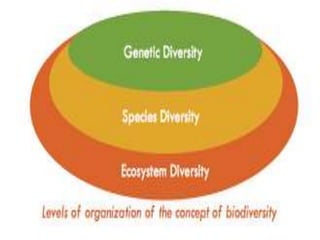
Biodiversity refers to the variety of plant and animal life on Earth or within a particular ecosystem. It exists at three main levels: genetic diversity within species, diversity of species within an area, and diversity of ecosystems within a region. Biodiversity is important for ecological, economic, and scientific reasons. Loss of biodiversity is occurring due to factors like increasing human population and land use, natural disasters, pollution, and overhunting. Conservation efforts aim to preserve endangered and vulnerable species and protect important habitats to maintain biodiversity and ecosystem balance.