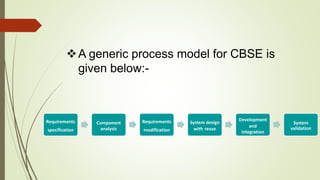
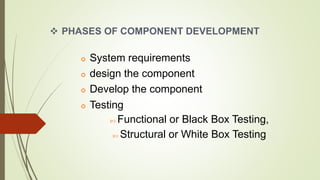
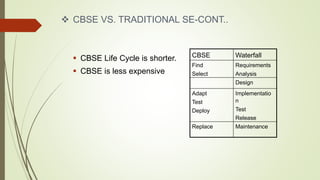
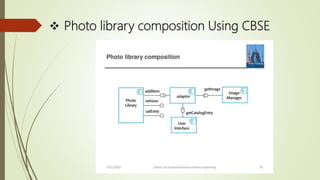
Component-based software engineering (CBSE) is a process that emphasizes designing and building computer systems using reusable software components. It focuses on integrating existing components rather than developing everything from scratch. A key benefit of CBSE is reducing development time and costs by leveraging reusable components. The CBSE process involves requirements specification, component analysis, system design using existing components, development and integration of components, and system validation. CBSE aims to increase quality, productivity, and shorten development time by facilitating reuse of well-tested components.