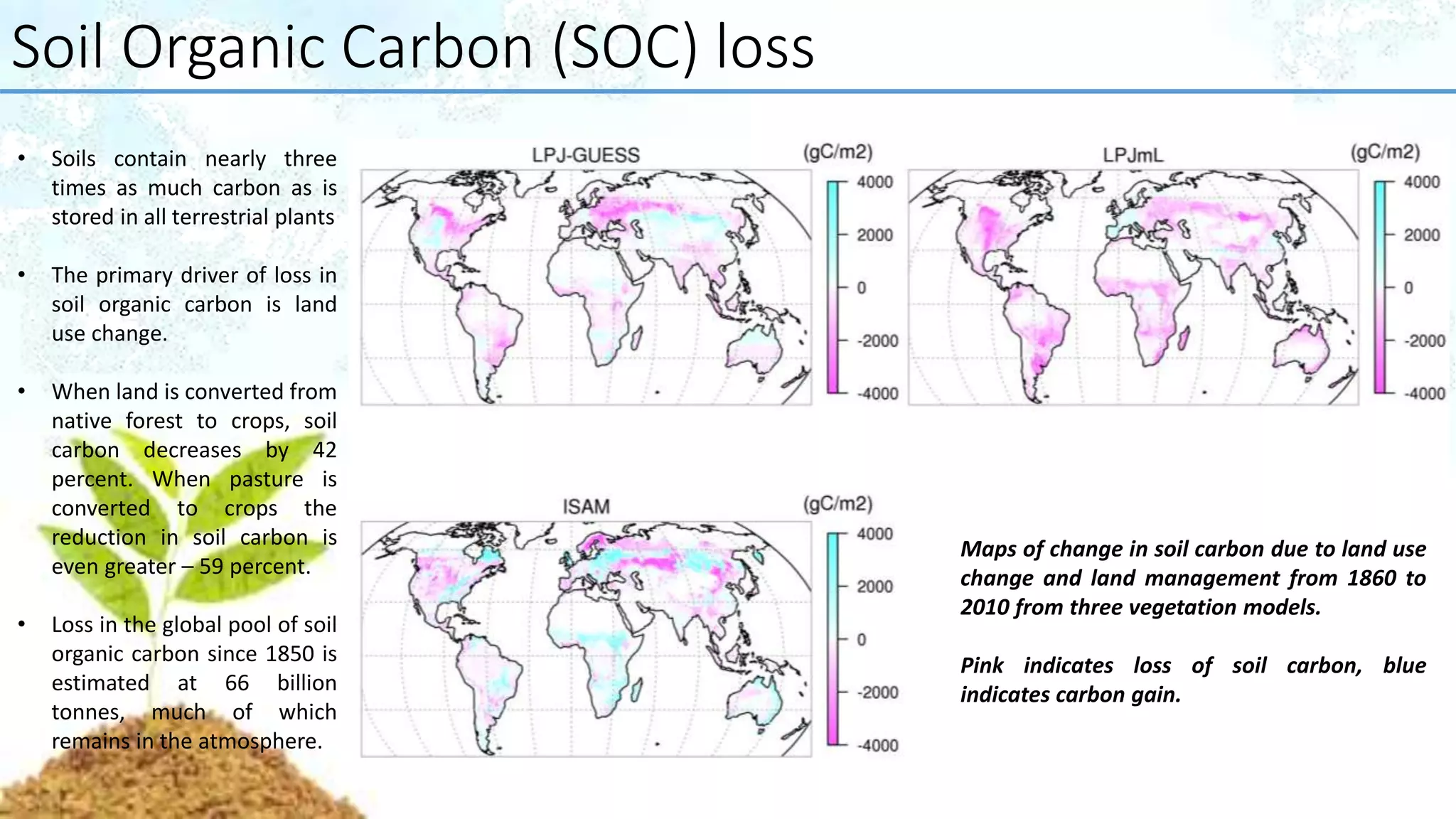
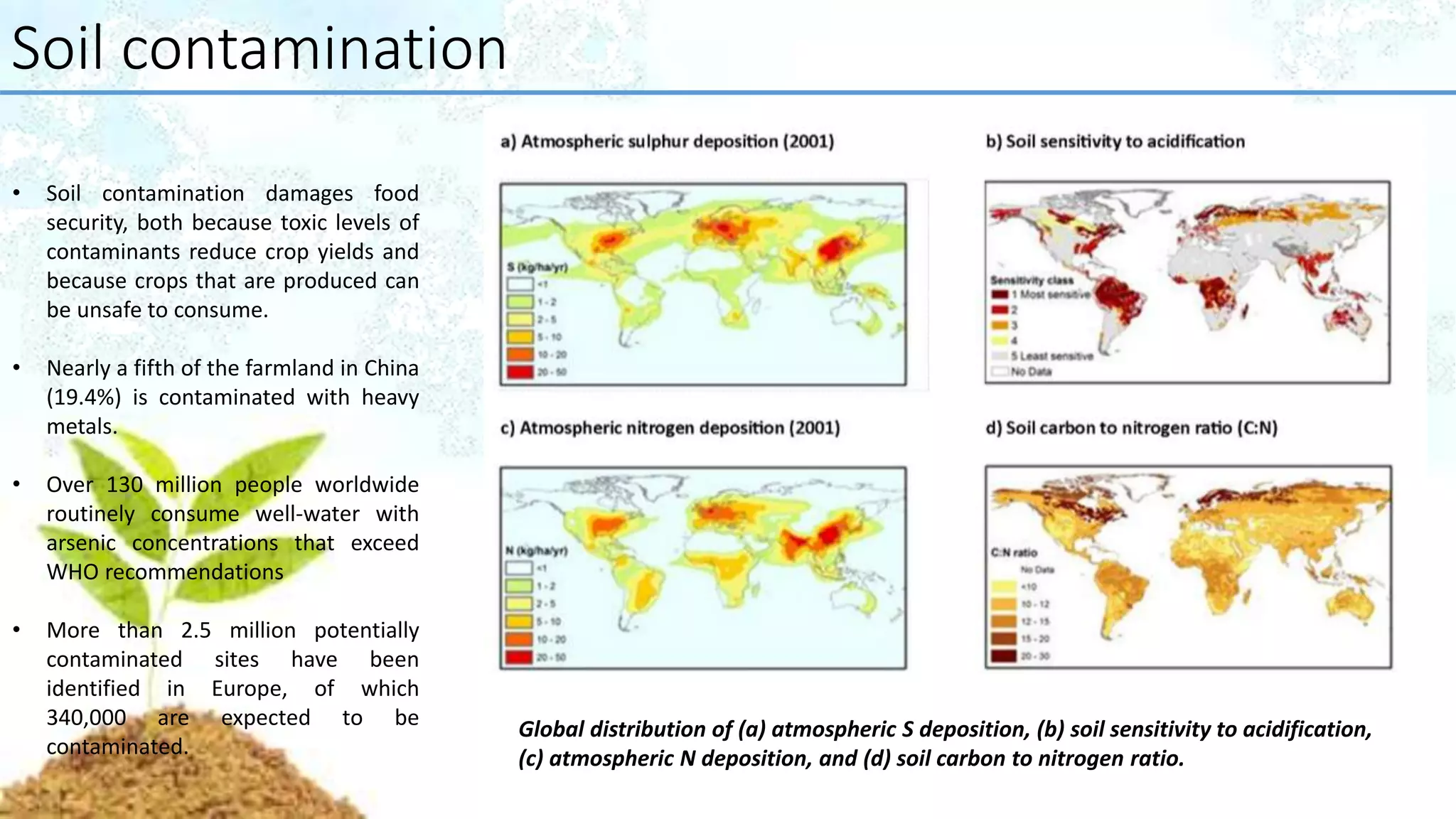
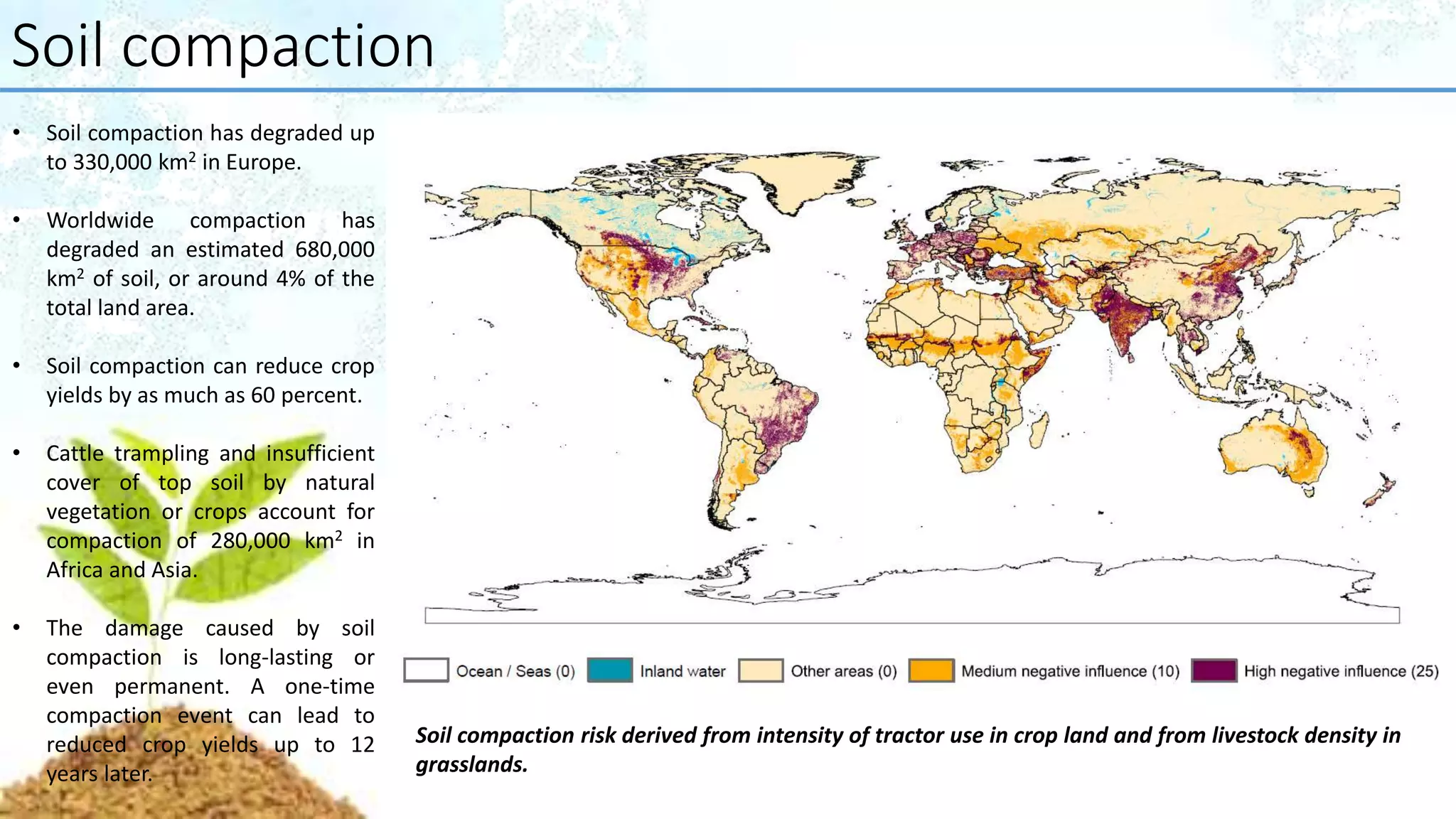
A report prepared by 200 soil scientists from 60 countries offers a comprehensive assessment of the world's soil resources, focusing on their significance for food security and ecosystem services, while identifying various threats to soil health. It highlights major concerns such as erosion, soil organic carbon loss, nutrient imbalance, salinization, contamination, acidification, biodiversity loss, sealing, compaction, and waterlogging. The report concludes with recommendations for policymakers and emphasizes the necessity for sustainable soil management to achieve global development goals.