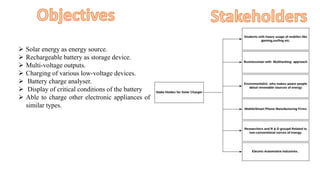
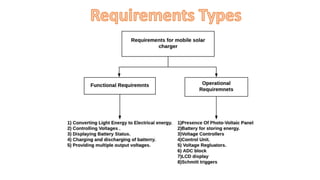
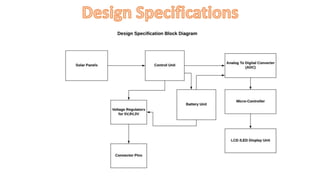
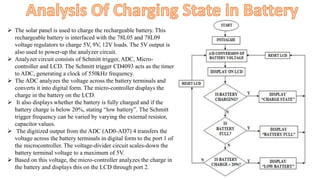
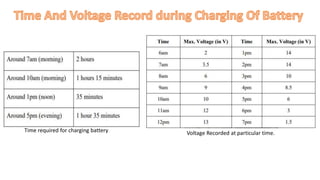
The document discusses a solar-based mobile charger that addresses the need for portable mobile charging, particularly in areas without access to electricity. It highlights the advantages of solar energy as a renewable resource, detailing the system's components such as a rechargeable battery, voltage regulators, and an analyzer circuit with an LCD display to monitor battery status. This innovative solution allows for the charging of various low-voltage devices while promoting environmentally friendly energy use.