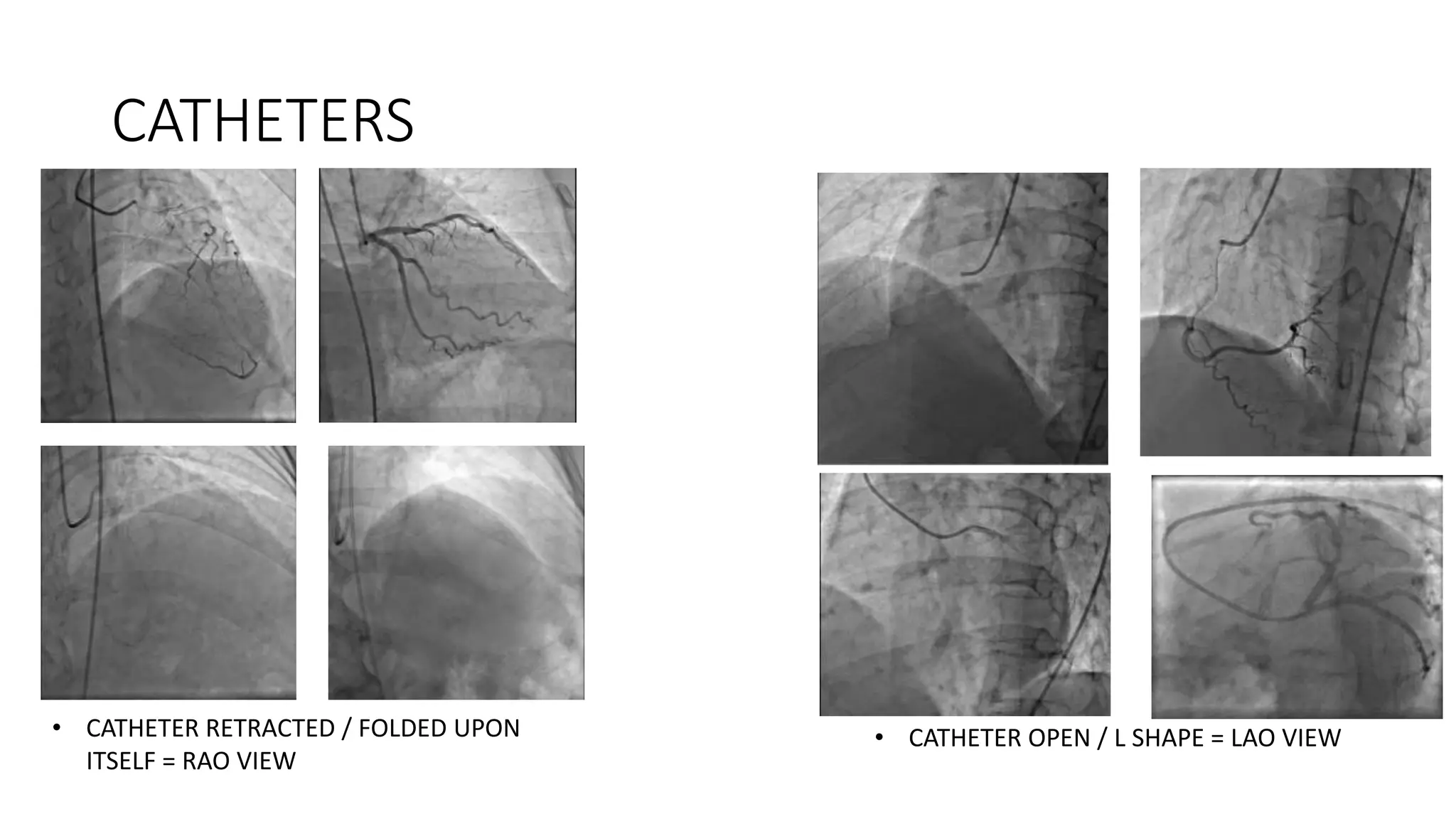
The document outlines the interpretation of coronary angiography, focusing on various views and their significance in assessing the left and right coronary systems. It details the capability of different views to visualize arterial structures, emphasizing specific characteristics such as bifurcation and branching. Additionally, it mentions factors affecting the functional severity of coronary artery stenosis, including stenosis length, collateral circulation, and vessel size.