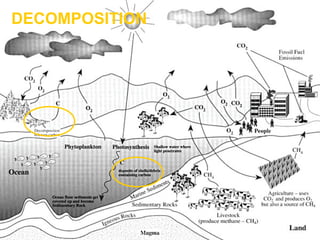
The document discusses the carbon/oxygen cycle which involves four main processes:
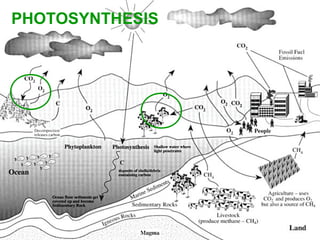
1. Photosynthesis where plants take in carbon dioxide and water to release oxygen and sugar using energy from the sun.
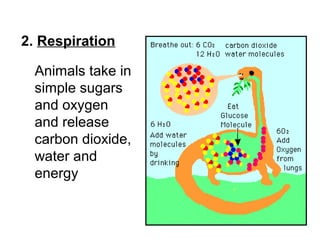
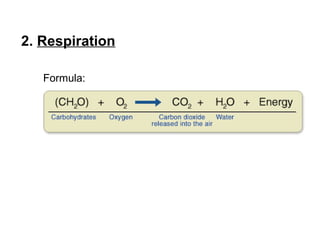
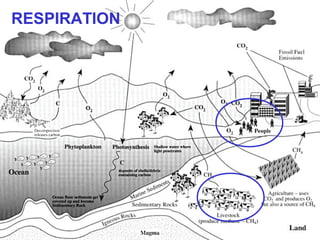
2. Respiration where animals take in oxygen and sugars to release carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
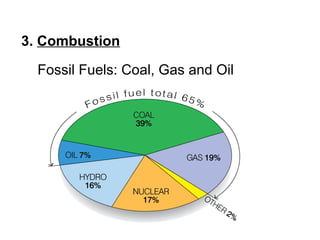
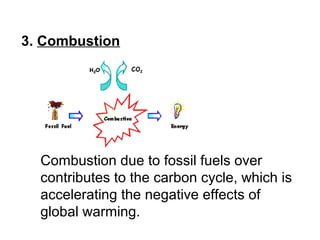
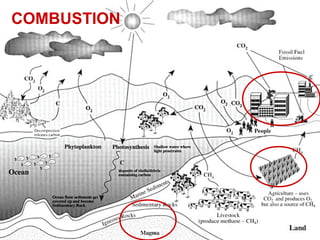
3. Combustion which is the burning of fossil fuels like coal, gas, and oil, releasing carbon dioxide. This over-contribution of carbon dioxide is accelerating global warming.
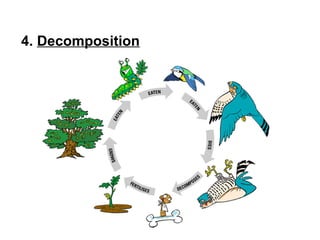
4. Decomposition where dead plants and animals are broken down by insects, fungi and bacteria, returning carbon and other elements to the soil and air.