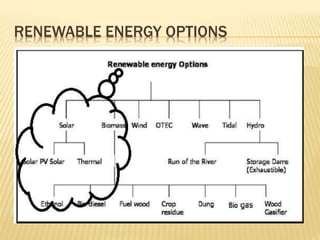
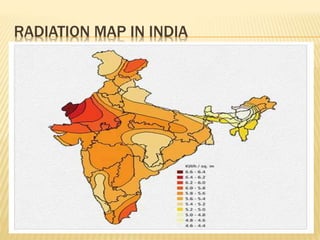
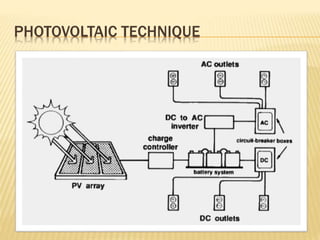
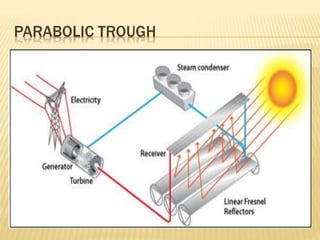
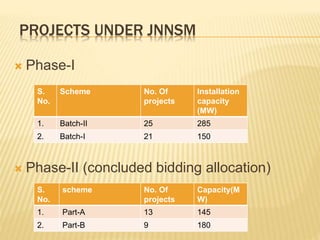
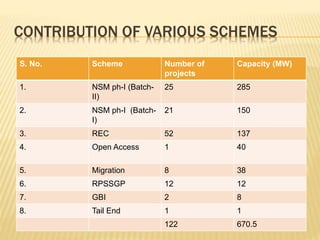
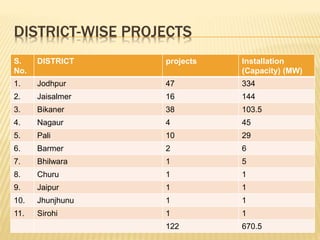
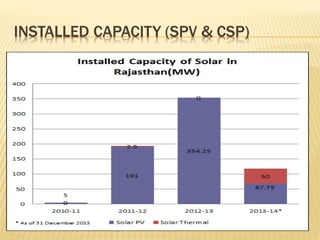
Rajasthan is well suited for solar power generation due to its high solar radiation levels and large swaths of underutilized land. The state has harnessed solar power through various projects and policies. Under Jawaharlal Nehrl National Solar Mission, Rajasthan received 46 projects totaling 285+150 MW of installed capacity. Major solar projects in Rajasthan include a 50MW project in Phalodi and a 40MW project in Dhurasar village. Rajasthan's Solar Policy 2011 aimed to allocate 12GW of solar power by 2022 through rooftop PV, ground-mounted PV and CSP projects. Harnessing solar power benefits rural electrification, agriculture, and generates employment