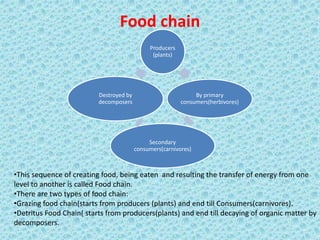
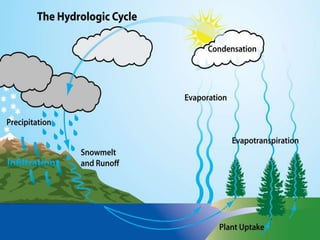
The document discusses key concepts relating to life on Earth, including the biosphere, ecosystems, and biogeochemical cycles. The biosphere encompasses all life and interactions between the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. Ecosystems refer to interactions between living and non-living factors within a defined area. Major biogeochemical cycles, like the carbon, water, oxygen, and nitrogen cycles, involve the exchange and reuse of key elements between organisms and the environment.