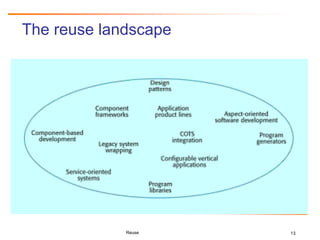
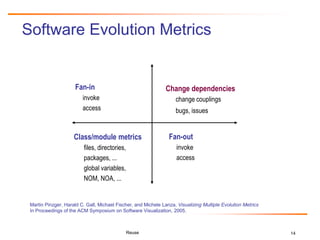
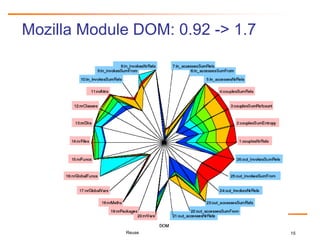
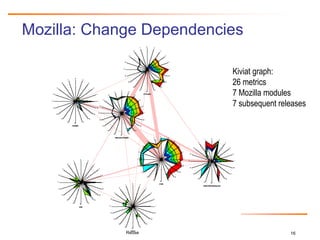
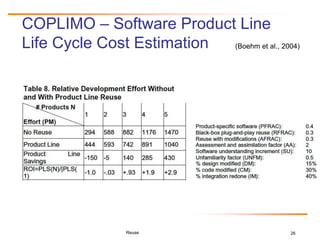
The document discusses challenges and business success related to software reuse. It outlines topics like reuse challenges, technologies, economics, case studies and empirical investigations. Regarding challenges, it notes organizational, technical, domain engineering, and economic aspects. For technologies, it discusses software analysis/visualization, product lines, and architectures. It also examines cost/benefit relationships, metrics, and legal issues regarding reuse. Case studies from HP and Ericsson demonstrate quality, productivity and economic benefits of large-scale reuse programs. Strategies for successful reuse include formal reuse programs with quality control and continuous improvement.












![27
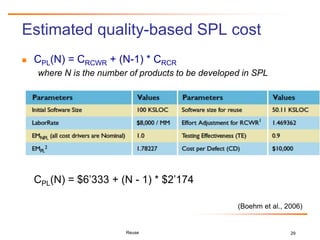
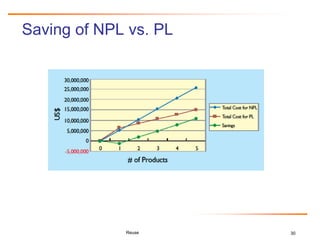
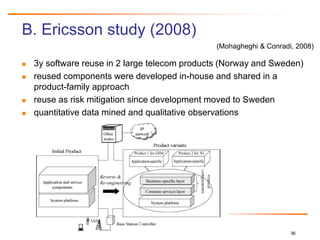
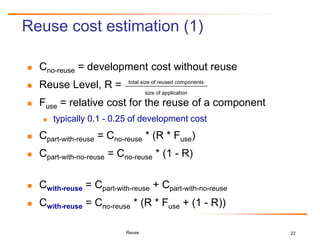
Relative Cost of Writing for Reuse
RCWR is the added cost of writing software to be most cost-effectively
reused across a product line family of applications, relative to the cost
of writing a standalone application.
CRCWR = LaborRate * COPLIMORCWR + SoftwareQualityCostRCWR
CRCWR = LaborRate * [COCOMO baseline (initialSoftwareSize) *
EffortAdjustment for RCWR] + [ CostPerDefect *
(1- TestingEffectiveness) *
(COQUALMO(initialSoftwareSize, EMPL)],
where EMPL is the Effort Multiplier of the COCOMO II cost drivers for the product line
development and COCOMO baseline is calculated as 2.94 * (software size1.0997 *
PI(EM)
Reuse
(Boehm et al., 2006)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reuse-hcgall-26nov2010-101126122949-phpapp01/85/Software-Reuse-Challenges-and-Business-Success-27-320.jpg)
![28
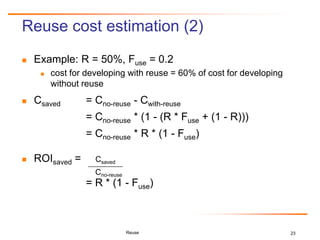
Relative Cost for Reuse
RCR is the cost of reusing the software in a new
application with the same product line family, relative to
developing newly built software for the application.
CRCR = LaborRate * COPLIMORCR + SoftwareQualityCostRCR
CRCR = LaborRate * [COCOMO baseline (softwareSizeForReuse)] +
[CostPerDefect * (1 – TestingEffectiveness) *
COQUALMO(softwareSizeForReuse, EMPL)]
Reuse
(Boehm et al., 2006)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reuse-hcgall-26nov2010-101126122949-phpapp01/85/Software-Reuse-Challenges-and-Business-Success-28-320.jpg)