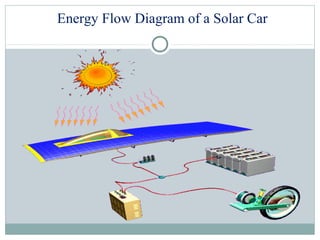
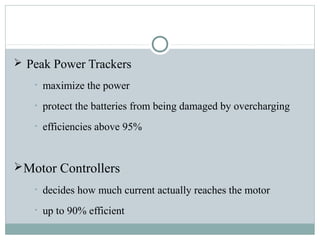
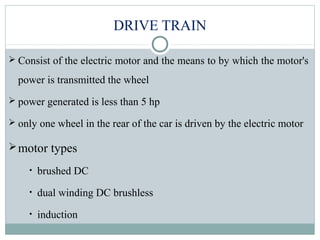
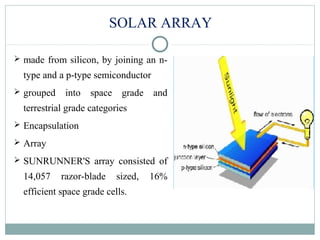
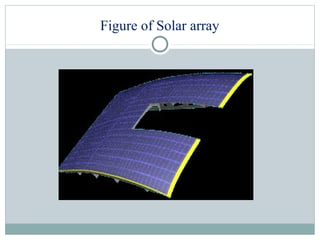
The document summarizes the history and components of solar cars. It discusses how the first solar car was created in 1955 and outlines the key parts of solar cars including the electrical system, drive train, solar array, materials used, and advantages. The electrical system uses batteries and power electronics to store and maximize energy from the solar panels. The drive train includes an electric motor and transmission to power the wheels. Solar arrays consist of solar cells that convert sunlight to electricity. Materials like carbon fiber and honeycomb structures are used due to their strength and lightweight properties. Advantages are that solar energy is renewable and doesn't cause pollution.