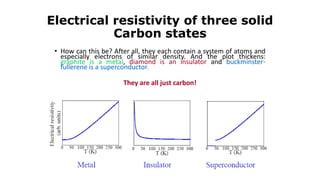
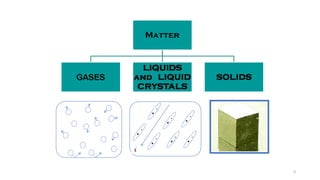
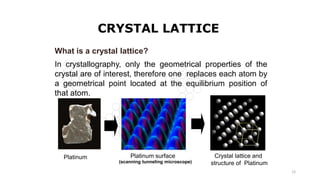
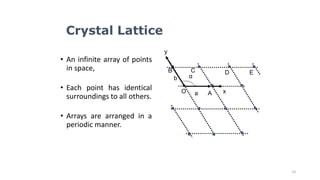
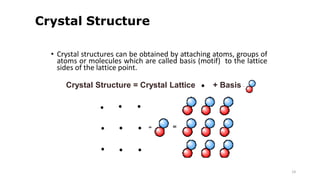
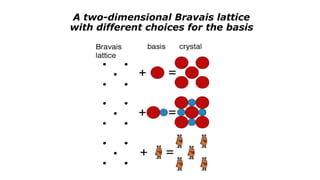
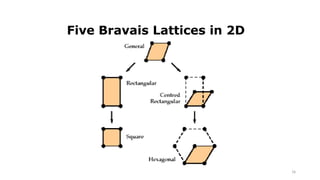
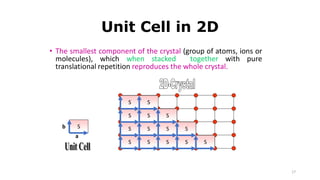
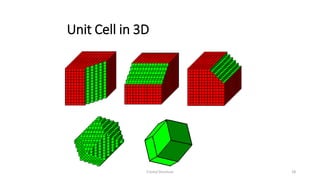
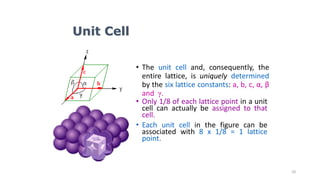
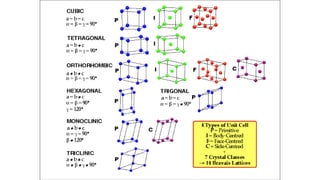
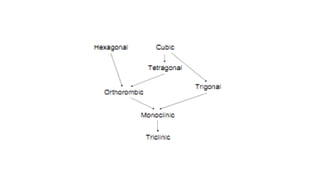
The document discusses solid state physics and the properties of solid materials. It explains that solid state physics formulates laws governing the behavior of solids and explores why materials like carbon can exist in different states with varying electrical properties. The document also classifies solids as crystalline, polycrystalline, or amorphous and discusses crystal structure, lattice, and unit cells - the basic repeating units that make up crystalline solids. Understanding these atomic arrangements is important for explaining the behavior and properties of different materials.