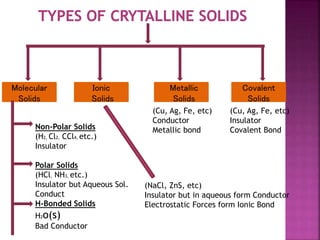
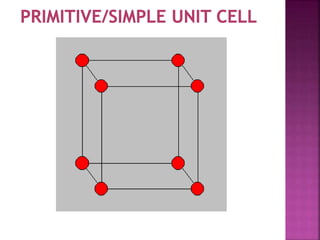
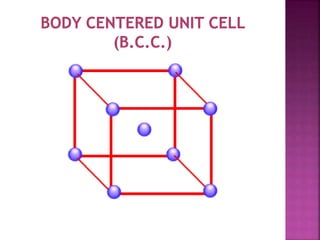
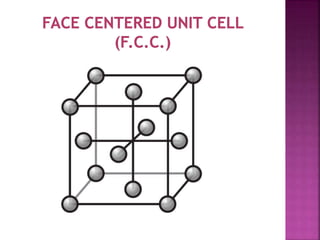
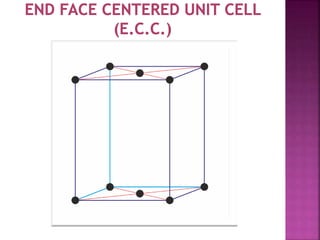
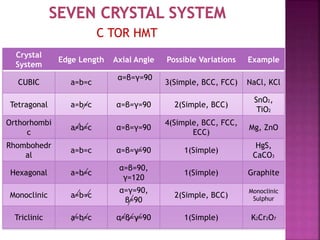
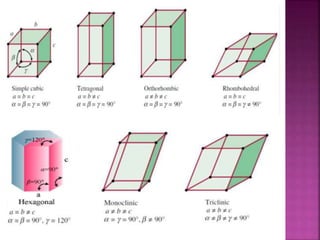
The document presents an overview of various types of solids, focusing on crystalline solids and their characteristics such as crystal lattice and unit cell structures. It describes different types of unit cells, their edge lengths, interfacial angles, and examples of solids corresponding to each unit cell type. Additionally, it discusses the electrical and magnetic properties of different solid types, including molecular, metallic, ionic, and covalent solids.