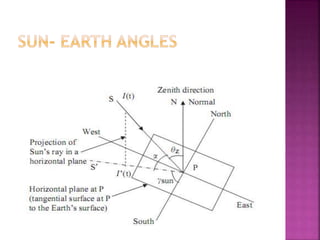
The document defines sunshine as direct sunlight of at least 120 w/m2 measured on the ground. It provides details on the sun's composition and radiation, including that 53.12% of its energy is in the infrared region. It also discusses how the Earth reflects 1/3 of sunlight and is inclined at 23.5 degrees on its axis. Finally, it describes various instruments used to measure solar radiation, including pyranometers and pyrheliometers, and concepts like beam radiation, diffuse radiation, and solar declination.