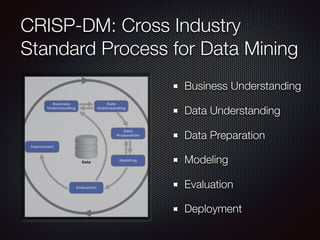
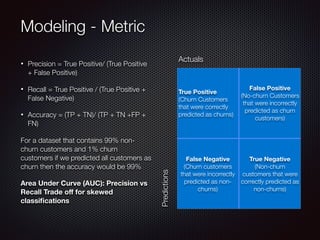
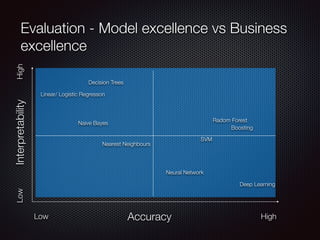
This document discusses customer churn prediction in the telecom industry. It outlines the business problem of reducing customer churn and retention costs. It describes collecting internal customer and transaction data as well as external data, preparing the data through ETL, feature selection including filtering and engineering added features, and modeling techniques like gradient boosting, random forest and neural networks. Key metrics for evaluating imbalanced classification models on churn are discussed, as well as balancing model excellence with business priorities in deployment.