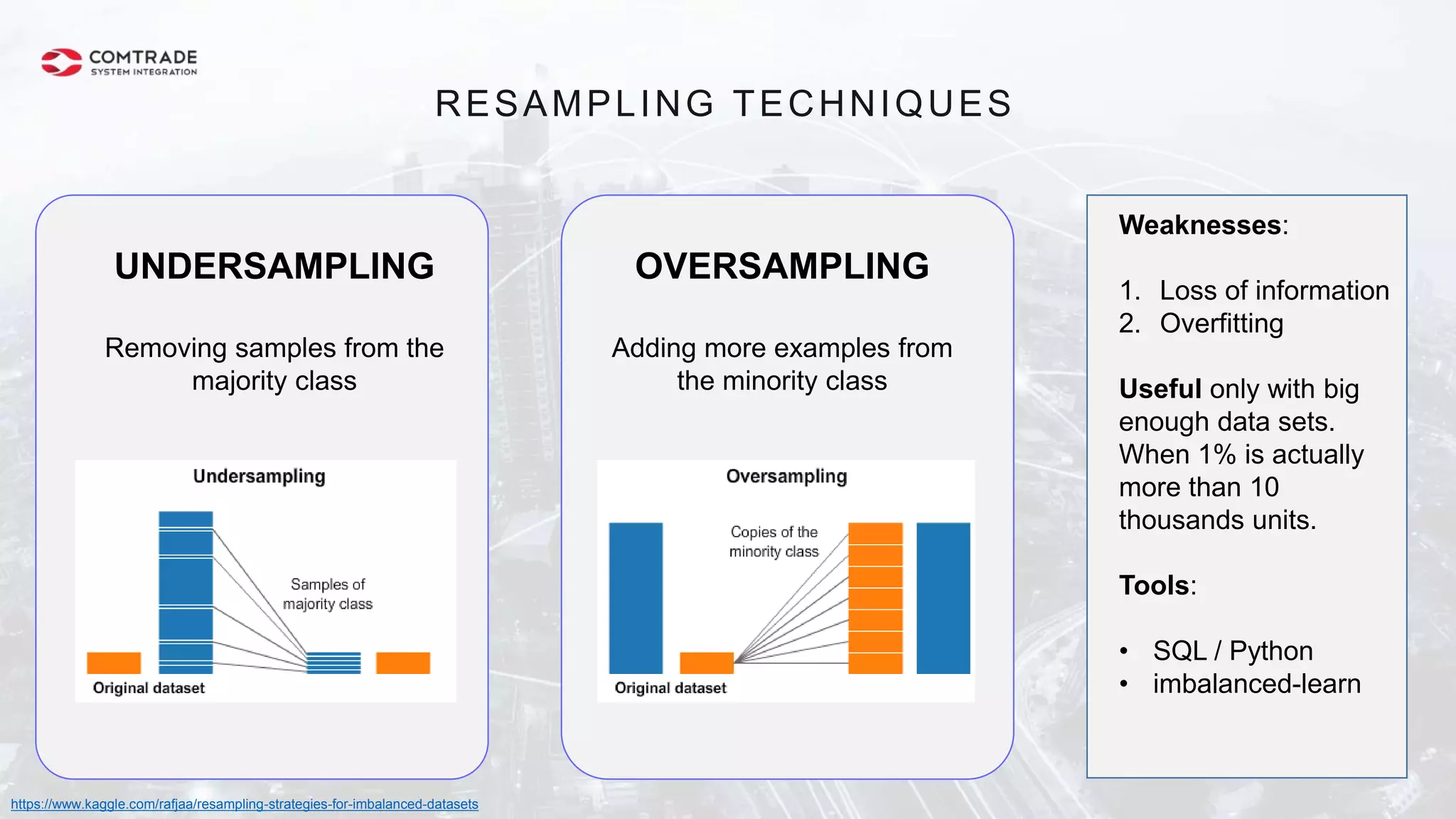
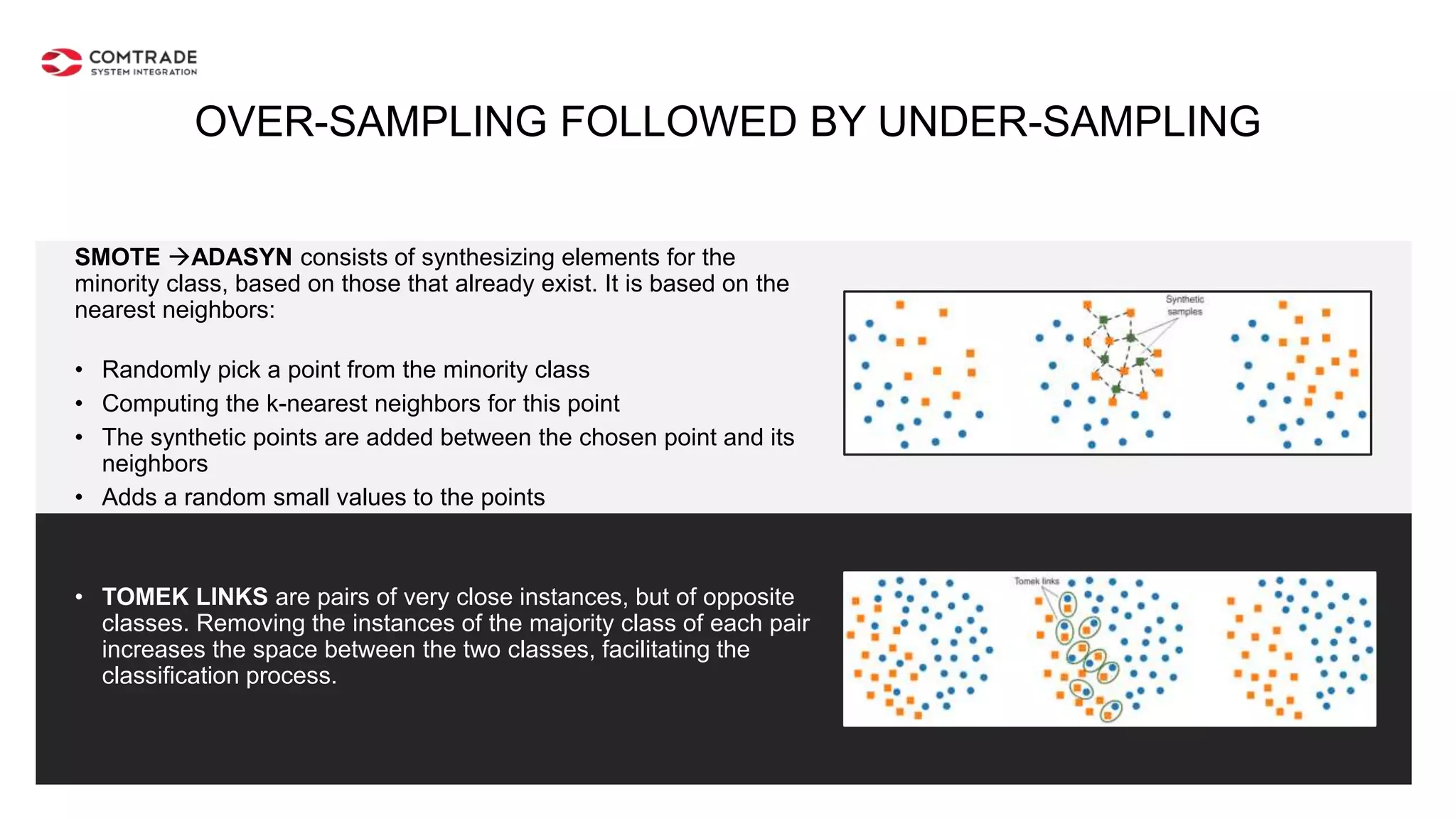
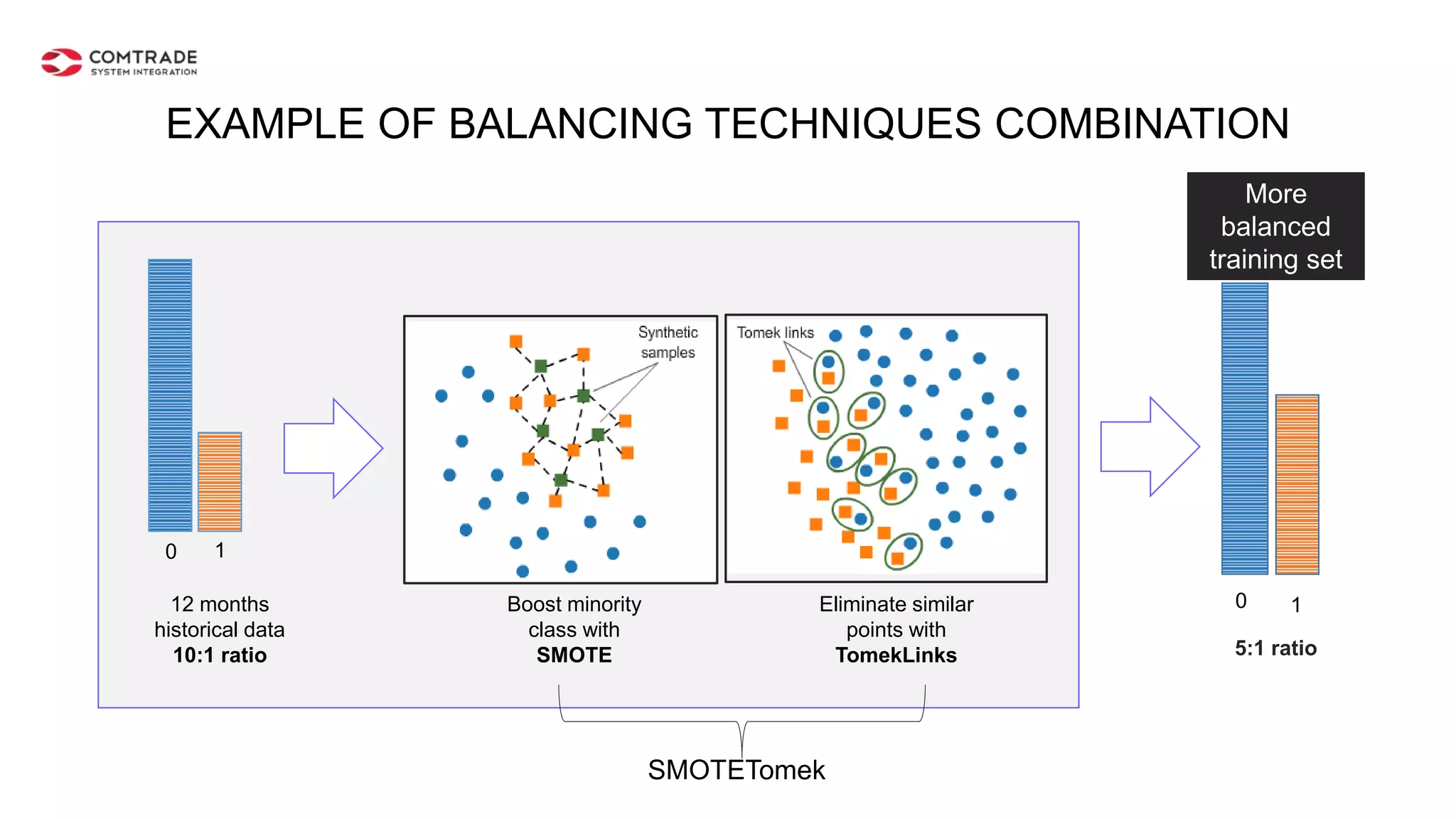
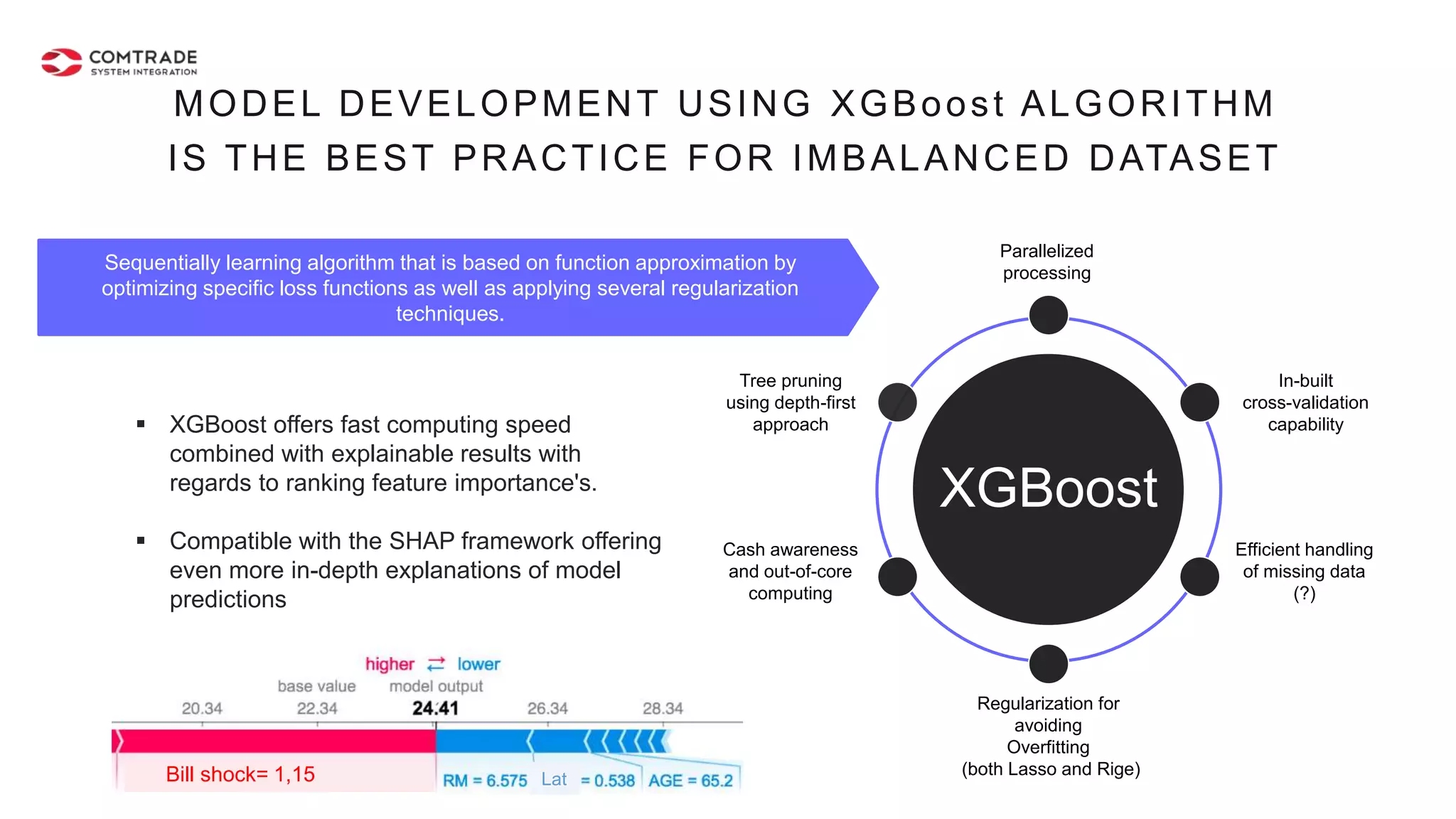
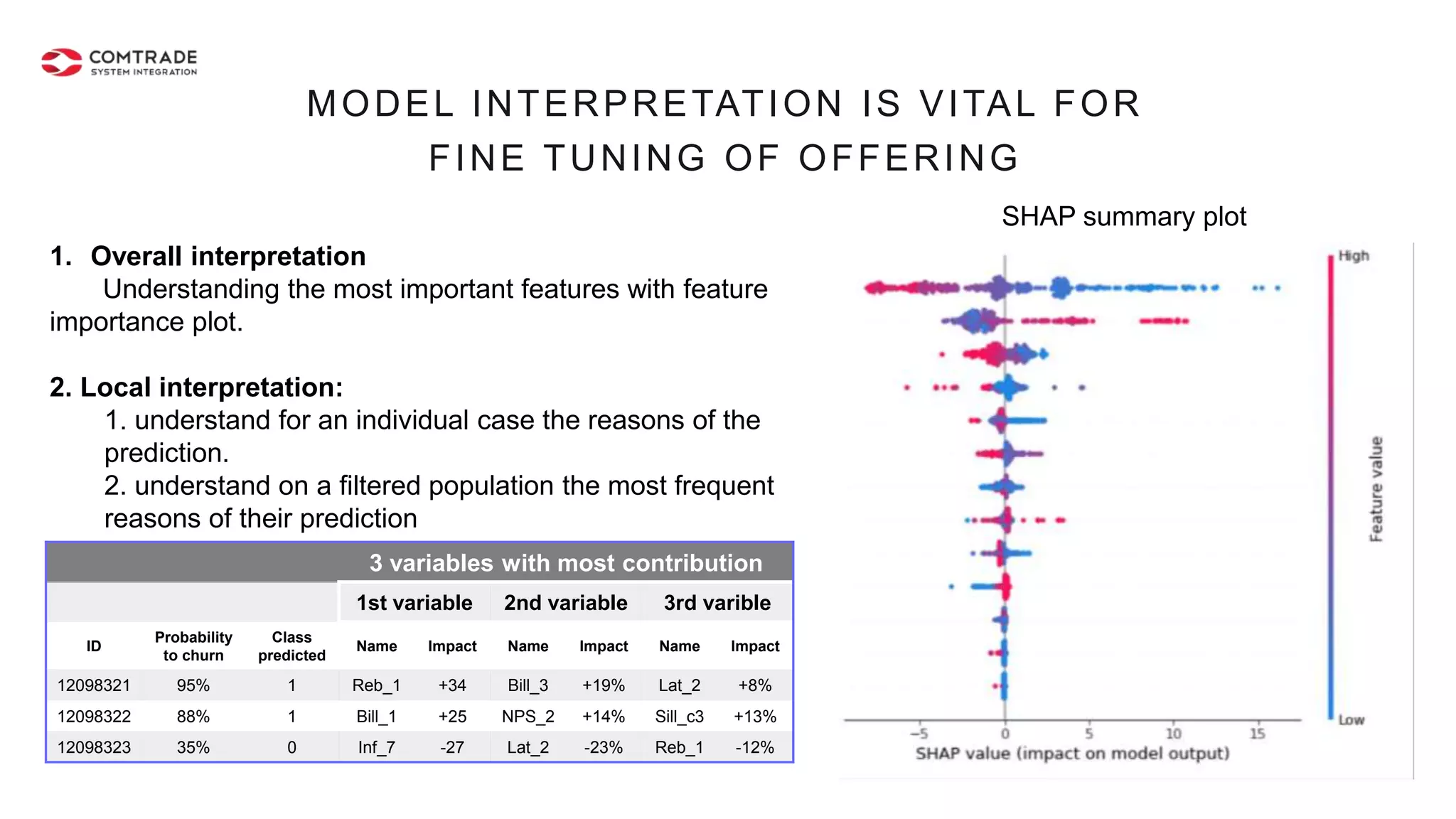
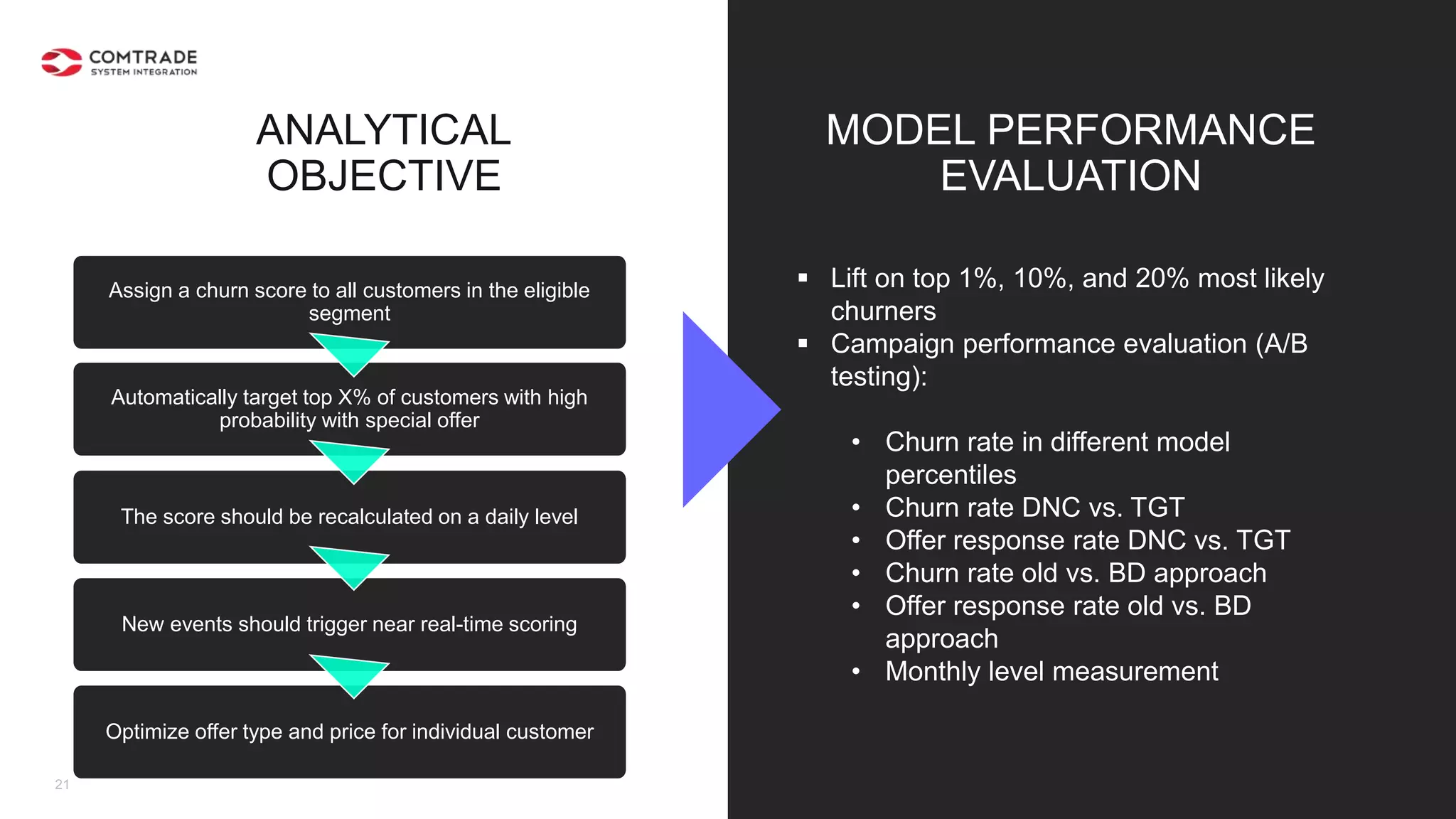
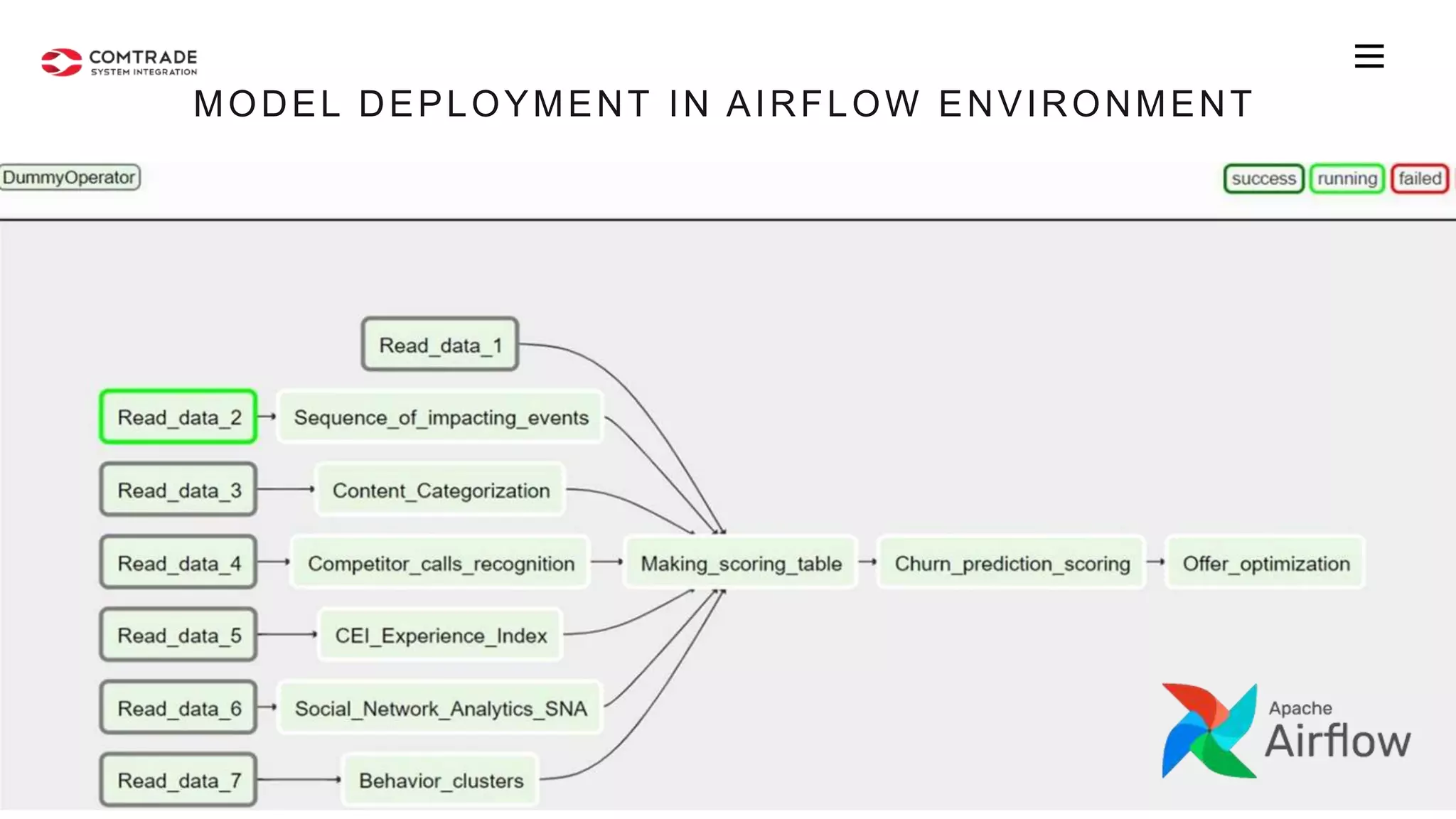
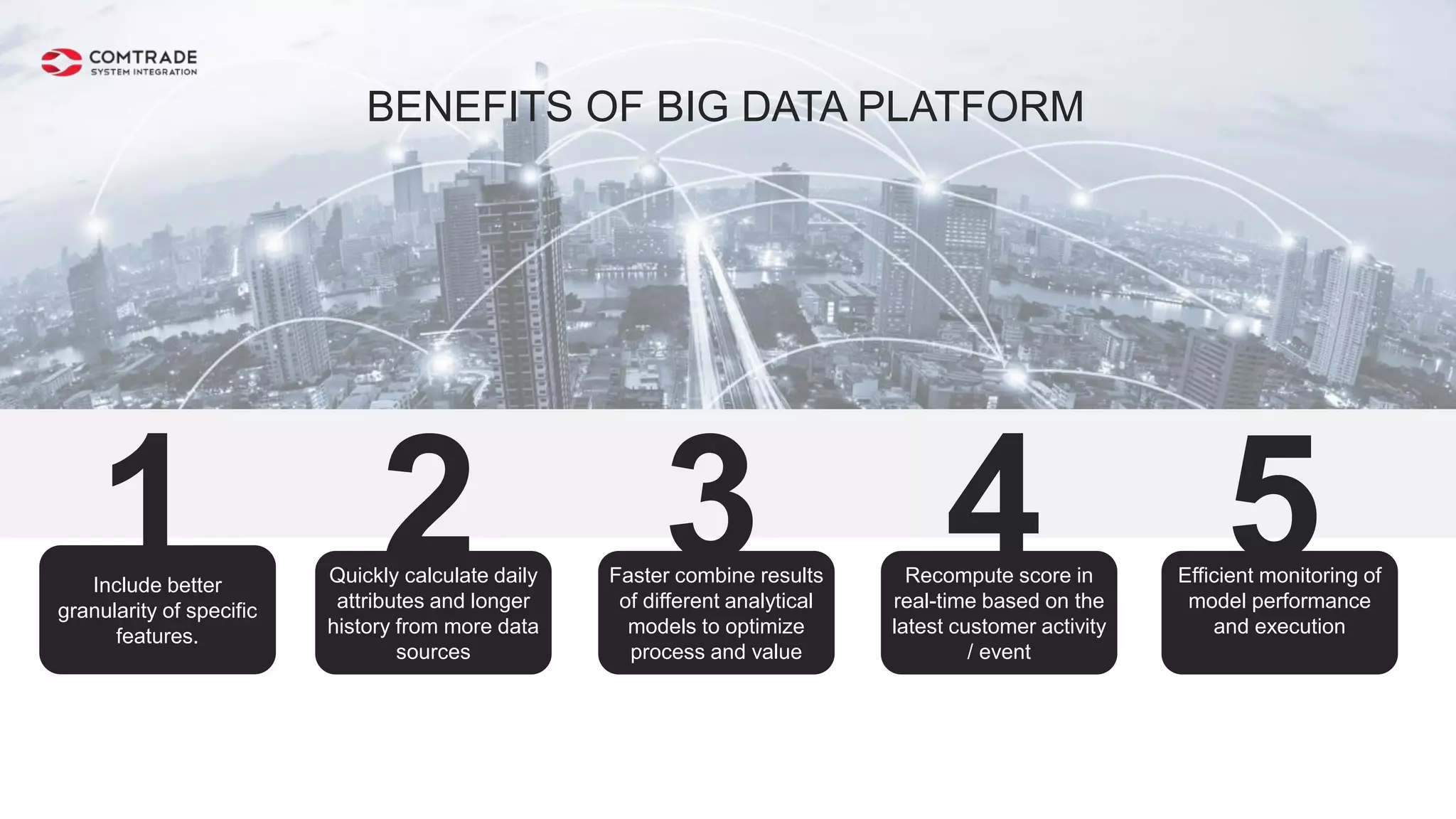
The document discusses strategies for managing customer churn in industries leveraging big data and analytics, focusing on enhancing retention by identifying high-risk customers through behavior patterns and data integration. It details methodologies for creating churn prediction models, including the preparation and analysis of various data sources to develop insights into customer behavior and churn triggers. The ultimate goal is to implement proactive outreach and optimize retention efforts using advanced analytics within a robust data framework.