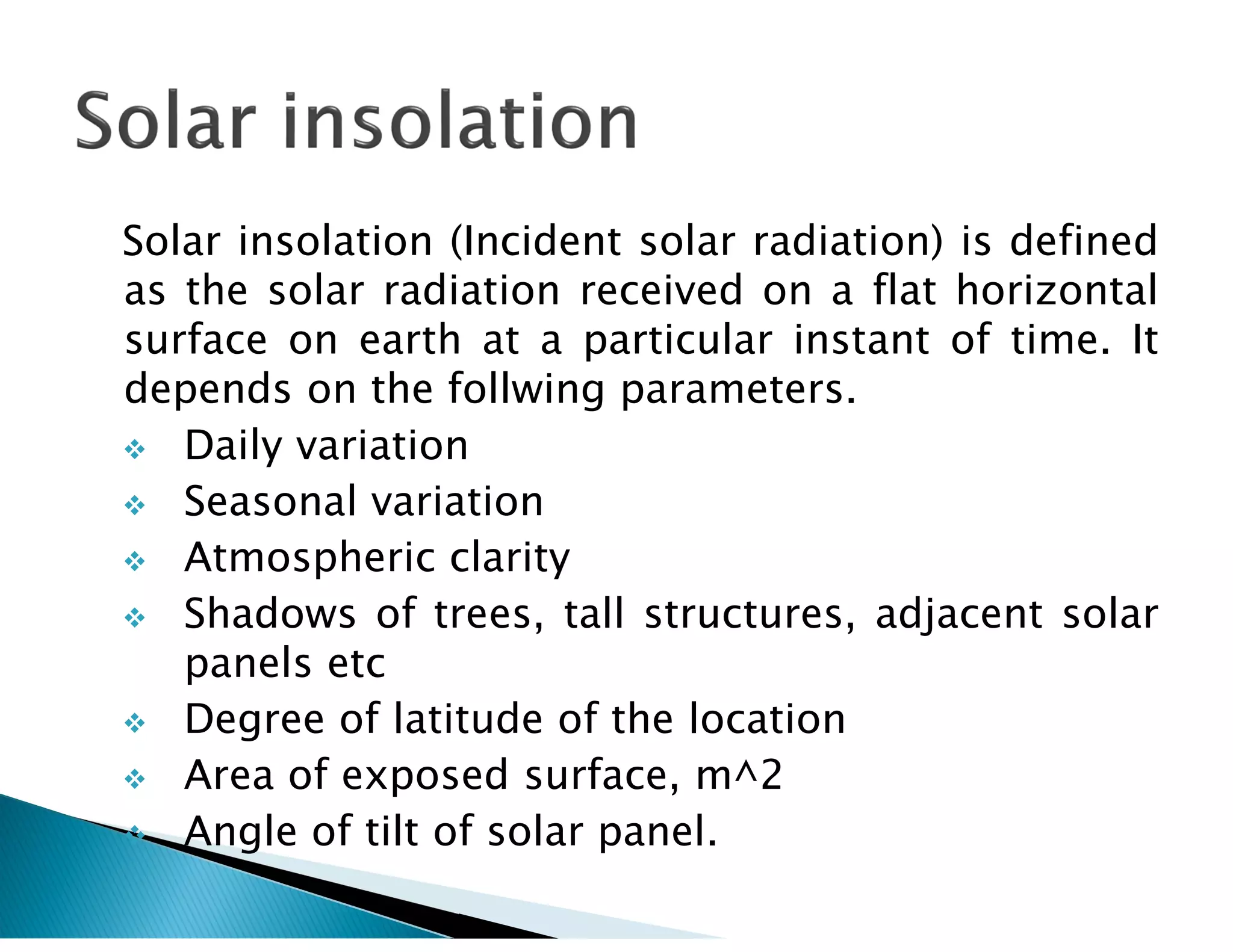
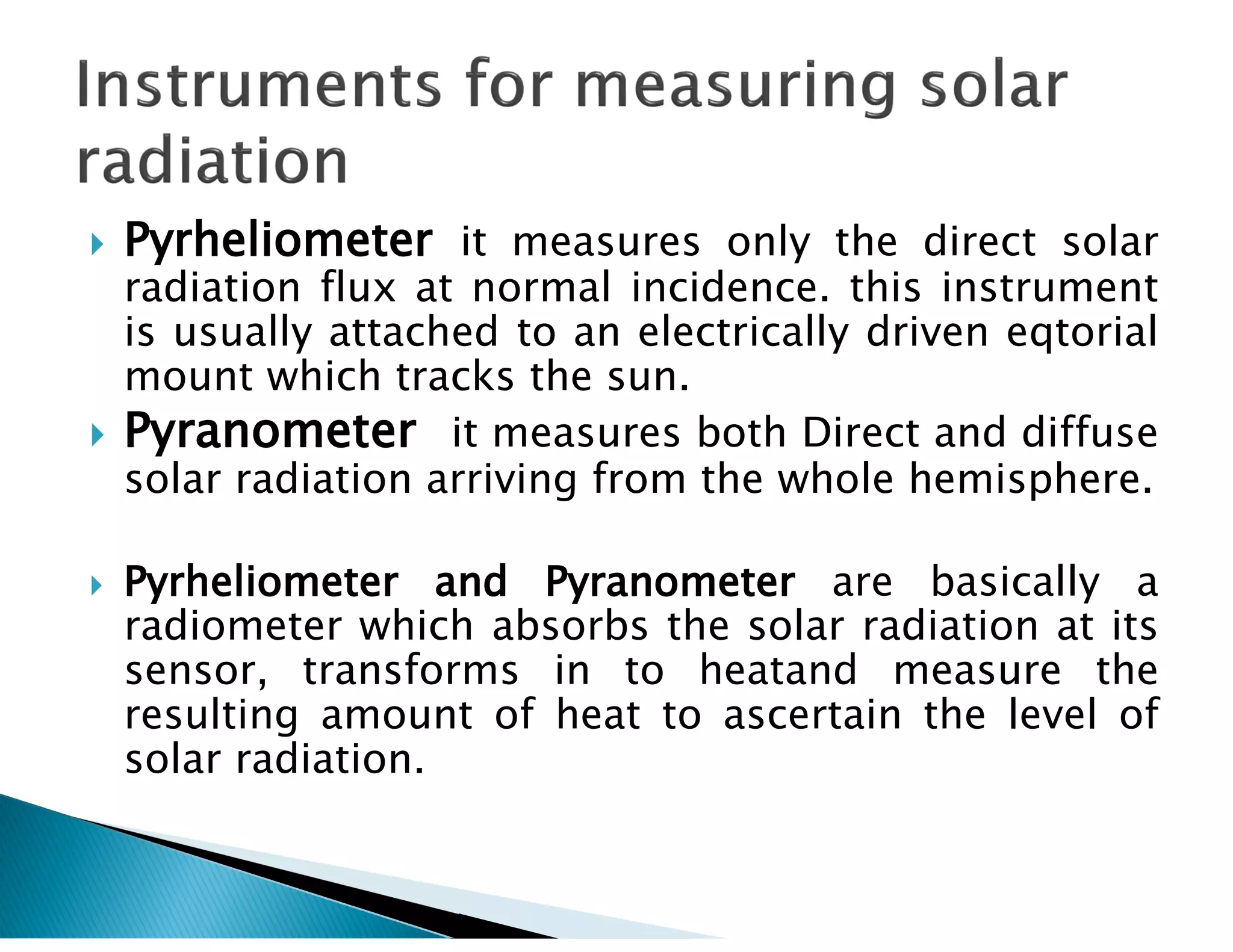
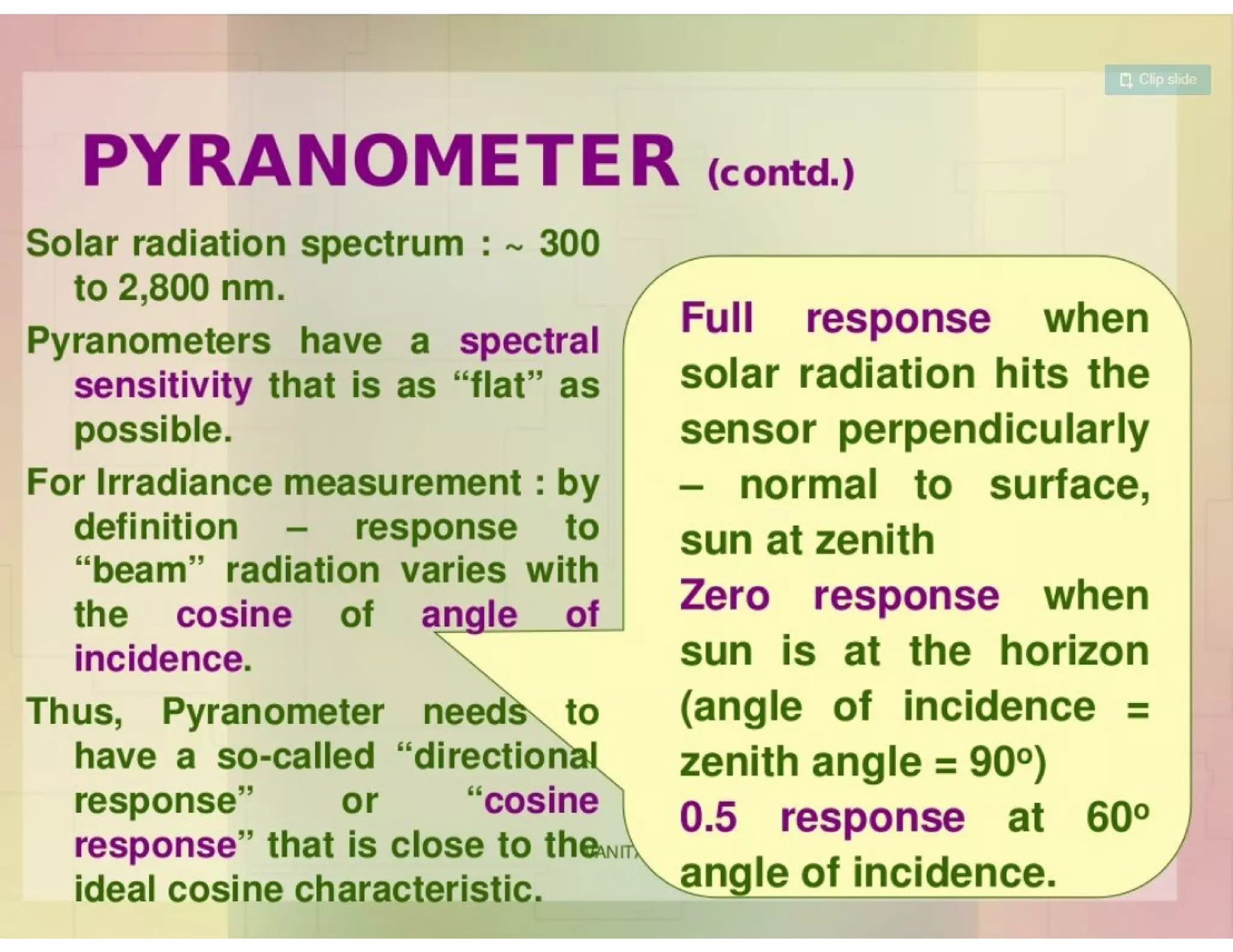
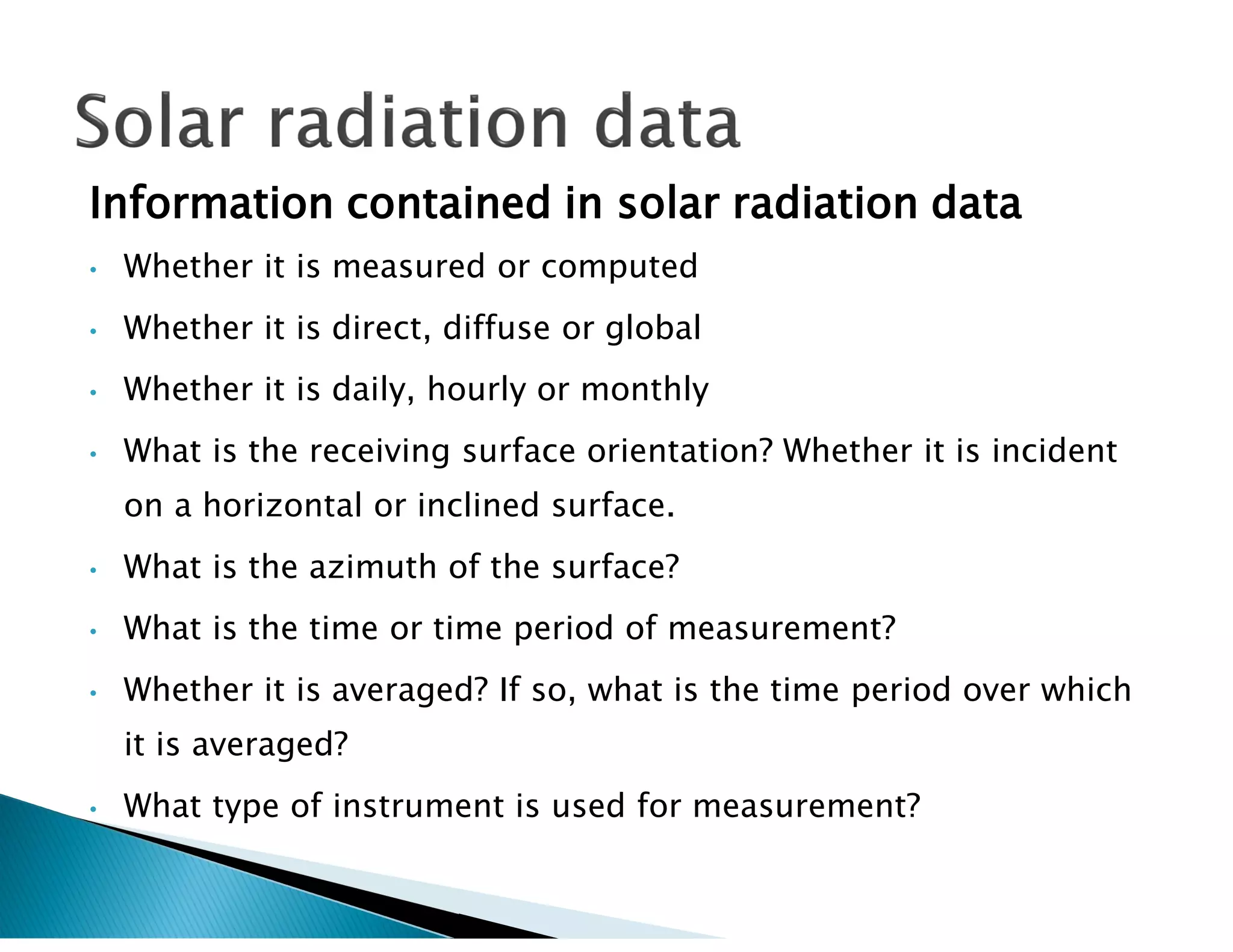
Clarity index is defined as the ratio of radiation received on Earth's surface compared to radiation beyond the atmosphere, and can range from 0.1 to 0.7. Concentration ratio is the ratio of solar power per unit area of a concentrator surface to a reference area, and can be up to 100 for parabolic trough collectors. Solar insolation is the solar radiation received on a horizontal surface, and depends on daily/seasonal variation, atmospheric clarity, shadows, latitude, exposed area, and tilt angle of solar panels. Pyrheliometers measure direct solar radiation flux, while pyranometers measure direct and diffuse radiation from the whole hemisphere. Solar radiation data contains information on whether values are measured or computed,